A suite of scripts to use OACIS docker.
git clone https://github.com/crest-cassia/oacis_docker_tools.git
cd oacis_docker_tools$ ./oacis_boot.shA container of OACIS launches. It takes some time until the launch completes.
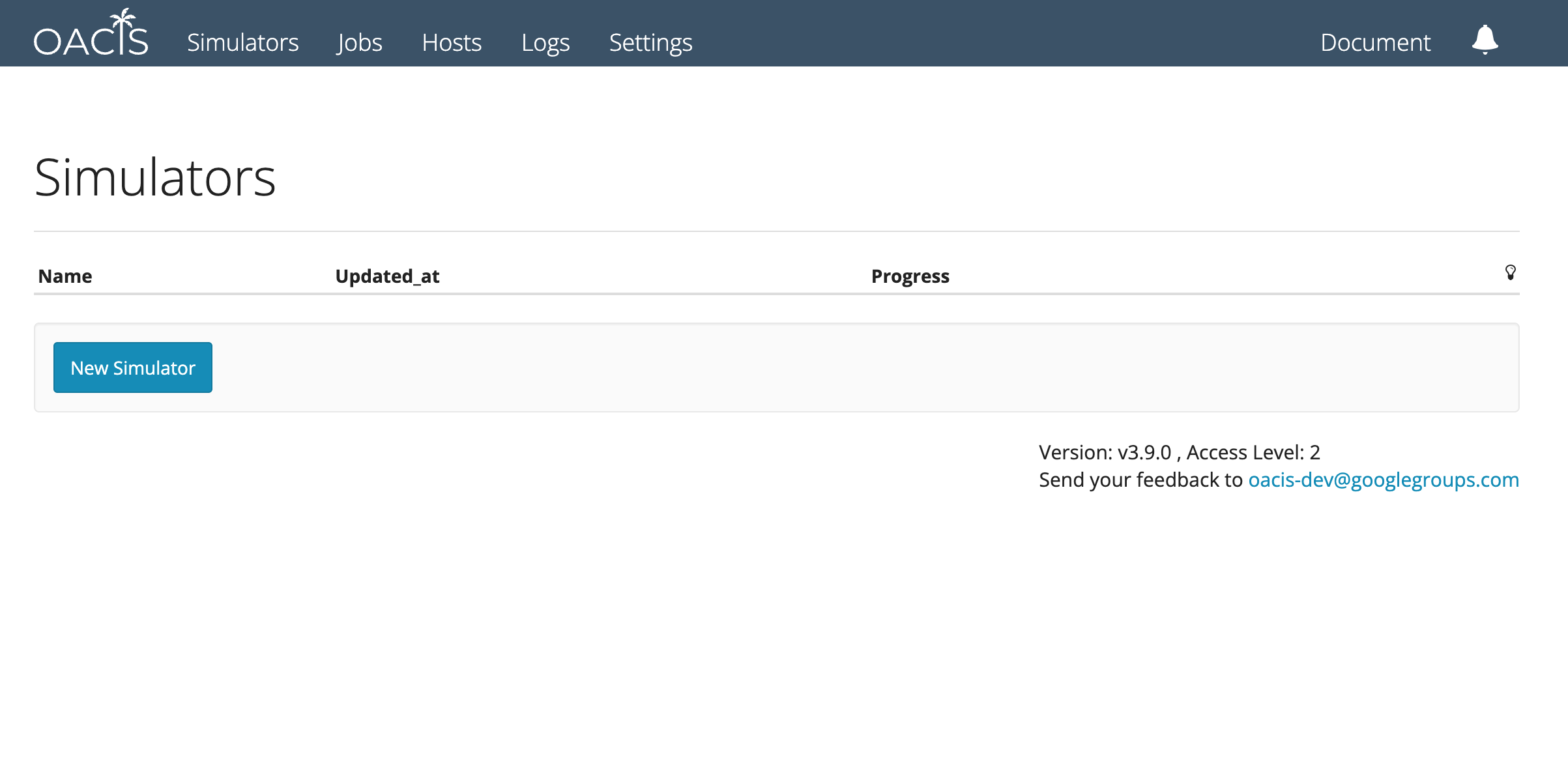
- Visit http://localhost:3000 to access OACIS like the following. You may change the port by specifying
-poption. - Visit http://localhost:8888 to access Jupyter notebook with OACIS API. The port may be changed by
-joption.
See OACIS documentation.
$ ./oacis_stop.shEven after the server is stopped, the data (including your simulation results) are not deleted. In other words, the virtual machine image still exists.
Restart the container by running oacis_start.sh.
$ ./oacis_start.shWhen you would like to remove the docker container as well as the docker volumes, run the following command:
$ ./oacis_terminate.shNote: The database is deleted. Make sure to make a backup if you want to save your results somewhere.
The simulation output files are stored in Result directory, which is NOT deleted by the above command. To delete all the files, remove Result directory as well.
$ rm -rf ResultWhen we would like to move all the data to other directory or make a backup, run the following command:
$ ./oacis_dump_db.shAll the data stored in the database running on the container are dumped into Result/db_dump.
After you run the above command, send Result directory to the place you like. For instance, run the following:
$ rsync -avhz --progress Result /path/to/backupTo restore the data from a backup, copy the backup to the Result directory first and then run the restore command.
Make sure that OACIS must be running when restoring the DB.
$ rsync -avhz --progress /path/to/backup Result
$ ./oacis_boot.sh # OACIS must be launched in advance
$ ./oacis_restore_db.shWhen you would like to login to the shell on the docker container for trouble shooting, run the following command:
$ ./oacis_shell.shOn the container, you can use the SSH agent running on the host OS. (Hereafter, the host on which docker is running is called host OS). If environemnt varialbe SSH_AUTH_SOCK is set in the host OS, the agent and ~.ssh/config are mounted on the container so that you can connect to remote hosts from OACIS.
Here is how to set up SSH agent.
OACIS requires an authentication by SSH keys. If you haven't made a SSH key-pair, create one in order to use it for your use.
$ ssh-keygen -t rsaYou may enter a passphrase when making a key-pair. The key pair will be created in ~/.ssh directory.
Set up ssh-agent on your host OS. Launch SSH agent as follows. On macOS, SSH agent is automatically launched so you can skip this step.
$ eval $(ssh-agent)
Agent pid 97280Edit ~/.ssh/config file. This file is mounted on the container when running oacis_boot.sh.
The information required for SSH connection is determined by this file.
You'll be required to enter the passphrase for this key.
$ ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsaNow you should be able to connect to a remote host wihtout entering a password.
$ ssh my_remote_host(If you are going to use the host OS as one of the computational hosts for OACIS) Add this key to the list of authorized_keys. Make sure the permission of the authorized_keys is 600 when you make this file for the first time. You should be able to login to the localhost without entering your password.
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ chmod 600 authorized_keys
$ ssh localhost # password should not be requiredSet up xsub or xsub_py on remote hosts. See README of the repository for the details.
When these set up are done, launch OACIS.
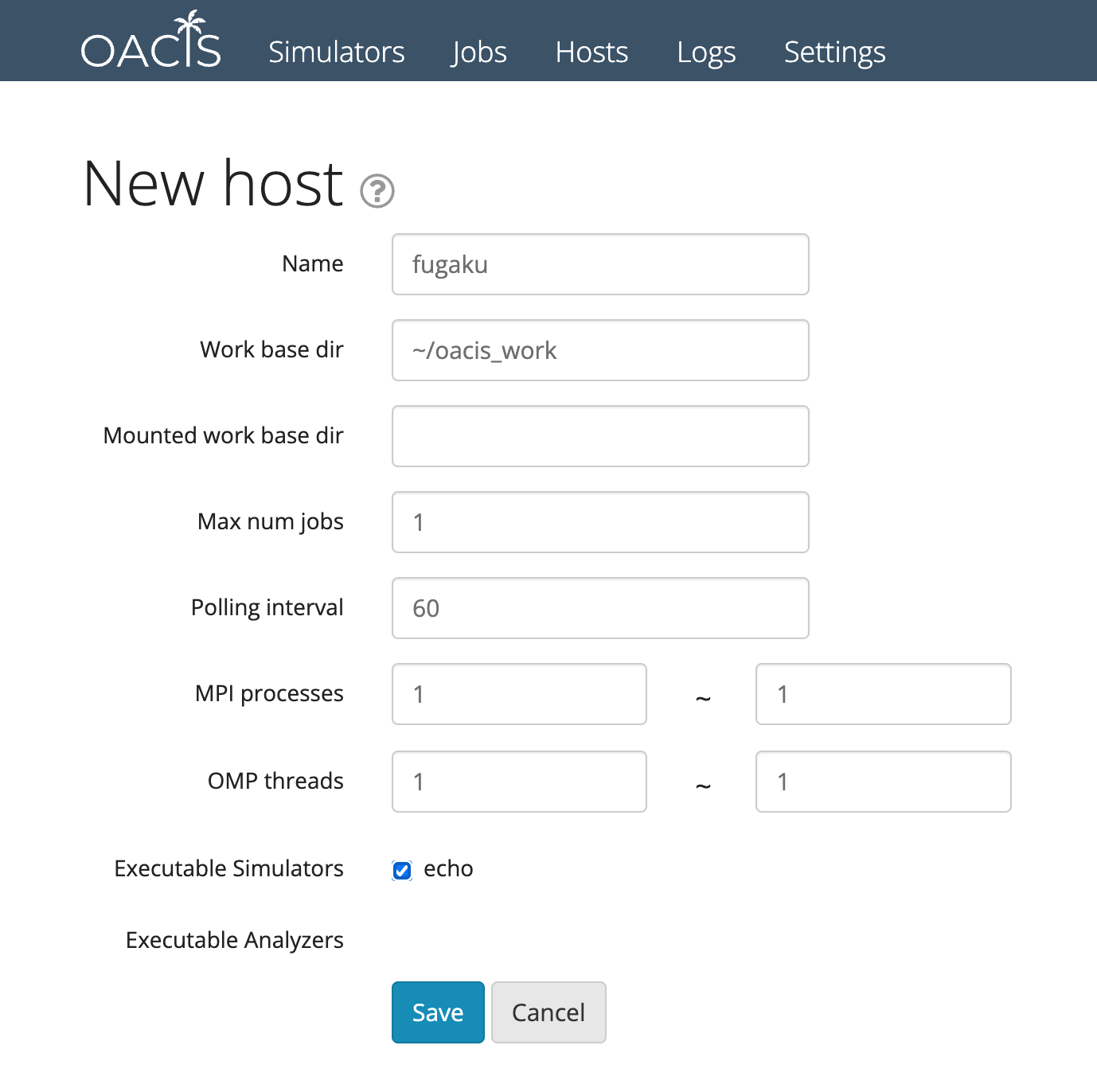
$ ./oacis_boot.shGo to the page of host list. http://localhost:3000/hosts
Select New Host and fill in the host information. You can add hosts that are listed in ~/.ssh/config.
See the document for details: How to setup host on OACIS
Add a host with the reserved name "docker-host" to use your host OS as a computational host. You'll be able to run your simulators on your host OS.
oacis_docker_tools is a part of OACIS. OACIS is published under the term of the MIT License (MIT). Copyright (c) 2014-2022 RIKEN AICS, RIKEN R-CCS