A lightweight VS Code extension that auto-loads your database. It provides a beautiful database GUI client experience, bringing Convention over Configuration into database management.
Built with 💖 for developers.
- VS Code 1.83 or newer
- A VS Code project that uses any of the supported databases
- Linux (Linux-x64, Linux-arm64, Linux-arm, Alpine-x64)
- macOS (Darwin-x64, Darwin-arm64 Apple Silicon)
- Windows (Win32-x64)
- In a VS Code project using any of the supported databases, ensure your database is properly set up and you are able to connect to your database as usual from your normal app code.
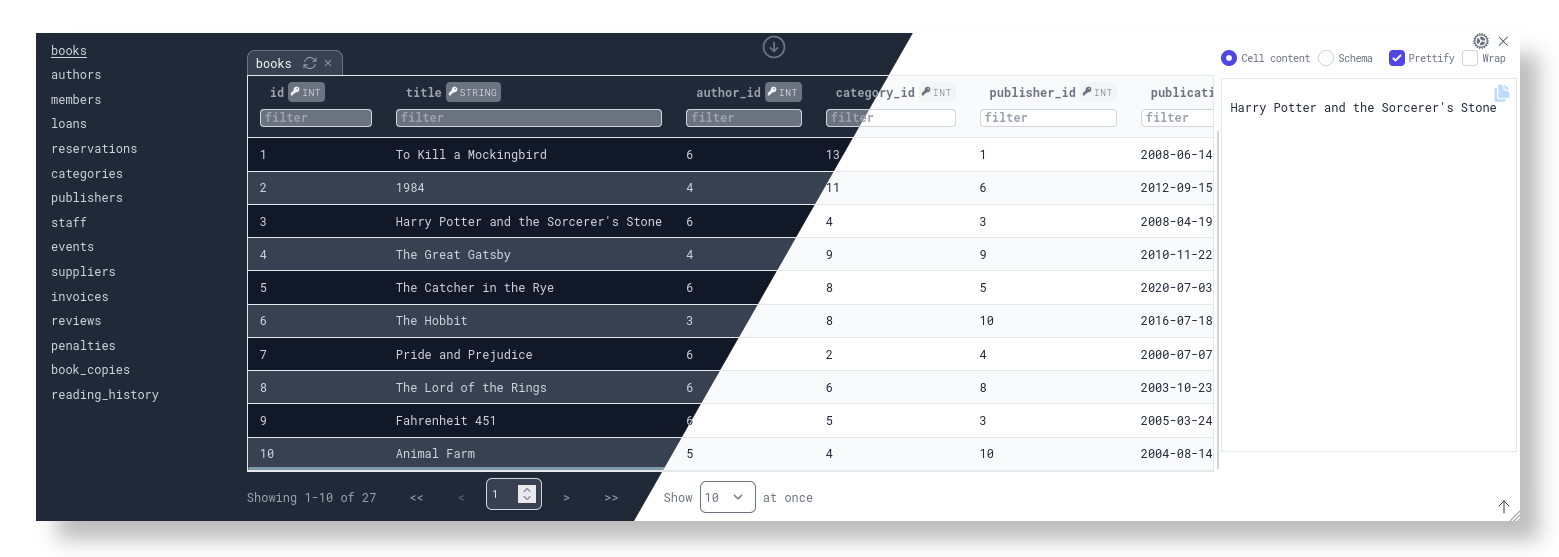
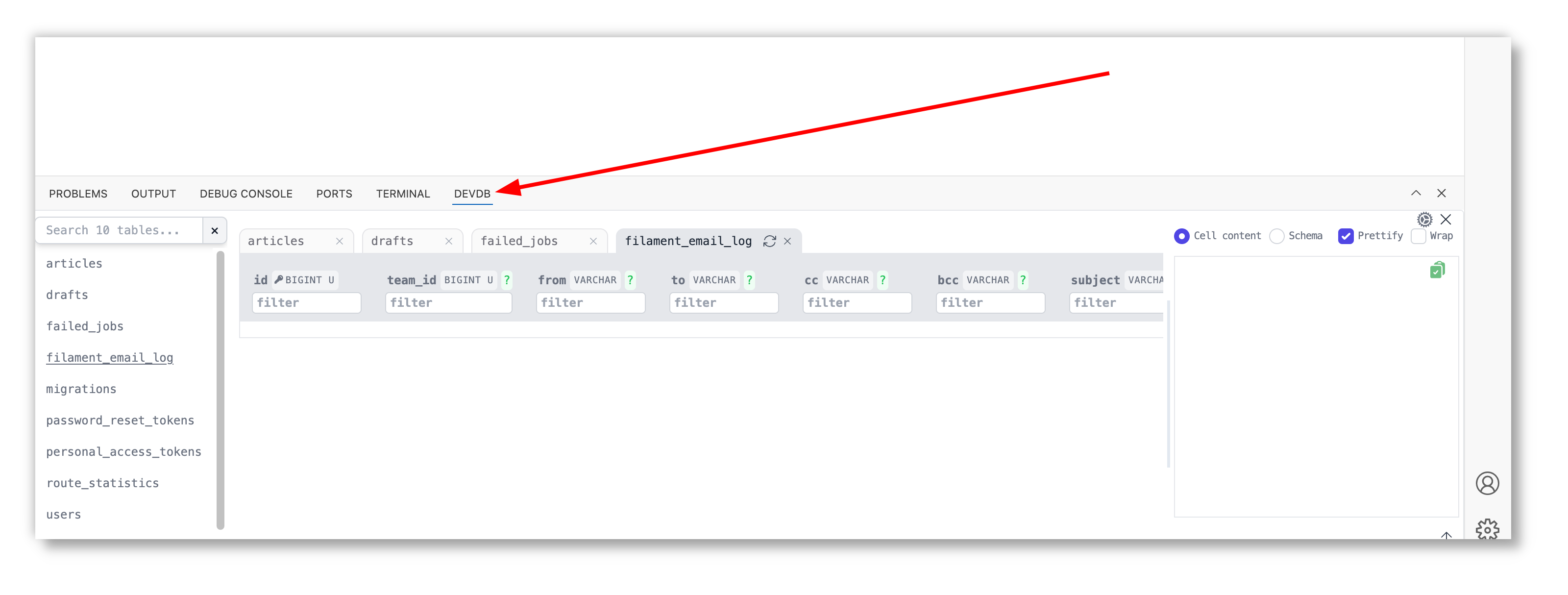
- DevDb loads your database. You can view your database by opening the DevDb (usually before the Terminal tab) as shown in the screenshot below, or by using the shortcut:
Note
Additionally, DevDb provides some Language and Framework Integrations
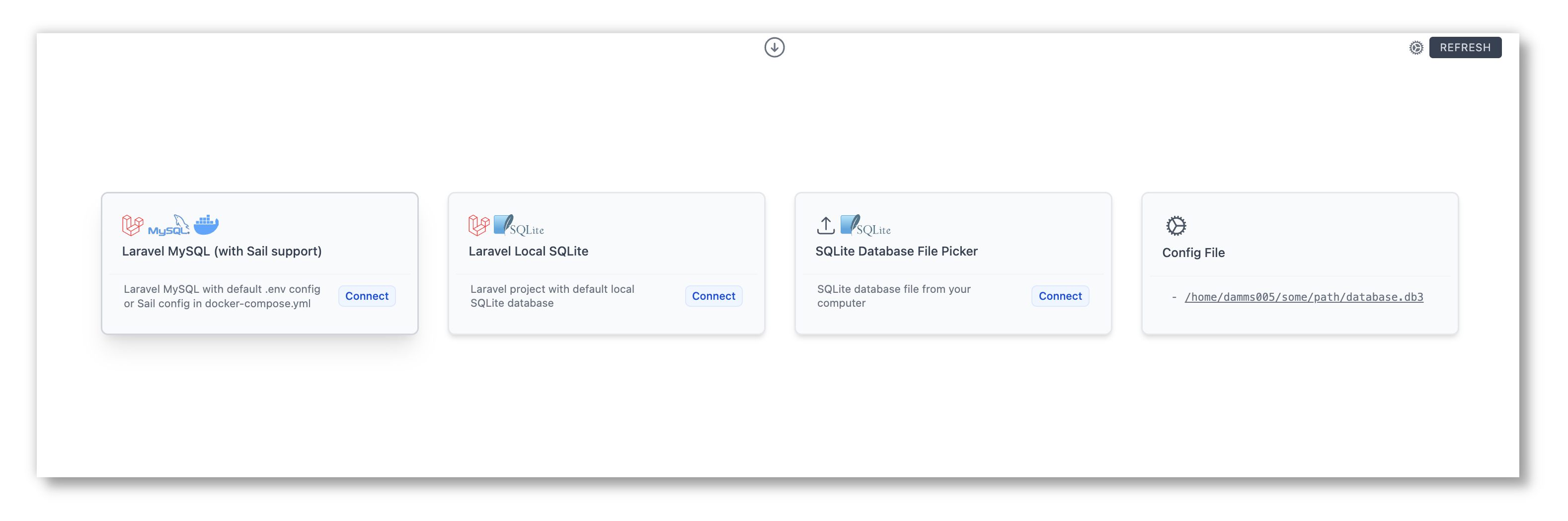
DevDb can automatically load your database using connection details from your VS Code workspace (zero-config mode). When zero-config support is not available for your development environment, configuration file option is available. These two options are explained below:
No configuration file is needed for these environments:
- Laravel with local default SQLite database
- Laravel MySQL/MariaDB with default .env config
- Containerized Laravel MySQL (Laravel Sail) with config in default .env/docker-compose.yml
- Laravel Postgres with default .env config
- Laravel Microsoft SQL Server with default .env config
If there is no zero-config support for your environment, simply provide a .devdbrc file in the root of your project containing your database connection details.
The content of the configuration file should be a single array containing database connection objects as shown below:
[
{
"type": "sqlite",
"path": "/home/path/to/database.sqlite"
}
]
[
{
"name": "My test MySQL database", // <-- to identify the connection
"type": "mysql", // <- or "mariadb" if you are using MariaDB
"host": "<host>",
"port": "<port>",
"username": "<username>",
"password": "<password>",
"database": "test" // <-- the database to show in VS Code DevDb view
}
]
[
{
"name": "My test Postgres database", // <-- to identify the connection
"type": "postgres",
"host": "<host>",
"port": "<port>",
"username": "<username>",
"password": "<password>",
"database": "test" // <-- the database to show in VS Code DevDb view
}
]
You can also have more than one connections in the configuration file, e.g.
[
{
"name": "My test MySQL database", // <-- to identify the connection
"type": "mysql",
"host": "<host>",
"port": "<port>",
"username": "<username>",
"password": "<password>",
"database": "test" // <-- the database to show in VS Code DevDb view
},
{
"type": "sqlite",
"path": "/home/path/to/database.sqlite"
}
]
Tip
You may not want to commit DevDb config file to your version control. This is because other devs in your team may be using different database connection details in their local environments.
Press Ctrl+K Ctrl+D to bring up DevDb view
The following databases are currently supported:
- SQLite
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- *Postgres
- Microsoft SQL Server
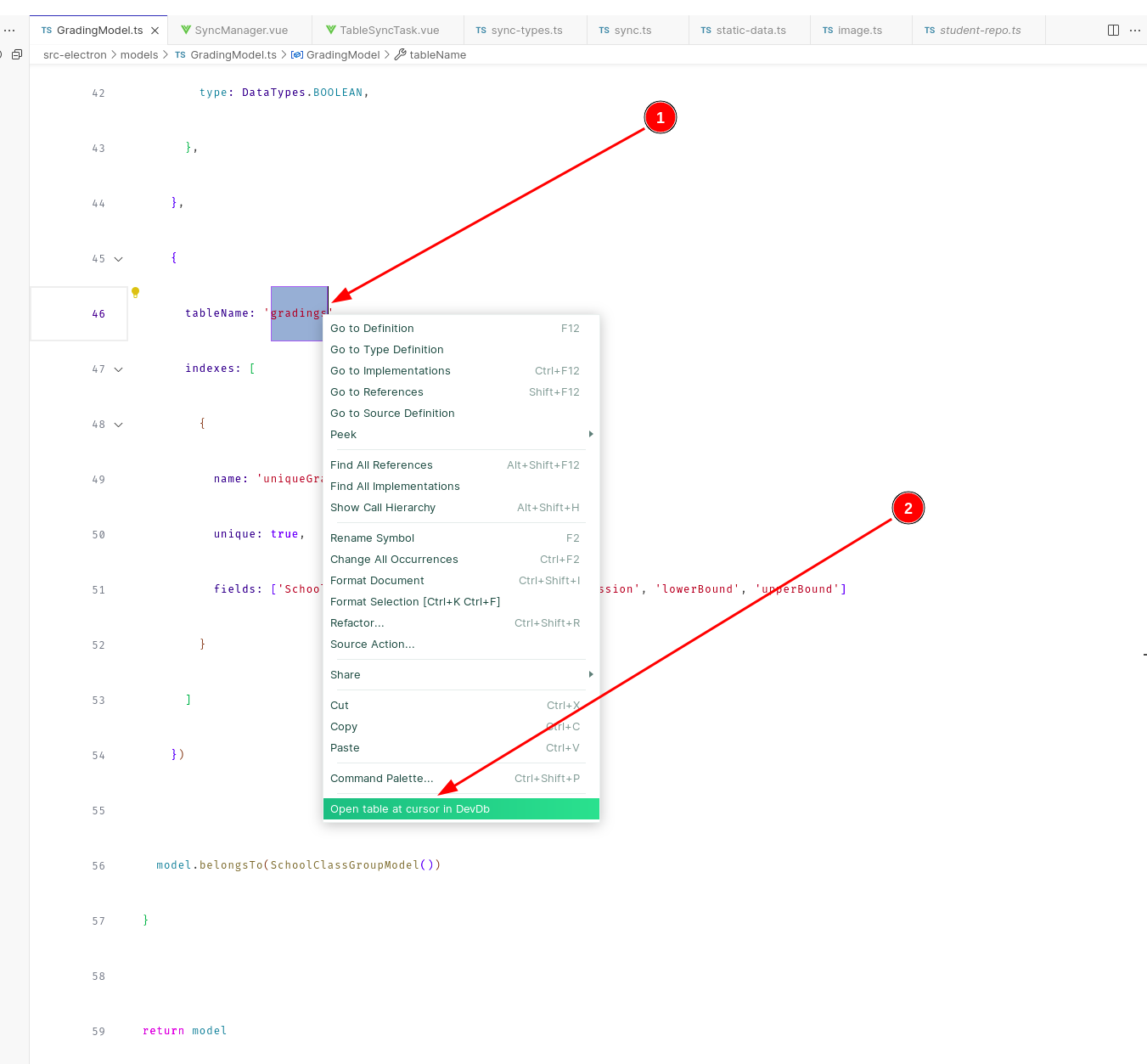
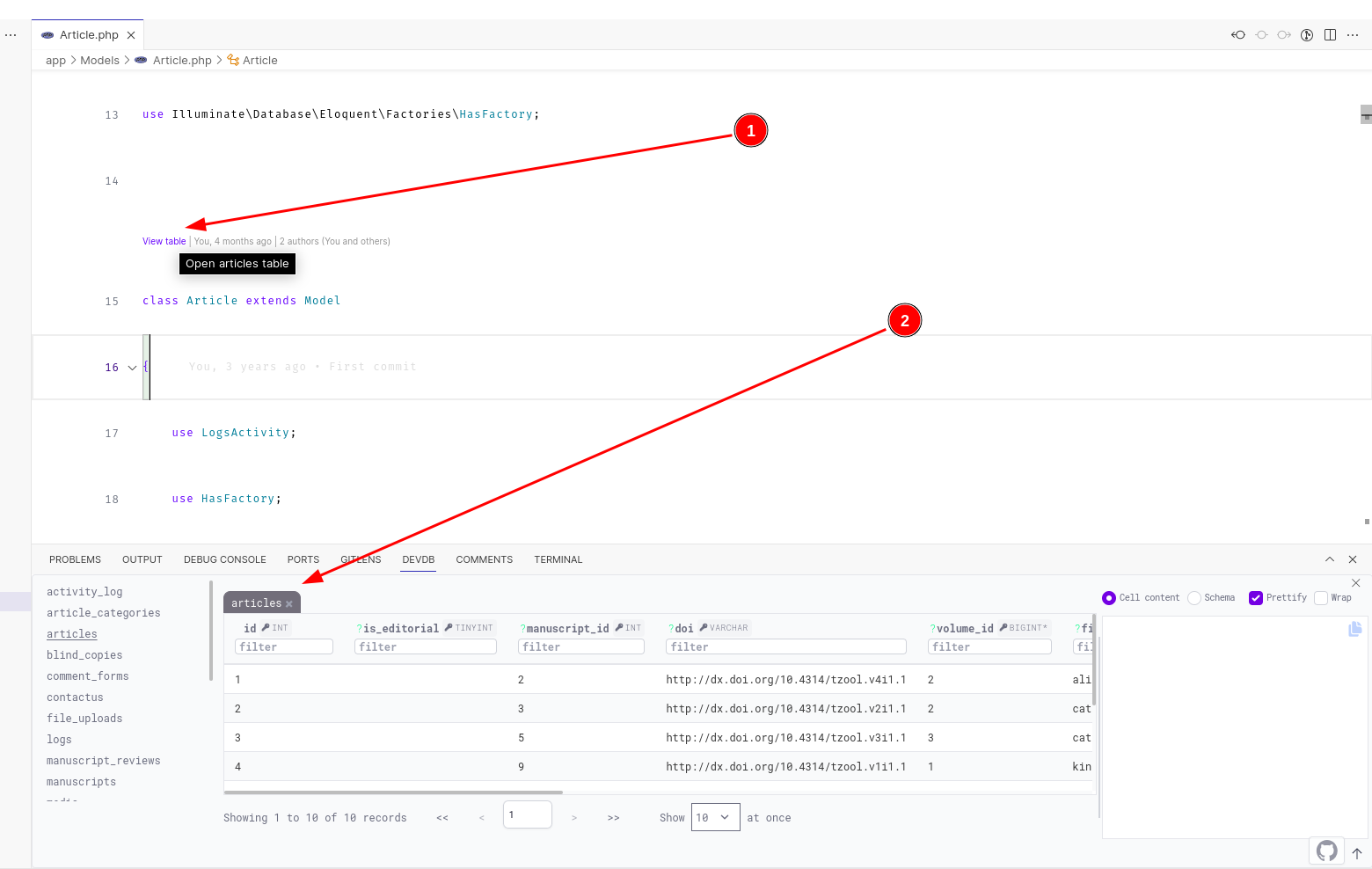
You can load a table by right-clicking on its name/model/entity from the editor (framework/programming language-agnostic) Example from a Node JS app (a Sequelize model definition)
If working in a Laravel project, DevDb provides Code Lens for viewing Eloquent model underlying table. NOTE: You need to first connect to a database in DevDb for Laravel Code Lens to be available.
Ctrl + Click(Meta + Clickon macOS) on a table from the sidebar to open the table in the current tab
Two words: Better DX.
DevDb aims to be a DB GUI client specifically designed for a much better development experience when working with databases. Specifically, these experiences:
- For any new project, it is usually required to setup db connection in the app project, and then in some other DB client.
- It is common to frequently tab-in and tab-out of project windows, switching between the IDE and DB client. Sometimes, frequent enough to want to view the DB data directly in the IDE. Think of how you've got your in-built terminal right in the IDE.
Local DX should be better than this.
Also, most of the DB clients are clunky or simply overwhelming, with bells and whistles that are not really useful during local development flow. Usually, being able to simply view DB data is all that is needed during local development.
Furthermore, who doesn't love beautiful UIs? DB clients have evolved to generally not have exciting UIs in my opinion, except just a few with excellent and intuitive UIs.
To address the above, there is a need for a database GUI tool that lives in the IDE, and mostly auto-detects and connects with the database configured in the currently opened workspace. It should be simple, fast, intuitive, and clean.
Hence, DevDb 🚀
DevDb does not aim to provide feature-parity with popular GUI database clients. This extension is focused on improving the experience of working with databases during application development.
Warning
Contributions are currently only accepted for the extension core code only.
Note
In order to contribute to the extension core, you may need to be conversant with VS Code Extension Guide.
- Fork this repo, then clone your fork to local
- Run
npm installto install dependencies - Make you contributions to the codebase locally
- Press
F5to launch the debugger to test your changes locally - Run the test suites with
npm run test-servicesand ensure existing tests pass (if you added tests with your changes, ensure those pass too) - Push your changes back to your fork
- Open a PR with your changes to this repo
- Take your flowers! 💐💐🎊🎊🎊