ZetaChain: Code4rena Alpha competition, Phase 1
Auditor acceleration
- Total Prize Pool: $50,000 USDC
- Phase 1 awards: $10,000 USDC
- Phase 2 awards: $30,000 USDC
- Judge awards: $10,000 USDC
- Guidelines for C4 Alpha competitions
- Starts October 27, 2023 20:00 UTC
- Phase 1 ends / Phase 2 begins October 30, 2023 20:00 UTC
- Phase 2 ends November 6, 2023 20:00 UTC
How to use this repo
This repo is intended to be forked by each team participating in ZetaChain's Alpha competition. Please follow these steps for your team:
- Fork this repo to your own private repo within the team captain's Github account
- Add the judges (
0xeananddmvt) and thec4-audituser to your repo, for oversight - Create a folder within your repo that includes your team name (or team members’ names, with captain's username first, e.g.
horsefacts-bytes032-Trust). Create an index readme.md file in that folder that outlines the contents of the folder and attributes specific contributions by team members. - At the conclusion of Phase 1, open a PR in this (C4) repo to share your submissions
Note: Alpha repos should be made public following the competition; threats repos should be managed with great caution.
Links
- ZetaChain on Github
- Architecture documentation: https://www.zetachain.com/docs/architecture/overview/
- Whitepaper
- ZetaChain website
- Discord
ZetaChain Overview
Usage of Cosmos SDK
ZetaChain is a EVM compatible blockchain based on Cosmos SDK. The blockchain imports the default Cosmos SDK module for DPoS chains:
authbankstakingslashingevidencegovdistributionupgradefeemarketauthzgroupcrisisparams
mint and IBC modules are not imported.
The blockchain also imports the evm module from Ethermint to be EVM compatible.
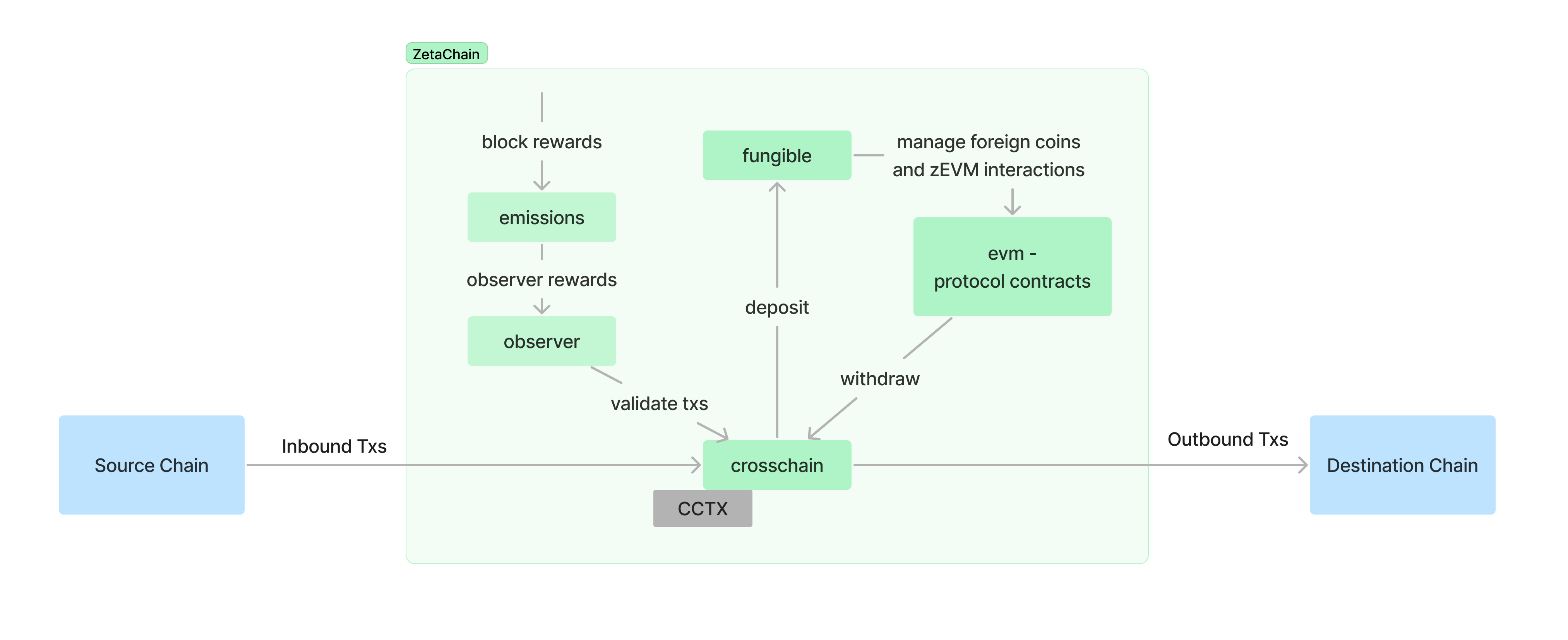
The blockchain is composed of 4 custom modules: crosschain, fungible, observer and emissions . Each play a specific role for cross-chain transactions.
The ZetaChain EVM is called zEVM.
The bank module is used to manage the supply of ZETA tokens. Every other assets in the protocol like foreign coins are represented through smart contracts in the zEVM.
SDK modules
crosschain
The crosschain module tracks the state of cross-chain transactions (CCTX). A CCTX is created when a source chain (external chain or ZetaChain) interacts with a destination chain (another external chain or ZetaChain if the source chain is not ZetaChain) through ZetaChain.
A CCTX objects contains the state of the transactions on external chains. There are two types of external transactions:
- Inbound Tx: a transaction initiated in a external chain to be observed in ZetaChain to create a new CCTX
- Outbound Tx: a transaction broadcasted to a external chain as a result of a CCTX creation
An inbound tx is initiated in the source chain. An outbound tx can be broadcasted in the destination chain for the processing of the CCTX or in the source chain in the case where a CCTX is being reverted.
The CCTX also holds a status that can contain the following values:
PendingInbound: observation of an inbound tx has been initiated but not voted yetPendingOutbound: an outbound tx has been broadcasted but not observed yetOutboundMined: the outbound tx has been observed, this is the final state of a successful CCTXPendingRevert: an outbound tx for revert has been broadcasted but not observed yetReverted: the outbound tx for revert has been observed, this is the final state of a unsuccessful CCTXAborted: something went wrong and a revert tx can’t be processed or create
fungible
The fungible module facilitates the deployment of fungible tokens of connected blockchains (called "foreign coins") on ZetaChain.
Foreign coins are represented as ZRC20 tokens on ZetaChain.
When a foreign coin is deployed on ZetaChain, a ZRC20 contract is deployed, a pool is created, liquidity is added to the pool, and the foreign coin is added to the list of foreign coins in the module's state. This is a manual process trigger by an admin group.
The module contains the logic for:
- Deploying a foreign coin on ZetaChain
- Deploying a system contract, Uniswap and wrapped ZETA
- Depositing to and calling omnichain smart contracts on ZetaChain from connected chains (
DepositZRC20AndCallContractandDepositZRC20)
fungible module represents in general the high-level logic of cross-chain transactions for interactions with ZetaChain while crosschain module represents low level logic.
observer
The observer module keeps track of ballots for voting, the observer accounts, a list of supported connected chains, core parameters (contract addresses, outbound transaction schedule interval, etc.), observer parameters (ballot threshold, min observer delegation, etc.), and admin policy parameters.
This is the module that validates the integrity of data from external chains for the crosschain module.
Ballots are used to vote on inbound and outbound transaction. The observer module keeps create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) operations for ballots, as well as helper functions to determine if a ballot has been finalized. The ballot system is used by other modules, such as the crosschain module when observer validators vote on transactions.
An observer validator is a validator that runs zetaclient alongside the zetacored (the blockchain node) and is authorized to vote on inbound and outbound cross-chain transactions.
emissions
The emissions module is responsible for orchestrating rewards distribution for observers, validators and TSS signers. Currently, it distributes rewards to validators and observers every block. TSS reward distribution is not implemented. The undistributed amount for TSS is stored in its respective pool.
Protocol contracts
Most of the logic for cross-chain functionalities is defined in the Cosmos modules described above but some of the functionalities are defined in contracts deployed in the zEVM, this includes:
- ZRC20 tokens for foreign coins
- Wrapped ZETA token
- System contract to interact with the zEVM through cross-chain txs
- Uniswap V2 pools to enable token swap
Protocol contracts can be founds in: protocol-contracts/contracts/zevm at main · zeta-chain/protocol-contracts (github.com)
Diagram
Important Areas
1 - CCTX lifecycle
CCTXs are what define cross-chain interactions. The logics triggered during a CCTX lifecycle is one of the most important part of the protocol. The transported assets in CCTXs must be correctly handled when minted/burned on Zeta, used to pay for outbound tx gas, etc…
Inbound Transaction Observation
If the destination chain is ZetaChain and the CCTX contains a message, ZRC20 tokens are deposited and a contract on ZetaChain is called. Destination contract address and the arguments for the contract call are contained within the message.
If the destination chain is not ZetaChain, the status of a transaction is changed to "pending outbound" and the CCTX to be processed as an outbound transaction.
More information on inbound tx observation can be found at ZetaDocs (zetachain.com)
Outbound Transaction Observation
Pending Outbound
Observers watch ZetaChain for pending outbound transactions. To process a pending outbound transactions observers enter into a TSS keysign ceremony to sign the transaction, and then broadcast the signed transaction to the connected blockchains.
**Observed Outbound**
Observers watch connected blockchains for the broadcasted outbound transactions. Once a transaction is "confirmed" (or "mined") on a connected blockchains, observers vote on ZetaChain by sending a VoteOnObservedOutboundTx message.
After the vote passes the threshold, the voting is finalized and a transaction's status is changed to final.
More information about outbound tx observation can be found at ZetaDocs (zetachain.com)
Gas Payment on ZetaChain for outbound tx
Gas for outbound txs are paid on ZetaChain using the amount of token in the cross-chain tx (cctx)
The gas payment functionality has been extended to support 3 types of cctx:
- Gas cctx: the cctx contains the gas token of the chain and therefore it is directly subtracted from the amount for gas payment
- Zeta cctx: zeta tokens are subtracted from the amount are swapped into the zrc20 gas tokens for the gas payment
- ERC20 cctx: erc20 are subtracted from the amount and swapped erc20→zeta→gas for the gas payment
→ The swaps use Uniswap pools, native to ZetaChain, and expects the liquidity to be maintained
Source code → node/x/crosschain/keeper/gas_payment.go at develop · zeta-chain/node (github.com)
Gas Price Increase for outbound tx
A mechanism allows increasing the gas price used for an outbound tx on an external chain if it is not being mined
- When outbound txs are mined, part of the remaining fees (surplus gasUsed/gasLimit) are sent to a “gas stability pool” → https://github.com/zeta-chain/node/blob/d41cf7f1af4d2cac20bec191b980d69d9d315348/x/crosschain/keeper/keeper_cross_chain_tx_vote_outbound_tx.go#L132
- Every n blocks, every pending outbound txs are iterated, if pending for too long, the gas price for the outbound tx is increase and, funds from the gas stability pool is used to pay for the increase → https://github.com/zeta-chain/node/blob/d41cf7f1af4d2cac20bec191b980d69d9d315348/x/crosschain/keeper/abci.go#L21
- Gas is not increase if not enough funds in the gas stability pool
2 - Permissionless Tx Validation Model
A new architecture has been developed in order to validate txs from external chains permissionlessly instead of requiring observers to vote on each of them.
- Observer votes on block headers of the external chains instead of the txs. The block headers are stored on-chain on ZetaChain
- An inbound/outbound tx can be sent by anyone with a proof. The proof is checked against the header of the chain to validate it
→ The system is currently only used to validate txs to be added in the tracker through MsgAddToInTxTracker and MsgAddToOutTxTracker and not to validate txs to be observed as part of the ZetaChain cross-chain tx workflow
→ The system is currently implemented for Ethereum/BSC and Bitcoin
→ In the future, the validation of inbound txs and outbound txs will be refactored to use this system instead of observers. The observers will only vote for the block headers of external chains. Then anyone can validate a inbound or outbound tx for a cross-chain tx.
Source Code
- Adding block header: node/x/observer/keeper/msg_server_add_block_header.go at develop · zeta-chain/node (github.com)
- Header structure: node/common/headers.go at develop · zeta-chain/node (github.com)
- Proof structure: node/common/proof.go at develop · zeta-chain/node (github.com)
- Usage to validate tx in inTxTracker: node/x/crosschain/keeper/msg_server_add_to_intx_tracker.go at develop · zeta-chain/node (github.com)
- Usage to validate outTxTracker: node/x/crosschain/keeper/msg_server_add_to_outtx_tracker.go at develop · zeta-chain/node (github.com)
3 - Permissions and Admin Groups
- Certain action in the blockchain can only be executed by a specific address (multi-sig). There are two admin groups:
- Group1
- Emergency actions: halt a workflow of the blockchain in case of emergency
- Example: freeze a ZRC20 if a vulnerabilty is found for this token
- Rapidity over security: represented by an address that would require a single signature from the multisig
- Should not concern action that can be financially exploitable
- Group2
- Operational: updating parameters influencing logic of the blockchain
- Example: updating the system contract
- Security over rapidity: requires several signature
- Group1
Permissions Table
| Message | Group | Description | Module |
|---|---|---|---|
| MsgAddToOutTxTracker | 1 | Add an outbound tx to the onchain tx tracked (msg to be removed) | crosschain |
| MsgRemoveFromOutTxTracker | 1 | Remove an outbound tx from the onchain tx tracked (msg to be removed) | crosschain |
| MsgAddToInTxTracker | 1 | Add an inbound tx to the onchain tx tracked (msg to be removed) | crosschain |
| MsgUpdateTssAddress | 2 | Update the address of the TSS | crosschain |
| MsgMigrateTssFunds | 2 | Send a tx to an external chain to migrate tss funds from one address to another one | crosschain |
| MsgWhitelistERC20 | 1 | Whitelist an ERC20 on an external chain so a zrc20 can be created | crosschain |
| MsgUpdateZRC20PausedStatus - Pause | 1 | Pause interaction with a provided list of zrc20 - no transfer or withdraw can be processed with the paused zrc20 | fungible |
| MsgUpdateZRC20PausedStatus - Unpause | 2 | Unpause a paused zrc20 | fungible |
| MsgDeployFungibleCoinZRC20 | 2 | Deploy a new ZRC20 (gas token or ERC20) | fungible |
| MsgRemoveForeignCoin | 2 | Remove a foreign coin object from ZetaChain. The ZRC20 will still exist on ZetaChain and can still be traded but cross-chain capabilities will no longer be available for it | fungible |
| MsgUpdateZRC20LiquidityCap | 2 | Set or remove a liquidity cap for a zrc20, the maximum supply that can exist for the ZRC20 on ZetaChain | fungible |
| MsgUpdateContractBytecode | 2 | Update the bytecode of a ZRC20 or a system contract | fungible |
| MsgUpdateSystemContract | 2 | Update the address of the system contract | fungible |
| MsgUpdateZRC20WithdrawFee | 2 | Update the withdraw protocol fees for a ZRC20. A flat fee paid for each | fungible |
| MsgUpdateCoreParams | 2 | Updates core parameters for a specific chain. Core parameters include: confirmation count, outbound transaction schedule interval, ZETA token, connector and ERC20 custody contract addresses, etc. | observer |
| MsgUpdateCrosschainFlags - Disabling outbounds/inbounds | 1 | Disable inbound txs or outbound txs to be observed on ZetaChain | observer |
| MsgUpdateCrosschainFlags - Other actions | 2 | Other actions for crosschain flags are: - Enabling disabled outbound/inbound - Changing parameters for gas price increase mechanism | observer |
| MsgUpdateKeygen | 1 | Update the block height of the keygen and sets the status to PendingKeygen |
observer |
Source Code