Component to link multiple Home-Assistant instances together.
This component will set up the following platforms.
| Platform | Description |
|---|---|
remote_homeassistant |
Link multiple Home-Assistant instances together . |
The main instance connects to the Websocket APIs of the remote instances (already enabled out of box), the connection options are specified via the host, port, and secure configuration parameters. If the remote instance requires an access token to connect (created on the Profile page), it can be set via the access_token parameter. To ignore SSL warnings in secure mode, set the verify_ssl parameter to false.
After the connection is completed, the remote states get populated into the master instance.
The entity ids can optionally be prefixed via the entity_prefix parameter.
The component keeps track which objects originate from which instance. Whenever a service is called on an object, the call gets forwarded to the particular remote instance.
When the connection to the remote instance is lost, all previously published states are removed again from the local state registry.
A possible use case for this is to be able to use different Z-Wave networks, on different Z-Wave sticks (with the second one possible running on another computer in a different location).
This component must be installed on both the main and remote instance of Home Assistant
If you use HACS:
- Click install.
Otherwise:
- To use this plugin, copy the
remote_homeassistantfolder into your custom_components folder.
Remote instance
On the remote instance you also need to add this to configuration.yaml:
remote_homeassistant:
instances:This is not needed on the main instance.
- Add a new Remote Home-Assistant integration
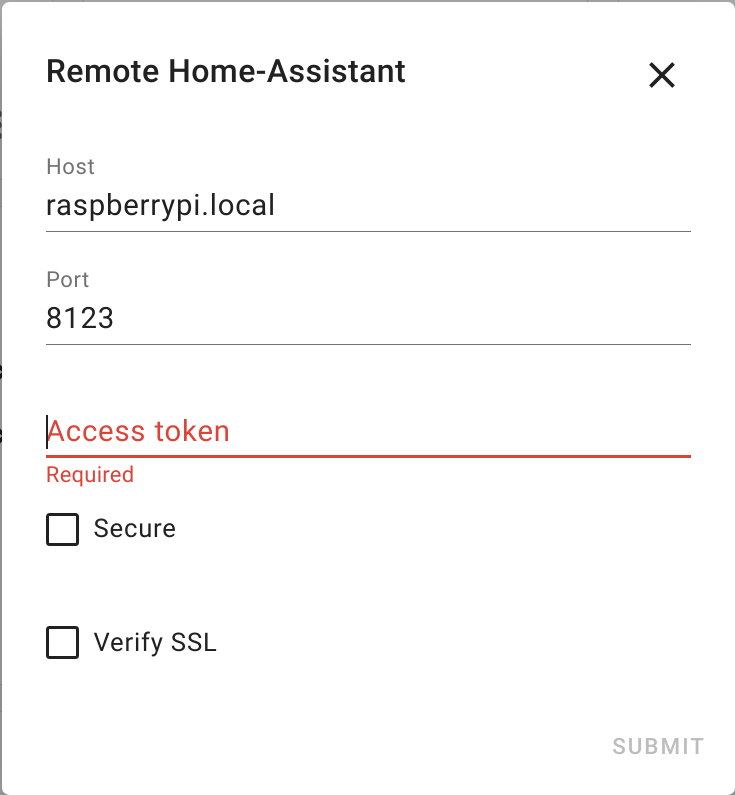
- Specify the connection details to the remote instance
You can generate an access token in the by logging into your remote instance, clicking on your user profile icon, and then selecting "Create Token" under "Long-Lived Access Tokens".
Check "Secure" if you want to connect via a secure (https/wss) connection
- After the instance is added, you can configure additional Options by clicking the "Options" button.
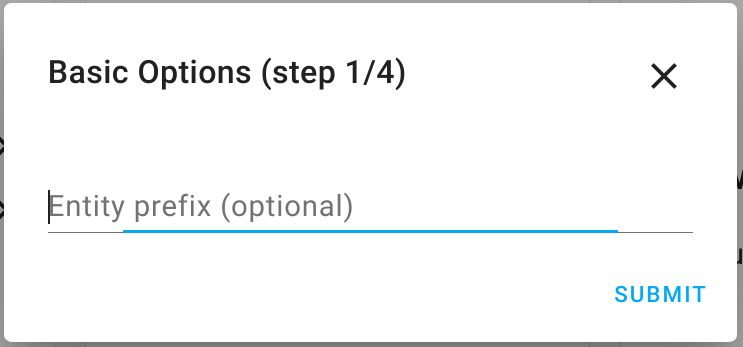
- You can configure an optional prefix that gets prepended to all remote entities (if unsure, leave this blank).
Click "Submit" to proceed to the next step.
- You can also define filters, that include/exclude specified entities or domains from the remote instance.
or via..
To integrate remote_homeassistant into Home Assistant, add the following section to your configuration.yaml file:
Simple example:
# Example configuration.yaml entry
remote_homeassistant:
instances:
- host: raspberrypi.localFull example:
# Example configuration.yaml entry
remote_homeassistant:
instances:
- host: localhost
port: 8124
- host: localhost
port: 8125
secure: true
verify_ssl: false
access_token: !secret access_token
entity_prefix: "instance02_"
include:
domains:
- sensor
- switch
- group
entities:
- zwave.controller
- zwave.desk_light
exclude:
domains:
- persistent_notification
entities:
- group.all_switches
filter:
- entity_id: sensor.faulty_pc_energy
above: 100
- unit_of_measurement: W
below: 0
above: 1000
- entity_id: sensor.faulty_*_power
unit_of_measurement: W
below: 500
subscribe_events:
- state_changed
- service_registered
- zwave.network_ready
- zwave.node_event
load_components:
- zwavehost:
host: Hostname or IP address of remote instance.
required: true
type: string
port:
description: Port of remote instance.
required: false
type: int
secure:
description: Use TLS (wss://) to connect to the remote instance.
required: false
type: bool
verify_ssl:
description: Enables / disables verification of the SSL certificate of the remote instance.
required: false
type: bool
default: true
access_token:
description: Access token of the remote instance, if set.
required: false
type: string
max_message_size:
description: Maximum message size, you can expand size limit in case of an error.
required: false
type: int
entity_prefix:
description: Prefix for all entities of the remote instance.
required: false
type: string
include:
description: Configures what should be included from the remote instance. Values set by the exclude lists will take precedence.
required: false
default: include everything
type: mapping of
entities:
description: The list of entity ids to be included from the remote instance
type: list
domains:
description: The list of domains to be included from the remote instance
type: list
exclude:
description: Configures what should be excluded from the remote instance
required: false
default: exclude nothing
type: mapping of
entities:
description: The list of entity ids to be excluded from the remote instance
type: list
domains:
description: The list of domains to be excluded from the remote instance
type: list
filter:
description: Filters out states above or below a certain threshold, e.g. outliers reported by faulty sensors
required: false
type: list of
entity_id:
description: which entities the filter should match, supports wildcards
required: false
type: string
unit_of_measurement
description: which units of measurement the filter should match
required: false
type: string
above:
description: states above this threshold will be ignored
required: false
type: float
below:
description: states below this threshold will be ignored
required: false
type: float
subscribe_events:
description: Further list of events, which should be forwarded from the remote instance. If you override this, you probably will want to add state_changed!!
required: false
type: list
default:
- state_changed
- service_registered
load_components:
description: Load components of specified domains only present on the remote instance, e.g. to register services that would otherwise not be available.
required: false
type: list
service_prefix: garage_
description: Prefix used for proxy services. Must be unique for all instances.
required: false
type: str
default: remote_
services:
description: Name of services to set up proxy services for.
required: false
type: list
If you have remote domains (e.g. switch), that are not loaded on the main instance you need to list them under load_components, otherwise you'll get a Call service failed error.
E.g. on the master:
remote_homeassistant:
instances:
- host: 10.0.0.2
load_components:
- zwave
to enable all zwave services. This can also be configured via options under Configuration->Integrations.
Some components do not use entities to handle service calls, but handle the
service calls themselves. One such example is hdmi_cec. This becomes a
problem as it is not possible to forward the service calls properly. To work
around this limitation, it's possible to set up a proxy service.
A proxy service is registered like a new service on the master instance, but it mirrors a service on the remote instance. When the proxy service is called on the master, the mirrored service is called on the remote instance. Any error is propagated back to the master. To distinguish proxy services from regular services, a service prefix must be provided.
Example: If a proxy service is set up for hdmi_cec.volume with service
prefix remote_, a new service called hdmi_cec.remote_volume will be
registered on the master instance. When called, the actual call will be forwarded
to hdmi_cec.volume on the remote instance. The YAML config would
look like this:
remote_homeassistant:
instances:
- host: 10.0.0.
service_prefix: remote_
services:
- hdmi_cec.volumeThis can also be set up via Options for the integration under Configuration -> Integrations.
See also the discussion on home-assistant/core#13876 and home-assistant/architecture#246 for this component