Welcome to the CTMC's GitHub Tutorial repository. This guide will walk you through the process of contributing to CTMC projects hosted on GitHub.
This tutorial has been designed with Windows users in mind so some steps may not reflect what you will need to do if using MacOS or Linux. In this case, feel free to reach out to Jevex on Discord at Jevex#3001 for guidance if you require additional assistance.
Additionally, during some parts of this tutorial you may read some terminology that you are unfamiliar with. No need to worry, you do not need to understand terms like "branch protection" to follow this tutorial, those details are simply provided in the event you would like to learn more about the topics that this tutorial covers.
To get started contributing to community repositories, you will need to have a GitHub account which you can sign up for here: https://github.com/signup.
You will need to enable 2FA on your account as it is required for all members of the ctm-community organization and will be required for all GitHub users by the end of 2023.
Once you have an account, contact Jevex on Discord at Jevex#3001 to get added to the mapmakers team. This will give you permission to push code to unprotected branches on the current community project.
In addition to a GitHub account, you will need to have either Git for Windows or GitHub Desktop installed on your computer.
On Windows, this can be done using the Windows Package Manager CLI (winget) by running the following commands in a terminal (e.g. Windows Terminal, PowerShell, Command Prompt):
Install Git for Windows:
winget install -e --id Git.Git
Install GitHub Desktop:
winget install -e --id GitHub.GitHubDesktop
After installing GitHub Desktop you will be welcomed by this screen upon launching it for the first time:
Select the Sign in to GitHub.com option to link your account and after following the prompts in your web browser, you will be asked to Configure Git with a window similar to this one:
The default settings should work just fine so you can proceed to the next step after clicking Finish.
Once you have been added to the mapmakers team, you will need to clone the repository by following the instructions below for GitHub Desktop or checking out GitHub's tutorial: https://github.com/git-guides/git-clone.
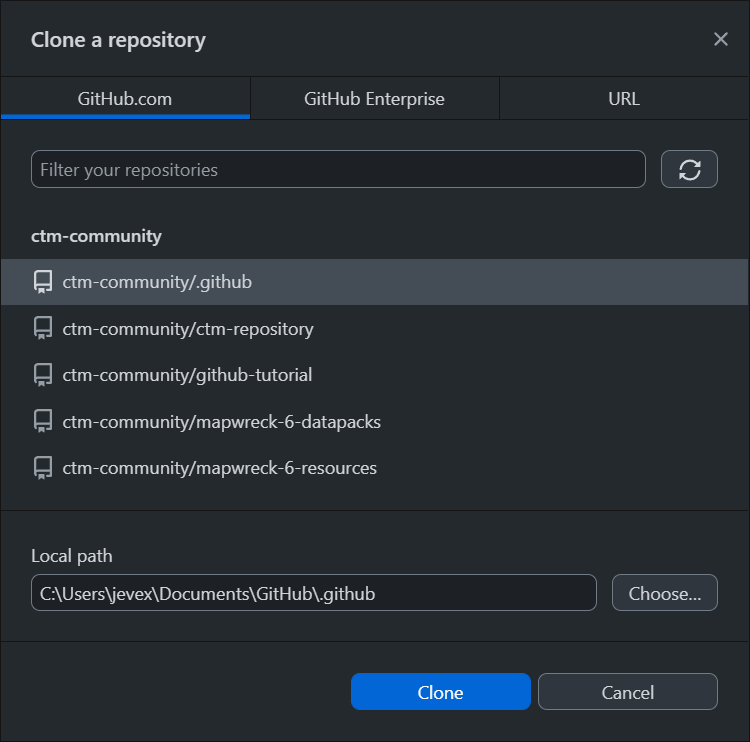
If you have linked your GitHub account to GitHub Desktop, then you can clone a repository by going into the File menu and selecting Clone repository... or using the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Shift+O on Windows.
This will bring up the Clone a Repository window where you can select the repository you would like to clone. If you are a member of the ctm-community organization, you should be able to filter the list for the repository you would like to clone. However, if you are still waiting to get added, you can also clone the repository in the URL tab by directly pasting in the repository's URL.
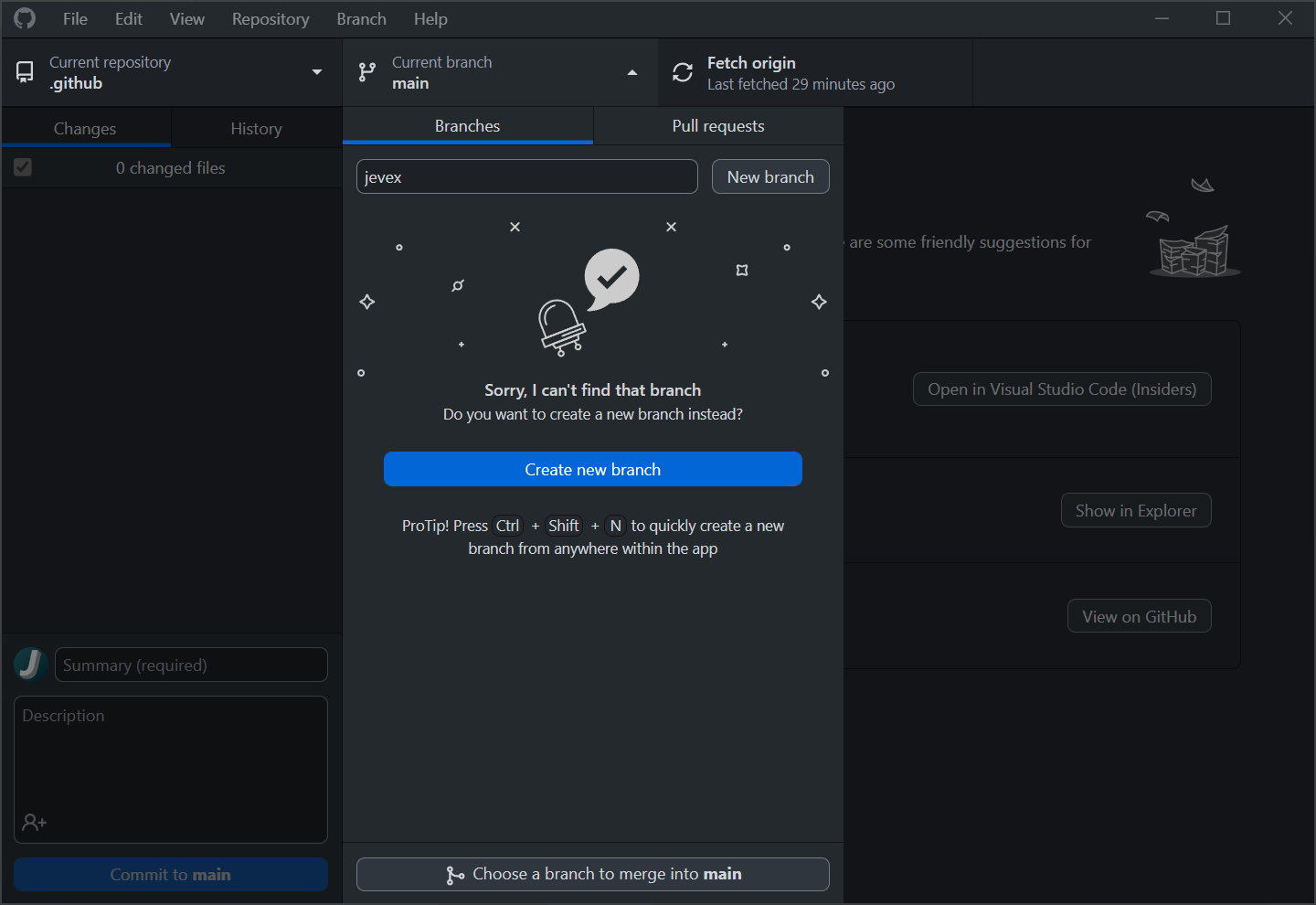
When you first clone a repository, you will be on the repository's main branch. Since this branch is the official branch, it is protected and you will not be allowed to modify it directly. Instead, you will need to create a feature branch to make your changes and you can do this by selecting the Current branch dropdown menu, typing in your username, and selecting Create a new branch:
Although the branch name could technically be anything, it is recommended to use your username as the name of your branch to make it easier to keep track of contributions and locate the branch of specific contributors.
After creating a new branch, you will want to publish it to GitHub. This option will appear to the right of the Current branch dropdown menu and in a blue prompt message if you have yet to make any changes to your branch.
Although you can wait to do this until after you have made changes, it is recommended to publish the branch now just to make sure you have set up your local repository correctly.
After you have made modifications to your local repository, you will eventually want to submit your changes to the remote GitHub repository. To do this you will first want to make sure that you have committed and pushed your changes to the repository on GitHub and then you will need to make a pull request so that someone on the events-team can merge your changes.
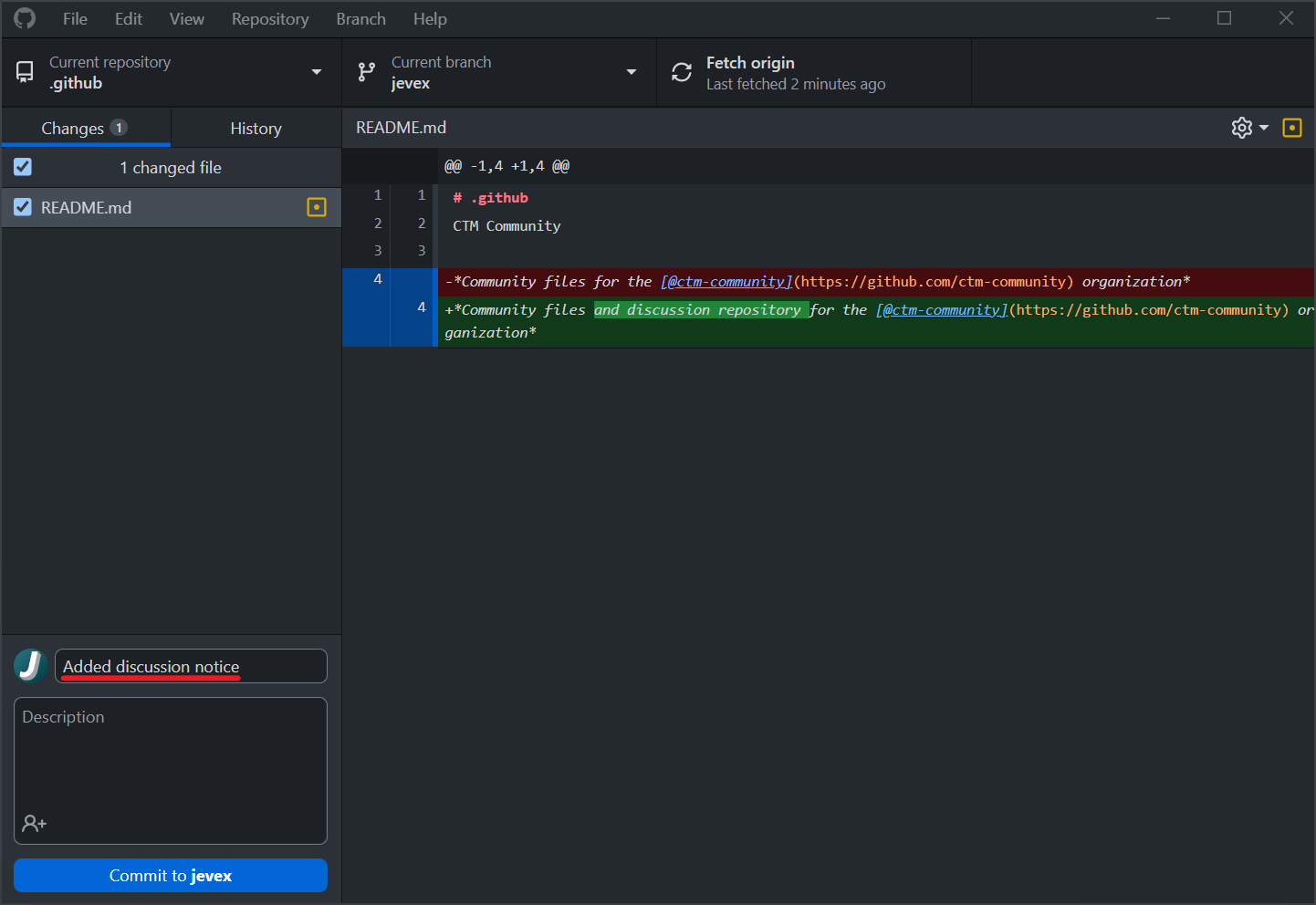
To begin, open GitHub Desktop and add a descriptive commit message like "Added model for obsidian broadsword" or "Added discussion notice" as shown in the example image below:
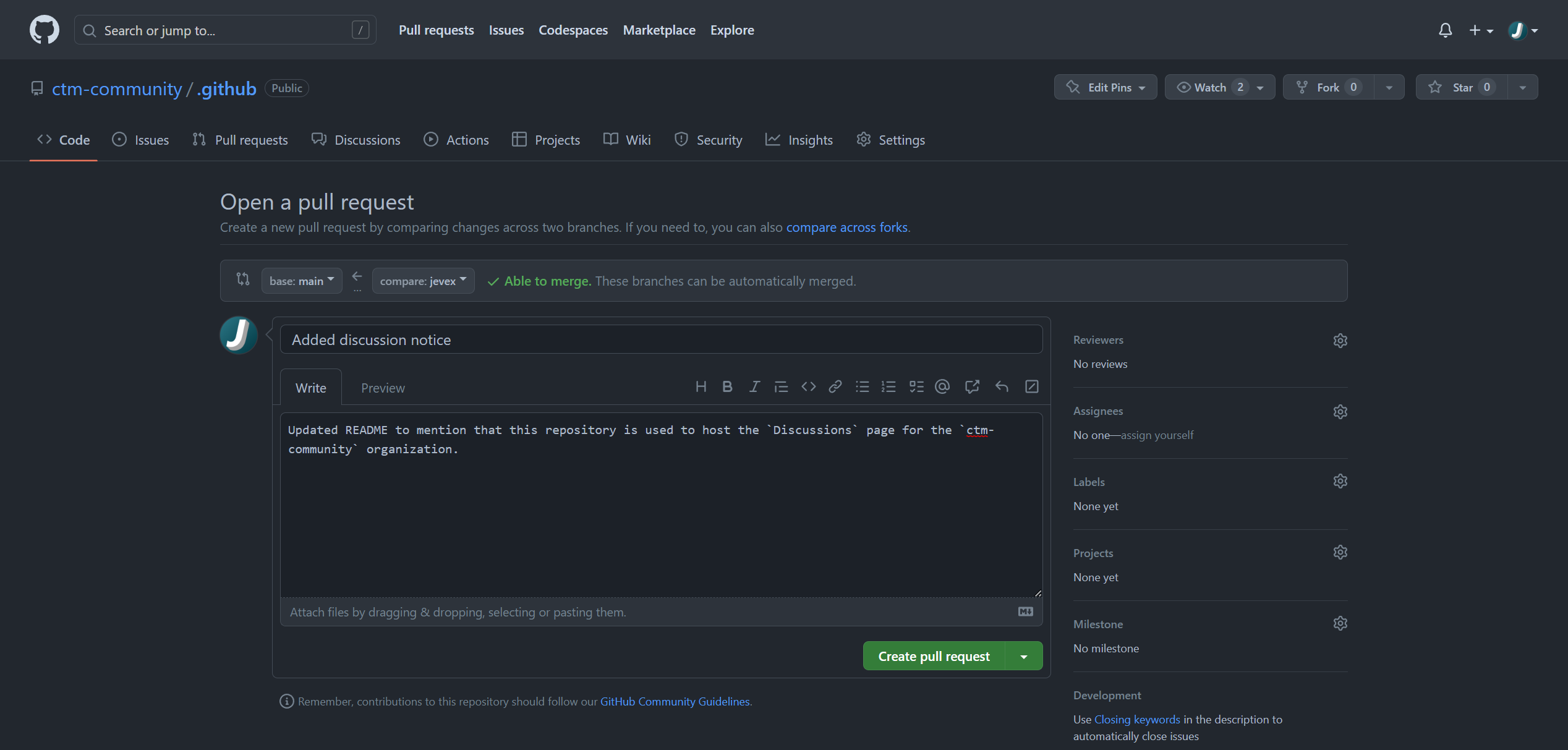
After writing your message, click the blue commit button and you should be prompted to Push origin to GitHub. Then you will be able to go to GitHub's website to create a pull request for your changes. GitHub Desktop should automatically prompt you to create a pull request with a button labeled Create Pull Request which will take you to a webpage where you can submit the request:
At this point, it would be helpful if you write a short description of the changes you have made and then open the pull request for review by clicking on the green Create pull request button.
A member of the events-team will then review your changes to try and spot any issues before informing you of changes you need to make or accepting your request and merging your changes into the main branch.