by Adrián Luján Muñoz
The nature of this document
After observing and questioning multiple people, I have realized the misinformation and lack of knowledge regarding computer security on the part of a large part of the users who use online services.
This document will address the following aspects of network security (more specifically in the use of the web browser)
In this article we will discuss some of the attacks most used by cybercriminals to violate the security of web browsers
Firefox,Chrome,Safari,etc
We will explain how to keep the data of our web browsers safe. How to treat our sensitive data to avoid the leaking of said data.
One of the attacks most used today to steal user accounts on Internet platforms Cookie-Hijacking. As its own name indicates, it consists of hijacking the user's session.
This attack has become very famous lately as multiple YouTube channels have been attacked, leaving their rightful owners without access suddenly and surprisingly. Many of these users who are affected state that they had the `Two-Factore authenticate` option activated, so they trusted that their accounts were completely secure.
The great potential for attackers of this and similar attacks is that it does not require a username, password (in order to gain access to the user's session) as well as being able to bypass most of the Two-Factore authenticate.
Sometimes the password may be necessary to perform actions within the account, this will depend on the actions that the attacker wants to perform within the account and the security level implemented by the web service provider.
This is a very superficial explanation. In case you want to learn a little more about this type of attack, you can search for information on your own or visit on this website which I think explains the bases of the attack very well.
- Faked Requests
- Cross-Site Request Forgery
- Cookie Theft and Manipulation
- Other methods
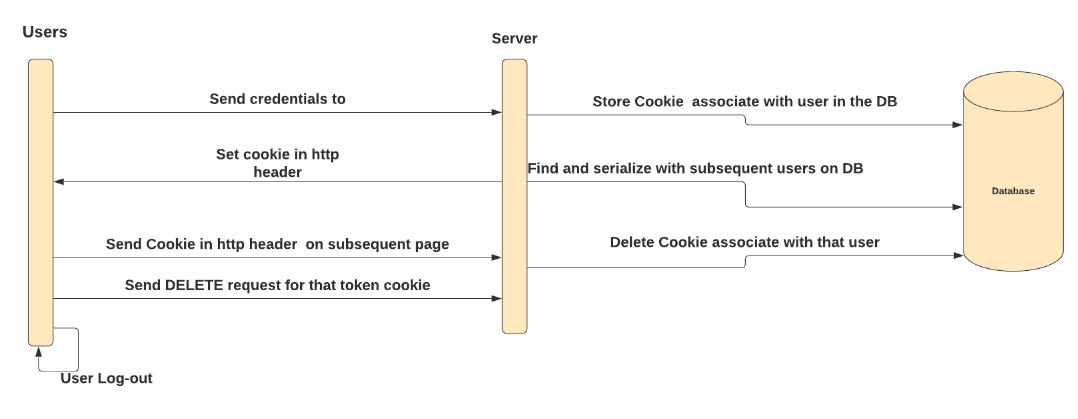
To understand how these types of attacks are carried out, we need to know what a session cookie is and how web services perform authentication.
In short, a session cookie allows the server to identify the user. This is very useful since http is a communications protocol that treats each request as a separate transaction that has no relation to any previous request (stateless protocol). This makes it necessary to use cookies to be able to identify the different clients.
As shown in the image, the user authenticates with her credentials and the server guive a cookie that identifies the session just opened. In case of not closing the session we can access without entering our credentials until the session expires.
The attackers take advantage of the fact that the session is valid to inject the stolen cookie into their browsers. Gained access to the user's account without having to enter any credentials, since the session is the same one that the legitimate user has opened.
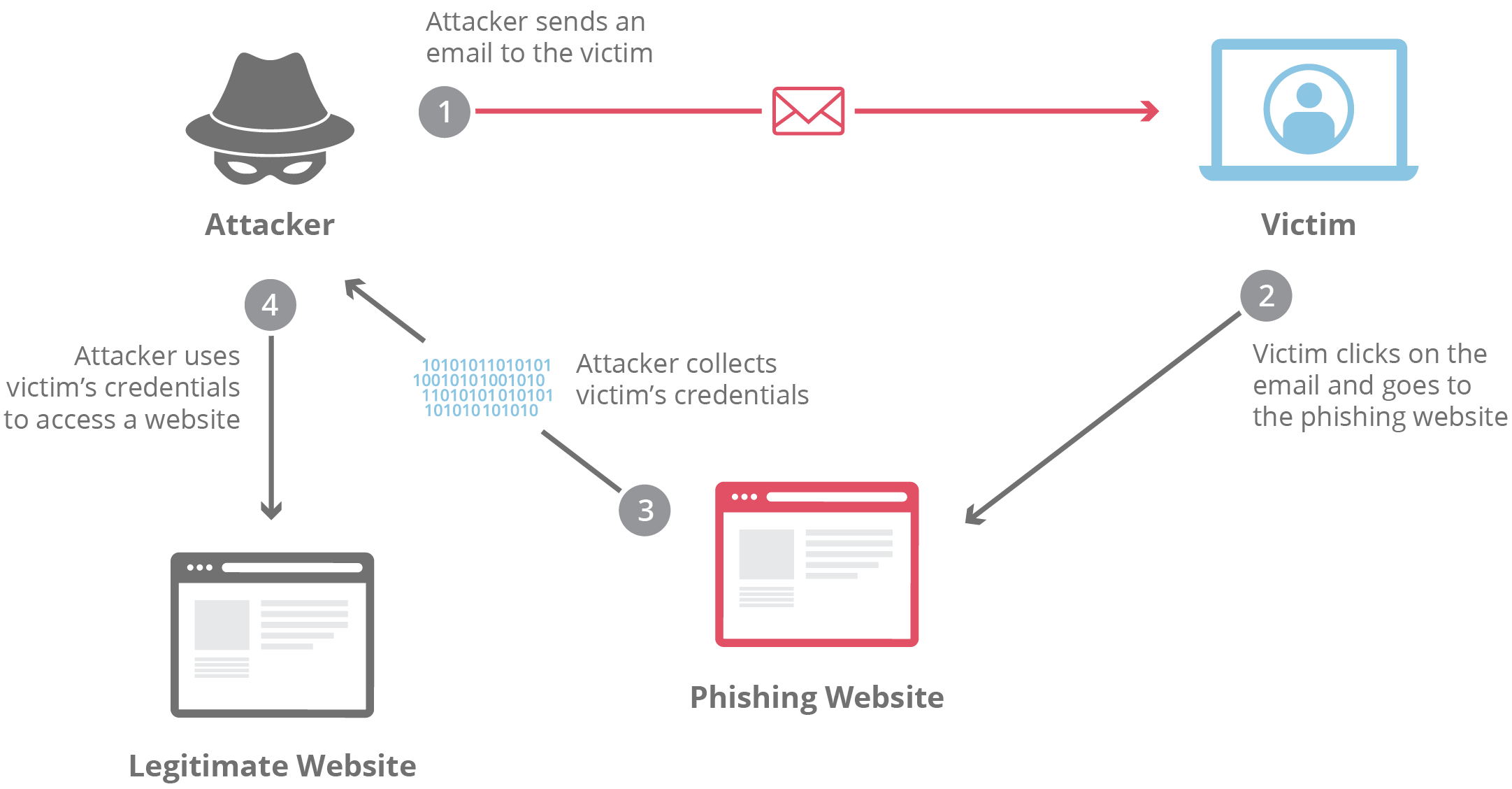
This is one of the most well-known methods by the non-specialized public, but even though it is so well known, it is still one of the most effective when it comes to obtaining user credentials. Both with massive phishing campaigns in the old fashioned way or with more targeted spear-phishing methodologies. In the latter, information is extracted from the person or group of people to whom it will be addressed through OSINT methodologies and techniques that allow the attacker to create an attack that is much more effective.
The following image shows a typical phishing attack in a very summarized form, the attacker sends a malicious message to the victim. The message contains a link that, when clicked, leads to a web page where the victim must enter his credentials, the victim enters them thinking that the site is legitimate. Subsequently, the data entered are sent to the attacker, usually the website shows you a login error and redirects you to the real website.
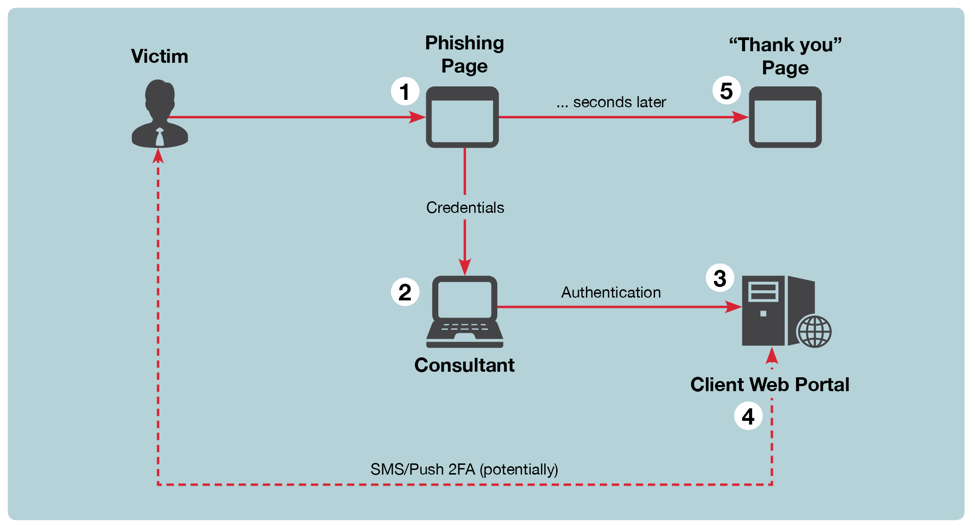
In more sophisticated Real-time Phishing attacks the malicious website handles a request with the real website to log the user into the real website to prevent the hoax from being discovered. Although in some cases a request is made to the real website and a check is made to see if the user has Two-Factore authenticate. If the Two-Factore authenticate is active, the user is prompted to obtain an authorized session to which the attacker will have access, then in some cases it is sent to a remote computer that automatically performs the actions desired by the attacker.
These types of attacks can get very complicated. If you want more information related to 'Real-time Phishing' attacks, how they work in depth and the danger of this type of attacks, I leave a couple of very interesting websites.
- https://blog.cloudflare.com/2022-07-sms-phishing-attacks/
- https://www.mandiant.com/resources/blog/reelphish-real-time-two-factor-phishing-tool
- https://gbhackers.com/real-time-two-factor-phishing-tool/
- https://www.phishdeck.com/blog/what-is-realtime-phishing/
- https://www.usenix.org/conference/usenixsecurity21/presentation/ulqinaku
One of the most used due to the amount of data that can be extracted from a computer, not just credentials such as PasswordStealer, there are many Stealers that are capable of extracting personal information from the user, monitoring their activities, I have informed the attacker . This can allow the theft of sensitive information such as identity documents, which can be used to falsify the person's identity.
Thanks to the data obtained with the Stealers, an attacker was able to carry out a large number of attacks and operations to gain access to multiple accounts, not only of the user himself but of all users who have ever logged in there. team and there left some trace. In addition to obtaining the information of all users who have left a trace on the computer. Here data analysis techniques and information gathering come into play, among many other techniques that can allow the attacker to obtain relevant and sensitive information (cookies, credentials, official documents, application database files, KeyPass files, etc).
This type of malware is usually of the Trojan type, which means that the user is tricked into the system, since the user is never aware that a malicious program is installed.
In this category I have included the attacks that in my opinion are the most relevant and widely used to exploit web browsers.
I am fully aware that there are still many attacks and methodologies to include, but my intention is to explain in a general way how vulnerable current web browsers are and the lack of training in computer security that users have about how vulnerable they are on the Internet. So I don't think it's necessary to explain attacks that are much more sophisticated or that are not so widely used to harm the common user.
Today there are many people who carry out advertising campaigns, some companies provide them with certain files that at first may seem like a harmless program or a document that seems harmless, but behind the scenes a series of tasks are being carried out to install malicious software.
The user does not usually find out until the antivirus detects it or they have already told him that the damage has already been done and there is not much to do.