It is a project when I was internship at the University of Washington in St. Louis under the guidance of Prof. Buhler.
It's a program which implements a parallel algorithm to get minhash sketches with DNA sequence as input under CUDA and CUB.
Minhash is a technique for quickly estimating how similar two sets are. For More information of similarity and minhash sketch, you can see Class Note 24 and Class Note 25 of Prof. Buhler.
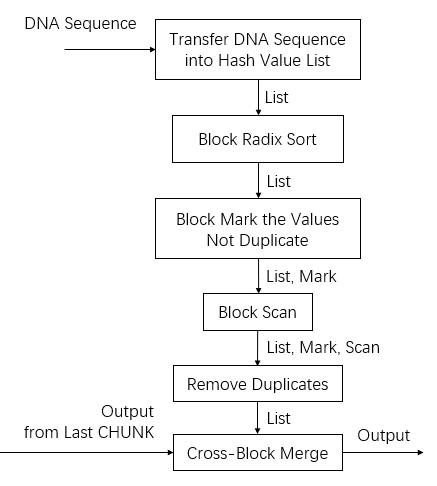
In general, the program divides the long DNA sequence into sevelral CHUNKs and cope with them respectively. For each CHUNK, it will get hash velues, radix sort, mark, scan and merge in GPU.
- DNA sequence. (e.g. we used E.coli K12 genome as experimental data)
- k: The length of subsequences (or k-mers).
- m: The number of sketches stored.
- t: The number of hash functions.
The output should be the minhash sketch of input DNA sequences and the similarity of them.
MinhashSketch
|
|-- src
| |-- main.cu # Main function and help, usage functions
| |-- MinhashSketch.cu # Key file for generating minhash sketches
| |-- Utils.cu # Some utilities
| |-- Utils.h
| |-- Hash.cu # Generate hash funtions or random parameters
| |-- Hash.h
| |-- SpookyV2.cu # SpookyHash function for host
| |-- SpookyV2.h
| |-- SpookyV2_d.cu # SpookyHash function for device
| |-- SpookyV2_d.h
|
|-- testing_files # Save files of DNA sequences
The first line of DNA files should be the file information, followed by the DNA sequence from the second line.
The key functions are all in MinhashSketch.cu.
signature genSig(const int k, const int m, const int t,
char \*dnaList, int length, uint64 \*hashes\_b);
This is a host window function. The input parameters, k, m and t, have been explained before. DNA sequence is stored in dnaList, where length is the number of bases. The hashes_b is a set of random numbers between 0 and UINT64_MAX. And the type of return values is defined as follows, whose first dimension represents hash functions and second dimension represents minhash sketches.
typedef vector<vector<uint64>> signature;
In this function, firstly, you can set three values, BLOCKS_NUM, BLOCK_THREADS and ITEMS_PER_THREAD according your GPU. (e.g. I set BLOCKS_NUM = 16, BLOCK_THREADS = 32 * 16, ITEMS_PER_THREAD = 4 here)
Then it calculate how many CHUNKS are needed and the starting index of each chunk.
Then we cope with each chunk of each hash function separately. (Hash function here means different random parameter hashes_b, because SpookyHash need a seed only)
The process of each CHUNK includes getBlockSketch and getAllSketch, which you will see information of below.
template<int BLOCK_THREADS, int ITEMS_PER_THREAD>
__global__ void getBlockSketch (const int k, const int m, char *dna_d,
uint64 *input_d, int numElem_dna, int numElem_list, uint64 hash_b);
This device function could get minhash values of each block. The input parameters, k and m, have been explained before. DNA sequence is stored in dna_d, where numElem_dna is the length of it. The input_d stores hash value list, sorted list and minhash sketch list, where numElem_list is the length of it. The hash_b is a random number between 0 and UINT64_MAX.
In this function, we first get hash value list using BlockGetHashValues, which is descripted detailedly later.
Then, we use primitives of CUB to radix-sort hash value list, mark discontinuity, scan mark list for the sake of removing duplicated items. And then, we write back and restore sorted list into input_d. For specific radix sort process, refer Harada et..
template<int BLOCK_THREADS, int ITEMS_PER_THREAD>
__device__ void BlockGetHashValues (const int k, char *dna_d, int thread_offset,
uint64 *thread_dataR, int hash_b);
It is a device function inorder to get hash value list.
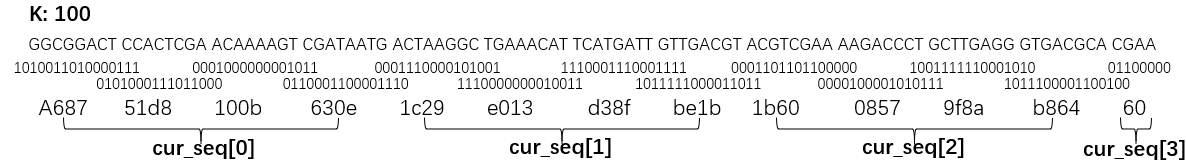
We use a pointer to access sequence, which need noly to record the last base read, and directly assign four bases(A, C, T, G) to four kinds of 2-bit values in binary. If the length of the subsequence exceeds 32 (i.e. one uint64 is not enough to indicate the length of subsequences), we need to use an array cur_seq[k / 32 + 1] instead of one uint64 to store subsequences.
For example, k is 100 here:
template<int BLOCKS_NUM, int BLOCK_THREADS, int ITEMS_PER_THREAD>
__global__ void getAllSketch (const int m, uint64 *input_d, int numElem_list)
This device function aimed to merge sketches of all blocks. The input parameters, m, have been explained before. The input_d stores minhash sketch list sorted on each block. And numElem_list is the length of it.
We first merge the sketches in adjacent blocks, getting half of the previous sketches, then merge the adjacent sketches again, and so on untill one left.
When merging sketches in every two blocks, I provide a method based on Cole in order to merge two ordered lists as quickly as possible. The previous algorithm did not solve the problem of duplicate elements in the two lists.
Input: listA, listB
definition:
rank(x|A) : The number of elements in A that are not greater than x.
rank(B|A) : An array (r1,r2,..., rn), where ri=rank(B[i]:A).
rank(x|AUB) : The number of elements in AUB that are not greater than x,
so, rank(x|AUB) = rank(X|A) + rank(x|B).
Merge two Ordered Lists:
rankA = rankB = {0, 1, 2, ...}
dupeA = dupeB = {0, 0, 0, ...}
for every elements listA[a] in listA:
Binary search for the index i of the smallest element of listB that
are not smaller than x.
rankA[a] = i
if listA[a] is equal to listB[i]:
dupeA[a] = 1
Do the same process to listB, rankB and dupeB.
Get scanA and scanB for dupeA and dupeB
for every i in range(0, m):
rankA[i] -= scanA[i]
rankB[i] -= scanB[i]
for every i in range(0, m):
if rankA[i] < m:
list_output[rankA[i]] = listA[i]
if rankB[i] < m:
list_output[rankB[i]] = listB[i]
In this way, we can use at least (2 * m) thread to solve the two-list-merge problem in O(log(m)) time.
If you want to compile the program, follow the instructions below:
Compile
$ nvcc -std=c++11 -I /export/project/hondius/opt/cub -rdc=true main.cu Utils.cu Hash.cu SpookyV2_d.cu -o minhash
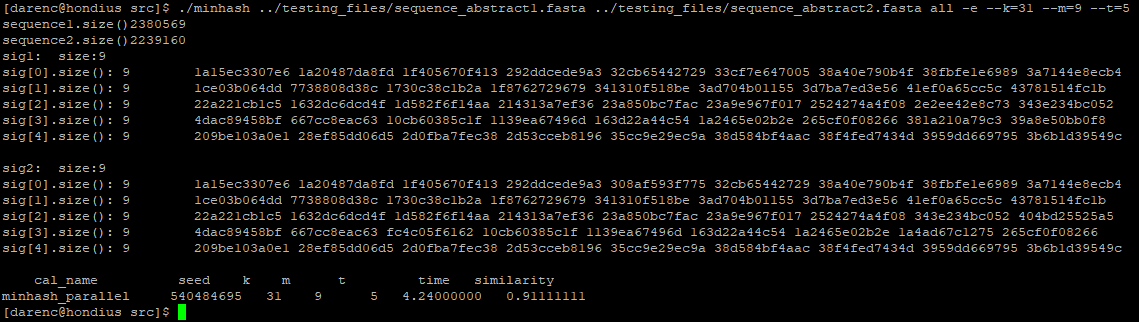
Run
$ ./minhash ../testing_files/sequence_abstract1.fasta ../testing_files/sequence_abstract2.fasta all -e --k=5 --m=10 --t=10
Or if you want to use MinhashSketch.cu, this an example about how to use it:
#include "MinhashSketch.cu"
#include "Hash.h"
#include "Utils.h"
int k, m, t;
char *dnaList1, *dnaList2;
(Get k, m, t, dnaList1, dnaList2)
uint64 *hashes_b = generateHashes_b(t, seed);
vector <vector<uint64>> sig1 = genSig(k, m, t, dnaList1, length1, hashes_b);
vector <vector<uint64>> sig2 = genSig(k, m, t, dnaList2, length2, hashes_b);
similarity = computeSim(sig1, sig2);
We pre-defined parameters BLOCKS_NUM, BLOCK_THREADS and ITEMS_PER_THREAD. Then we can process BLOCKS_NUM * BLOCK_THREADS * ITEMS_PER_THREAD values at a time, which is also the length of a chunk.
If the length of a chunk is (BLOCKS_NUM * BLOCK_THREADS * ITEMS_PER_THREAD), the length of a sebsequence of DNA is (BLOCKS_NUM * BLOCK_THREADS * ITEMS_PER_THREAD + k - 1). And the number of chunks is
if (length % (BLOCKS_NUM * BLOCK_THREADS * ITEMS_PER_THREAD) == 0)
CHUNKS_NUM = (length - k + 1) / (BLOCKS_NUM * BLOCK_THREADS * ITEMS_PER_THREAD);
else
CHUNKS_NUM = (length - k + 1) / (BLOCKS_NUM * BLOCK_THREADS * ITEMS_PER_THREAD) + 1;
In general, merge two ordered lists into one need O(m + n) time complexity. But we could use a efficient algorithm to merge two ordered lists with O(log(n)).
Given two ordered Lists A and B
rank(x | A) : The number of elements in A that are not greater than x.
rank(B | A) : An array (r1,r2,..., rn), where ri = rank(B[i]:A).
rank(x | AUB) : The number of elements in the AUB that are not greater than x, so rank(x | AUB) = rank(X | A) + rank(x | B).
Further : rank(A | AUB)= rank(A | A) + rank(A | B).
rank(A | AUB) is offset vector of elements in A. We could get rank(A | AUB) and rank(B | AUB) with time complexity O(log(n)), where n is number of elements in A (or B). Then write back m smallest values according to offset.
And I considered the duplicating situation, that is, there are values in the two lists are duplicates. In this case, we can give it a mark, do not write back and then reduce the offset of values which bigger than that the mark value by one.
- CUDA Nvidia CUDA Home Page.
- CUB CUB Documentation.
- Harada et. Harada, Takahiro, and Lee Howes. "Introduction to GPU radix sort." Heterogeneous Computing with OpenCL. Morgan Kaufman (2011).
- Cole Cole, Richard. "Parallel merge sort." SIAM Journal on Computing 17.4 (1988): 770-785.
It is a project when I was internship at the University of Washington in St. Louis under the guidance of Prof. Buhler.