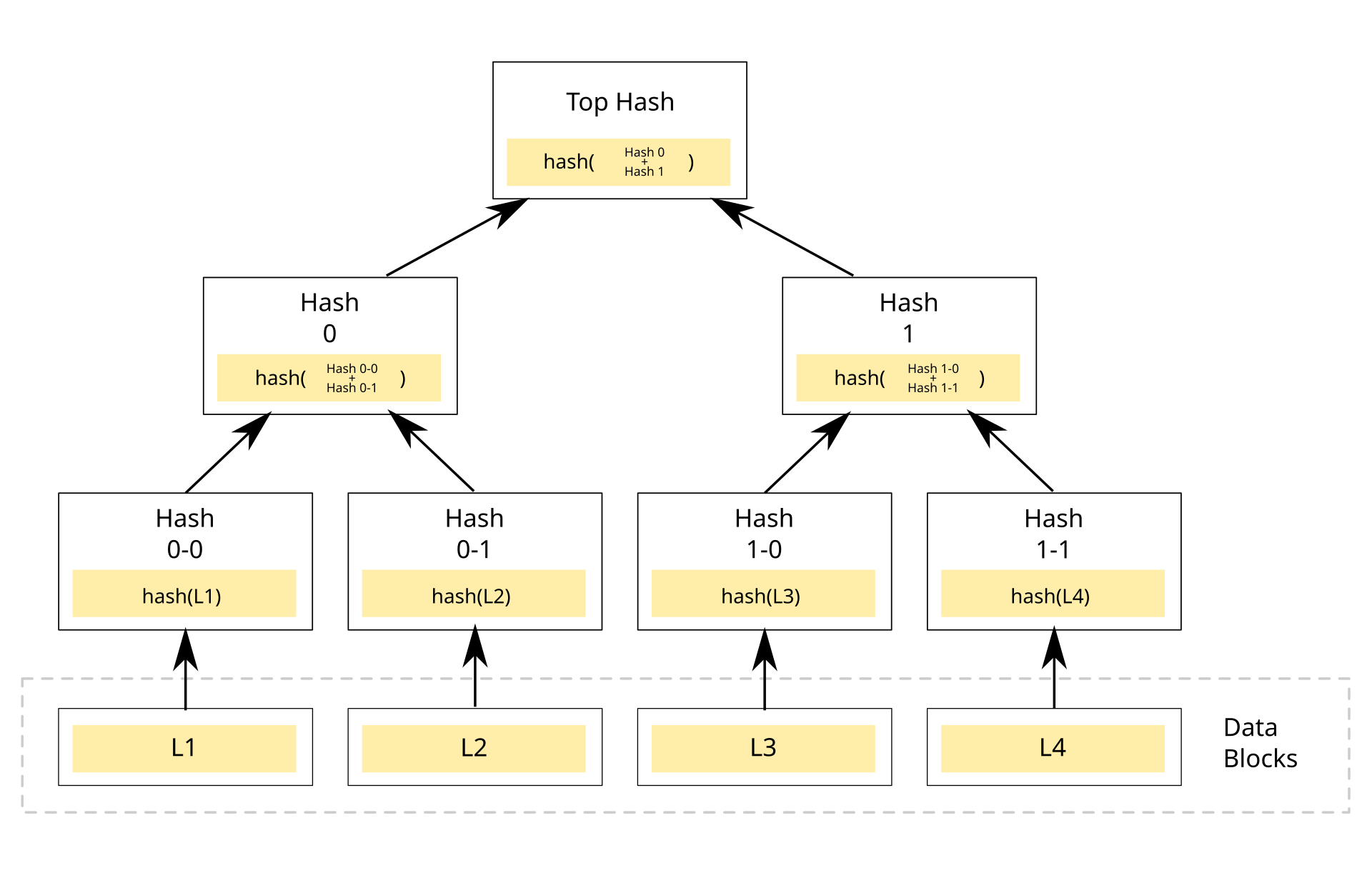
A Merkle tree is a hash-based data structure that is a generalization of the hash list. It is a tree structure in which each leaf node is a hash of a block of data, and each non-leaf node is a hash of its children. Merkle trees have a branching factor of 2, meaning that each node has up to 2 children. They are used in distributed systems for efficient data verification. They are a key part of blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
In this assignment, you have to write some code to generate the merkle root and merkle proof for a given list of transactions.
-
Hash all the transactions (like L1, L2, L3, L4 in the above diagram) using a hashing algorithm. For this assignment, we will be using the SHA256 hash.
-
These hashes are grouped into pairs. The hash is computed for each pair and this is stored in the parent node. Now the parent nodes are grouped into pairs and their hash is stored one level up in the tree. This continues till the root of the tree.
-
In case of odd number of transactions, lonely transaction hashes are promoted to the next level up, as depicted in the diagram below (where A, B, C, D, E are the hashes of transactions):
ROOT=Hash(H+E) / \ / \ H=Hash(F+G) E / \ \ / \ \ F=Hash(A+B) G=Hash(C+D) E / \ / \ \ / \ / \ \ A B C D E -
Note: You might find different implementations of Merkle trees on the web. For the purpose of this assignment, we are following the standard which libraries such as merkle-lib (from bitcoinjs), merkle-tools, merkletreejs, pymerkletools, and merkleib use.
So, internally, the leaves will be stored as Buffers. The tree is generated by hashing together the Buffer values.
- Suppose for the first diagram, a miner wanted to prove that the transaction
L1belonged to the Merkle proof. - In order to do that, the miner needs to present the transaction with all the nodes which lie on the path between the transaction and the root.
- If there are n nodes in the tree then only log(n) nodes need to be examined.
- Hence even if there are a large number of nodes in the Merkle tree, proof of membership can be computed in a relatively short time.
The list of all the nodes which lie on the path between the transaction and the root is the merkle proof.
These examples will illustrate how you can compute the merkle root and merkle proof for a given list of transactions and leaf index:
transactions: a
merkleRoot: ca978112ca1bbdcafac231b39a23dc4da786eff8147c4e72b9807785afee48bb
Explanation: Above merkleRoot is the SHA256 hash of a
javascript code for sha256 (from js-boilerplate/utils.js)
crypto.createHash("sha256").update(tx).digest().toString("hex");merkleProof for the middle leaf: []
Explanation: In this case, the middle leaf is at index 0. As this is the only leaf in the tree, we don't need any other object to compute the merkle root and hence the output is an empty array.
transactions: a,b i.e. ["a", "b"]
merkleRoot: e5a01fee14e0ed5c48714f22180f25ad8365b53f9779f79dc4a3d7e93963f94a
Explanation: Above merkleRoot is obtained by hashing the hashes of the two transactions a and b.
javascript code for hasing a pair (from js-boilerplate/utils.js)
const sha256 = (tx) => crypto.createHash("sha256").update(tx).digest();
const hashPair = (hashA, hashB, hashFunction = sha256) =>
hashFunction(Buffer.concat([hashA, hashB]));
const a = sha256("a");
const b = sha256("b");
hashPair(a, b).toString("hex");merkleProof for the middle leaf:
[{ "left": "ca978112ca1bbdcafac231b39a23dc4da786eff8147c4e72b9807785afee48bb" }]Explanation: In this case, the middle leaf is at index 1. To generate the merkle proof, we need to provide the hash of the transaction a so that the pair of hashes can be used to compute and verify the merkle proof. The "left" key indicates that the transaction a occcured before transaction b and hence the hash should be calculated as hashPair(a + b) and not hashPair(b + a).
-
Read data.csv
Some sample test cases and the output format is present in the first three rows.
-
For each row
-
Read the transactions column
-
Compute the value for the merkle root and the merkle proof (of the middle leaf) columns. Use the SHA256 hash for hashing transactions.
Merkle proofs are calculated for a specific leaf. In this assignment, we require you to calculate the merkle proof for the middle leaf i.e. the
Math.floor(transactionsLength/2)index of the transactions.So, In case there are 3 transactions, the middle leaf will be the 1st index i.e. the 2nd leaf. In case there are 4 transactions, the middle leaf will be the 2nd index i.e. the 3rd leaf.
Note: The merkle proof array will contain a set of merkle sibling objects. Each object contains the sibling hash, with the key value of either right or left. The right or left value tells you where that sibling was in relation to the current hash being evaluated.
-
Update the columns
-
Save the updated file
-
-
Whenever you push a commit to GitHub or open a pull request, our automated tests will tell you if the roots and proofs you provided are correct or not.
You are free to use any language to attempt this assignment.
If you are comfortable with javascript, you can use our boilerplate code to solve the assignment. You will only need to finish the implementations of the two functions in tree.js to generate the final result. Below are the commands to get started with the boilerplate:
# Navigate to project directory
cd js-boilerplate
# Install dependencies
npm install
# Once you implement the functions in tree.js, run index.js to update the data.csv file
node index.js