A tool that can parse, filter, split, merge rdb and analyze memory usage offline. It can also sync 2 redis data and allow user define there own sink service to migrate redis data to somewhere.
jdk 1.8+wget https://github.com/leonchen83/redis-rdb-cli/releases/download/${version}/redis-rdb-cli-release.zip
unzip redis-rdb-cli-release.zip
cd ./redis-rdb-cli/bin
./rct -hjdk 1.8+
maven-3.3.1+git clone https://github.com/leonchen83/redis-rdb-cli.git
cd redis-rdb-cli
mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true
cd target/redis-rdb-cli-release/redis-rdb-cli/bin
./rct -h docker run -it --rm redisrdbcli/redis-rdb-cli
rct -vAdd /path/to/redis-rdb-cli/bin to Path environment variable
usage: rct -f <format> -s <source> -o <file> [-d <num num...>] [-e
<escape>] [-k <regex regex...>] [-t <type type...>] [-b
<bytes>] [-l <n>] [-r]
options:
-b,--bytes <bytes> limit memory output(--format mem) to keys
greater to or equal to this value (in bytes)
-d,--db <num num...> database number. multiple databases can be
provided. if not specified, all databases
will be included.
-e,--escape <escape> escape strings to encoding: raw (default),
redis, json.
-f,--format <format> format to export. valid formats are json,
jsonl, dump, diff, key, keyval, count, mem
and resp
-h,--help rct usage.
-k,--key <regex regex...> keys to export. this can be a regex. if not
specified, all keys will be returned.
-l,--largest <n> limit memory output(--format mem) to only the
top n keys (by size).
-o,--out <file> output file.
-r,--replace whether the generated aof with <replace>
parameter(--format dump). if not specified,
default value is false.
-s,--source <source> <source> eg:
/path/to/dump.rdb
redis://host:port?authPassword=foobar
redis:///path/to/dump.rdb.
-t,--type <type type...> data type to export. possible values are
string, hash, set, sortedset, list, module,
stream. multiple types can be provided. if
not specified, all data types will be
returned.
-v,--version rct version.
examples:
rct -f dump -s ./dump.rdb -o ./appendonly.aof -r
rct -f resp -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -o ./target.aof -d 0 1
rct -f json -s ./dump.rdb -o ./target.json -k user.* product.*
rct -f mem -s ./dump.rdb -o ./target.aof -e redis -t list -l 10 -b 1024usage: rmt -s <source> [-m <uri> | -c <file>] [-d <num num...>] [-k <regex
regex...>] [-t <type type...>] [-r] [-l]
options:
-c,--config <file> migrate data to cluster via redis cluster's
<nodes.conf> file, if specified, no need to
specify --migrate.
-d,--db <num num...> database number. multiple databases can be
provided. if not specified, all databases
will be included.
-h,--help rmt usage.
-k,--key <regex regex...> keys to export. this can be a regex. if not
specified, all keys will be returned.
-l,--legacy if specify the <replace> and this parameter.
then use lua script to migrate data to
target. if target redis version is greater
than 3.0. no need to add this parameter.
-m,--migrate <uri> migrate to uri. eg:
redis://host:port?authPassword=foobar.
-r,--replace replace exist key value. if not specified,
default value is false.
-s,--source <source> <source> eg:
/path/to/dump.rdb
redis://host:port?authPassword=foobar
redis:///path/to/dump.rdb
-t,--type <type type...> data type to export. possible values are
string, hash, set, sortedset, list, module,
stream. multiple types can be provided. if
not specified, all data types will be
returned.
-v,--version rmt version.
examples:
rmt -s ./dump.rdb -c ./nodes.conf -t string -r
rmt -s ./dump.rdb -m redis://127.0.0.1:6380 -t list -d 0
rmt -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -m redis://127.0.0.1:6380 -d 0usage: rdt [-b <source> | -s <source> -c <file> | -m <file file...>] -o
<file> [-d <num num...>] [-k <regex regex...>] [-t <type
type...>]
options:
-b,--backup <source> backup <source> to local rdb file. eg:
/path/to/dump.rdb
redis://host:port?authPassword=foobar
redis:///path/to/dump.rdb
-c,--config <file> redis cluster's <nodes.conf> file(--split
<source>).
-d,--db <num num...> database number. multiple databases can be
provided. if not specified, all databases
will be included.
-h,--help rdt usage.
-k,--key <regex regex...> keys to export. this can be a regex. if not
specified, all keys will be returned.
-m,--merge <file file...> merge multi rdb files to one rdb file.
-o,--out <file> if --backup <source> or --merge <file
file...> specified. the <file> is the target
file. if --split <source> specified. the
<file> is the target path.
-s,--split <source> split rdb to multi rdb files via cluster's
<nodes.conf>. eg:
/path/to/dump.rdb
redis://host:port?authPassword=foobar
redis:///path/to/dump
-t,--type <type type...> data type to export. possible values are
string, hash, set, sortedset, list, module,
stream. multiple types can be provided. if
not specified, all data types will be
returned.
-v,--version rdt version.
examples:
rdt -b ./dump.rdb -o ./dump.rdb1 -d 0 1
rdt -b redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -o ./dump.rdb -k user.*
rdt -m ./dump1.rdb ./dump2.rdb -o ./dump.rdb -t hash
rdt -s ./dump.rdb -c ./nodes.conf -o /path/to/folder -t hash -d 0
rdt -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -c ./nodes.conf -o /path/to/folder -d 0usage: rst -s <source> [-m <uri> | -c <file>] [-d <num num...>] [-r] [-l]
options:
-c,--config <file> migrate data to cluster via redis cluster's
<nodes.conf> file, if specified, no need to
specify --migrate.
-d,--db <num num...> database number. multiple databases can be
provided. if not specified, all databases will be
included.
-h,--help rst usage.
-l,--legacy if specify the <replace> and this parameter. then
use lua script to migrate data to target. if
target redis version is greater than 3.0. no need
to add this parameter.
-m,--migrate <uri> migrate to uri. eg:
redis://host:port?authPassword=foobar.
-r,--replace replace exist key value. if not specified, default
value is false.
-s,--source <source> <source> eg:
redis://host:port?authPassword=foobar
-v,--version rst version.
examples:
rst -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -c ./nodes.conf -r
rst -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -m redis://127.0.0.1:6380 -d 0usage: ret -s <source> [-c <file>] [-p <parser>] -n <sink>
options:
-c,--config <file> external config file, if not specified, default
value is null
-h,--help ret usage.
-n,--name <sink> sink service name, registered sink service:
example
-p,--parser <parser> parser service name, registered parser service:
default, dump. if not specified, default value is
default
-s,--source <source> <source> eg:
redis://host:port?authPassword=foobar
-v,--version ret version.
examples:
ret -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -c ./config.conf -n example
ret -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -c ./config.conf -p dump -n examplerct,rdtandrmtthese 3 commands support data filter bytype,dbandkeyRegEx(Java style).rstthis command only support data filter bydb.
For example:
rct -f dump -s /path/to/dump.rdb -o /path/to/dump.aof -d 0
rct -f dump -s /path/to/dump.rdb -o /path/to/dump.aof -t string hash
rmt -s /path/to/dump.rdb -m redis://192.168.1.105:6379 -r -d 0 1 -t list
rst -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -m redis://127.0.0.1:6380 -d 0rct -f dump -s /path/to/dump.rdb -o /path/to/dump.aof -r
cat /path/to/dump.aof | /redis/src/redis-cli -p 6379 --piperct -f dump -s /path/to/dump.rdb -o /path/to/dump.aofrct -f json -s /path/to/dump.rdb -o /path/to/dump.jsonrct -f count -s /path/to/dump.rdb -o /path/to/dump.csvrct -f mem -s /path/to/dump.rdb -o /path/to/dump.mem -l 50rct -f diff -s /path/to/dump1.rdb -o /path/to/dump1.diff
rct -f diff -s /path/to/dump2.rdb -o /path/to/dump2.diff
diff /path/to/dump1.diff /path/to/dump2.diffrct -f resp -s /path/to/dump.rdb -o /path/to/appendonly.aofrst -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -m redis://127.0.0.1:6380 -rrst -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -m redis://127.0.0.1:30001 -r -d 0rmt -s /path/to/dump.rdb -m redis://192.168.1.105:6379 -rrmt -s /path/to/dump.rdb -c ./nodes-30001.conf -ror simply use following cmd without nodes-30001.conf
rmt -s /path/to/dump.rdb -m redis://127.0.0.1:30001 -rrdt -b redis://192.168.1.105:6379 -o /path/to/dump.rdbrdt -b /path/to/dump.rdb -o /path/to/filtered-dump.rdb -d 0 -t stringrdt -s ./dump.rdb -c ./nodes.conf -o /path/to/folder -d 0rdt -m ./dump1.rdb ./dump2.rdb -o ./dump.rdb -t hashMore configurable parameter can be modified in /path/to/redis-rdb-cli/conf/redis-rdb-cli.conf
- When
rmtstarted. source redis first doBGSAVEand generate a snapshot rdb file.rmtcommand migrate this snapshot file to target redis. after this process done,rmtterminated. rstnot only migrate snapshot rdb file but also incremental data from source redis. sorstnever terminated except typeCTRL+C.rstonly supportdbfilter more details please refer to Limitation of migration
Since v0.1.9, the rct -f mem support showing result in grafana dashboard like the following:
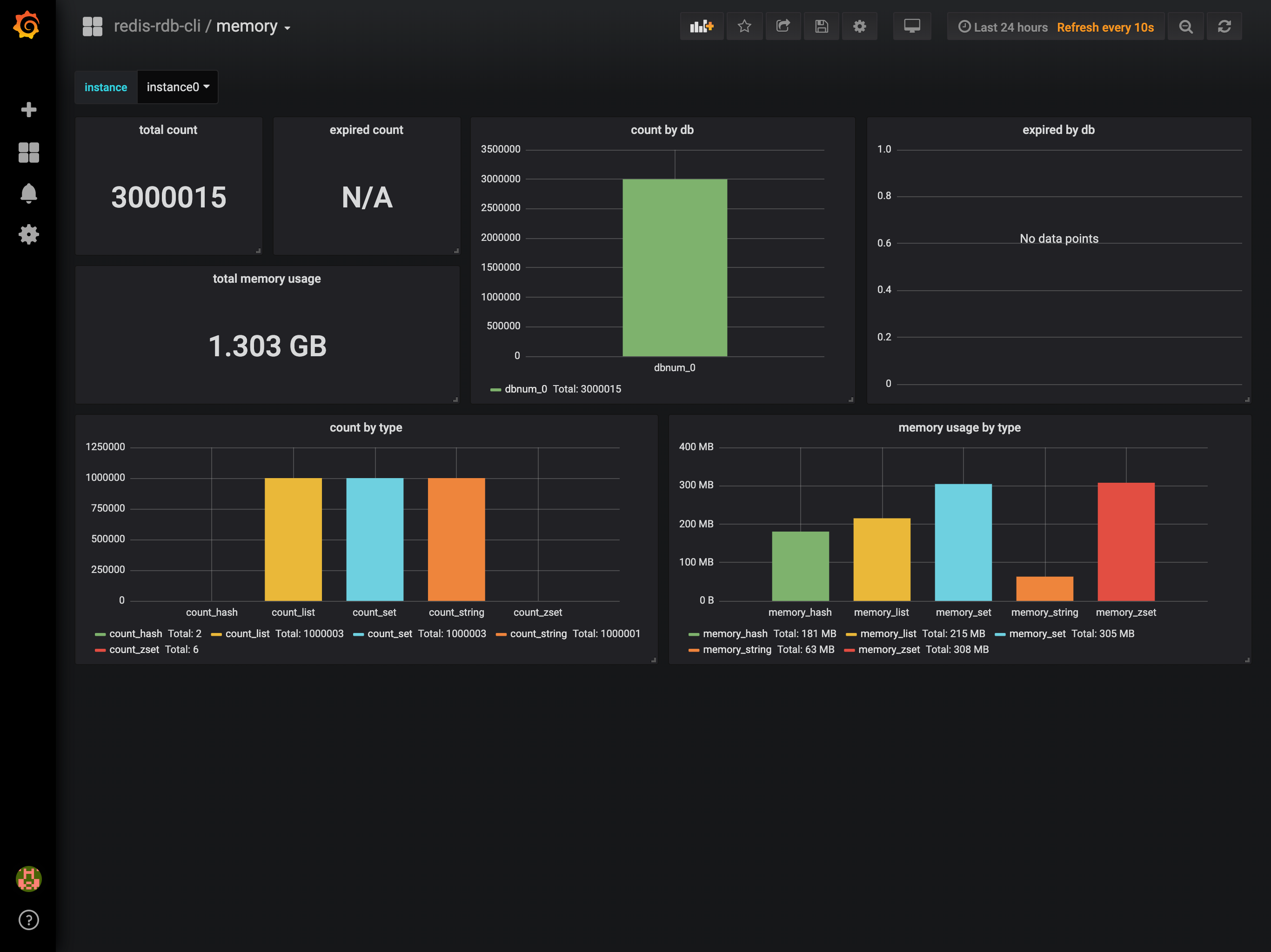
If you want to turn it on. you MUST install docker and docker-compose first, the installation please refer to docker
Then run the following command:
cd /path/to/redis-rdb-cli/dashboard
# start
docker-compose up -d
# stop
docker-compose downcd /path/to/redis-rdb-cli/conf/redis-rdb-cli.conf
Then change parameter metric_gateway from none to influxdb.
Open http://localhost:3000 to check the rct -f mem's result.
If you deployed this tool in multi instance, you need to change parameter metric_instance to make sure unique between instances.
- use openssl to generate keystore
$cd /path/to/redis-6.0-rc1
$./utils/gen-test-certs.sh
$cd tests/tls
$openssl pkcs12 -export -CAfile ca.crt -in redis.crt -inkey redis.key -out redis.p12
-
If source redis and target redis use the same keystore. then config following parameters
source_keystore_path and target_keystore_path to point to/path/to/redis-6.0-rc1/tests/tls/redis.p12
set source_keystore_pass and target_keystore_pass -
after config ssl parameters use
rediss://host:portin your command to open ssl, for example:rst -s rediss://127.0.0.1:6379 -m rediss://127.0.0.1:30001 -r -d 0
- use following URI to open redis ACL support
rst -s redis://user:pass@127.0.0.1:6379 -m redis://user:pass@127.0.0.1:6380 -r -d 0userMUST have+@allpermission to handle commands
The rmt command use the following 4 parameters(redis-rdb-cli.conf) to migrate data to remote.
migrate_batch_size=4096
migrate_threads=4
migrate_flush=yes
migrate_retries=1The most important parameter is migrate_threads=4. this means we use the following threading model to migrate data.
single redis ----> single redis
+--------------+ +----------+ thread 1 +--------------+
| | +----| Endpoint |-------------------| |
| | | +----------+ | |
| | | | |
| | | +----------+ thread 2 | |
| | |----| Endpoint |-------------------| |
| | | +----------+ | |
| Source Redis |----| | Target Redis |
| | | +----------+ thread 3 | |
| | |----| Endpoint |-------------------| |
| | | +----------+ | |
| | | | |
| | | +----------+ thread 4 | |
| | +----| Endpoint |-------------------| |
+--------------+ +----------+ +--------------+single redis ----> redis cluster
+--------------+ +----------+ thread 1 +--------------+
| | +----| Endpoints|-------------------| |
| | | +----------+ | |
| | | | |
| | | +----------+ thread 2 | |
| | |----| Endpoints|-------------------| |
| | | +----------+ | |
| Source Redis |----| | Redis cluster|
| | | +----------+ thread 3 | |
| | |----| Endpoints|-------------------| |
| | | +----------+ | |
| | | | |
| | | +----------+ thread 4 | |
| | +----| Endpoints|-------------------| |
+--------------+ +----------+ +--------------+The difference between cluster migration and single migration is Endpoint and Endpoints. In cluster migration the Endpoints contains multi Endpoint to point to every master instance in cluster. For example:
3 masters 3 replicas redis cluster. if migrate_threads=4 then we have 3 * 4 = 12 connections that connected with master instance.
The following 3 parameters affect migration performance
migrate_batch_size=4096
migrate_retries=1
migrate_flush=yesmigrate_batch_size: By default we use redispipelineto migrate data to remote. themigrate_batch_sizeis thepipelinebatch size. ifmigrate_batch_size=1then thepipelinedevolved into 1 single command to sent and wait the response from remote.migrate_retries: Themigrate_retries=1means if socket error occurred. we recreate a new socket and retry to send that failed command to target redis withmigrate_retriestimes.migrate_flush: Themigrate_flush=yesmeans we write every 1 command to socket. then we invokeSocketOutputStream.flush()immediately. ifmigrate_flush=nowe invokeSocketOutputStream.flush()when write to socket every 64KB. notice that this parameter also affectmigrate_retries. themigrate_retriesonly take effect whenmigrate_flush=yes.
+---------------+ +-------------------+ restore +---------------+
| | | redis dump format |---------------->| |
| | |-------------------| restore | |
| | convert | redis dump format |---------------->| |
| Dump rdb |------------>|-------------------| restore | Targe Redis |
| | | redis dump format |---------------->| |
| | |-------------------| restore | |
| | | redis dump format |---------------->| |
+---------------+ +-------------------+ +---------------+- We use cluster's
nodes.confto migrate data to cluster. because of we did't handle theMOVEDASKredirection. so limitation of cluster migration is that the cluster MUST in stable state during the migration. this means the cluster MUST have nomigrating,importingslot and no switch slave to master. - If use
rstmigrate data to cluster. the following commands not supportedSWAPDB,MOVE,FLUSHALL,FLUSHDB,PUBLISH,MULTI,EXEC,SCRIPT FLUSH,SCRIPT LOAD,EVAL,EVALSHA. and the following commandsRPOPLPUSH,SDIFFSTORE,SINTERSTORE,SMOVE,ZINTERSTORE,ZUNIONSTORE,DEL,UNLINK,RENAME,RENAMENX,PFMERGE,PFCOUNT,MSETNX,BRPOPLPUSH,BITOP,MSET,COPY,BLMOVE,LMOVE,ZDIFFSTORE,GEOSEARCHSTOREONLY SUPPORT WHEN THESE COMMAND KEYS IN THE SAME SLOT(eg:del {user}:1 {user}:2)
retcommand that allow user define there own sink service like sink redis data tomysqlormongodb.retcommand using Java SPI extension to do this job.
User should follow the steps below to implement a sink service.
- create a java project using maven pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.your.company</groupId>
<artifactId>your-sink-service</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.moilioncircle</groupId>
<artifactId>redis-rdb-cli-api</artifactId>
<version>1.5.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.moilioncircle</groupId>
<artifactId>redis-replicator</artifactId>
<version>[3.4.0, )</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--
<dependency>
other dependencies
</dependency>
-->
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<configuration>
<descriptorRefs>
<descriptorRef>jar-with-dependencies</descriptorRef>
</descriptorRefs>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>make-assembly</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
<encoding>${project.build.sourceEncoding}</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>- implement
SinkServiceinterface
public class YourSinkService implements SinkService {
@Override
public String sink() {
return "your-sink-service";
}
@Override
public void init(File config) throws IOException {
// parse your external sink config
}
@Override
public void onEvent(Replicator replicator, Event event) {
// your sink business
}
}- register this service using Java SPI
# create com.moilioncircle.redis.rdb.cli.api.sink.SinkService file in src/main/resources/META-INF/services/
|-src
|____main
| |____resources
| | |____META-INF
| | | |____services
| | | | |____com.moilioncircle.redis.rdb.cli.api.sink.SinkService
# add following content in com.moilioncircle.redis.rdb.cli.api.sink.SinkService
your.package.YourSinkService- package and deploy
mvn clean install
cp ./target/your-sink-service-1.0.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar /path/to/redis-rdb-cli/lib- run your sink service
ret -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -c config.conf -n your-sink-service- debug your sink service
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Replicator replicator = new RedisReplicator("redis://127.0.0.1:6379");
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> {
Replicators.closeQuietly(replicator);
}));
replicator.addExceptionListener((rep, tx, e) -> {
throw new RuntimeException(tx.getMessage(), tx);
});
SinkService sink = new YourSinkService();
sink.init(new File("/path/to/your-sink.conf"));
replicator.addEventListener(new AsyncEventListener(sink, replicator, 4, Executors.defaultThreadFactory()));
replicator.open();
}- create
YourFormatterServiceextendAbstractFormatterService
public class YourFormatterService extends AbstractFormatterService {
@Override
public String format() {
return "test";
}
@Override
public Event applyString(Replicator replicator, RedisInputStream in, int version, byte[] key, int type, ContextKeyValuePair context) throws IOException {
byte[] val = new DefaultRdbValueVisitor(replicator).applyString(in, version);
getEscaper().encode(key, getOutputStream());
getEscaper().encode(val, getOutputStream());
getOutputStream().write('\n');
return context;
}
}- register this formatter using Java SPI
# create com.moilioncircle.redis.rdb.cli.api.format.FormatterService file in src/main/resources/META-INF/services/
|-src
|____main
| |____resources
| | |____META-INF
| | | |____services
| | | | |____com.moilioncircle.redis.rdb.cli.api.format.FormatterService
# add following content in com.moilioncircle.redis.rdb.cli.api.format.FormatterService
your.package.YourFormatterService- package and deploy
mvn clean install
cp ./target/your-service-1.0.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar /path/to/redis-rdb-cli/lib- run your formatter service
rct -f test -s redis://127.0.0.1:6379 -o ./out.csv -t string -d 0 -e json- Baoyi Chen
- TaoBeier
- Maz Ahmadi
- Anish Karandikar
- Special thanks to Kater Technologies

