ALLaMo
This repository is intended as a simple, hackable and fast implementation for training/finetuning/inference LLaMA-based models (arXiv).
If you want to see how we have trained a 1B model for the Polish language, please read this article on our website.
Install
Dependencies:
- Python 3
- pytorch
- numpy
- huggingface transformers
- huggingface tokenizers - optional
- tiktoken - optional
- gradio - optional, for demo UI
- FlashAttention - optional, for FlashAttention 2
Datasets
Before you start training a new model, you need to create train and test datasets. The script train.py expects 2 files: train.bin and val.bin. You can create the both files using prepare_datasets.py or implementing a simple script like this:
import numpy as np
import tiktoken
def encode_file(input_file_path, output_file_path, tokenizer_name):
tokenizer = tiktoken.get_encoding(tokenizer_name)
with open(input_file_path, 'r') as f:
data = f.read()
enc_data = tokenizer.encode(data)
enc_data = np.array(enc_data, dtype=np.uint32)
enc_data.tofile(output_file_path)
encode_file('raw/dataset1/train.txt', 'data/dataset1/train.bin', 'cl100k_base')
Training
Use the script train.py to start your training. It reads a train.bin and val.bin files from the dataset directory.
The training script can be run on both a single node with one or more GPUs, as well as on multiple nodes with Distributed Data Parallel (DDP).
To run on a single node with 1 GPU, example:
$ python train.py \
--config="./config/train_1B.json" \
--wandb_log=True
To run on a single node with 8 GPU with DDP, example:
$ torchrun --standalone --nnodes=1 --nproc-per-node=8 train.py \
--config="./config/train_1B.json" \
--wandb_log=True
To run on 2+ nodes with DDP, example:
- Run on the first (master) node with example IP 123.456.123.456:
$ torchrun --nnodes=2 --nproc-per-node=8 --node-rank=0 --master_addr=123.456.123.456 --master_port=1234 train.py \
--config="./config/train_1B.json" \
--wandb_log=True
- Run on the worker node(s):
$ torchrun --nnodes=2 --nproc-per-node=8 --node-rank=1 --master_addr=123.456.123.456 --master_port=1234 train.py \
--config="./config/train_1B.json" \
--wandb_log=True
Note: in case your cluster does not have Infiniband interconnect prepend NCCL_IB_DISABLE=1.
Finetuning
The process of finetuning is similar to regular training, but we initialize from a pretrained model and use a smaller learning rate during training. In addition, it is essential to ensure that the model parameters used for finetuning are consistent with those used during pre-training.
Extending Context Window
As part of the fine-tuning process, you can easily extend the context window (block size) by modifying the block_size, rope_freq_base (default value is 10000), and rope_freq_scale (default value is 1.0) parameters. Please note that these parameters are also stored as part of a model checkpoint. Therefore, you must either modify them within the checkpoint or compel the framework to overwrite them by hardcoding the new values into train.py immediately after the checkpoint is loaded. For more information on Position Interpolation, you can refer to this paper or this blog post.
Below are some empirically derived example values for extending the context window. However, we encourage you to experiment and adjust these values to suit the specific needs of your model:
| context scaling factor | rope_freq_base | rope_freq_scale |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 20000 | 0.83 |
| 3 | 40000 | 0.86 |
| 4 | 57200 | 0.75 |
| 16 | 26000 | 0.125 |
Import LLaMA models
Use the script import_llama_weights.py to import LLaMA model weights and tokenizer, and create a checkpoint for further finetuning. In order to obtain the weights, fill this google form. Example script execution:
python import_llama_weights.py \
--input_data_dir="../llama/7B/" \
--input_tokenizer_path="../llama/tokenizer.model" \
--output_data_dir="../data/llama-7b/"
Notes:
- the import process of the 7B LLaMA model takes ~14GB of RAM and generates 13.5GB output files.
- the script doesn't support sharded models.
- the LLaMA tokenizer is loaded using HuggingFace Transformers. Check if your installed version supports
LlamaTokenizer.
Export your model to Hugging Face format
When you have trained your model, you may want to run it in the Hugging Face ecosystem. Using the export_to_hf.py script, you can easily convert your model to an HF-compatible LLaMA format. Here's an example of how to run it:
$ python export_to_hf.py \
--input_dir="../data/my-llama/" \
--output_dir="../data/my-llama-hf/"
Sampling / Inference
Use the script sample.py to sample from a model you trained. For example:
$ python sample.py \
--config="./config/train_1B.json" \
--max_new_tokens=100 \
--temperature=0.7 \
--top_k=200 \
--num_samples=5 \
--prompt="Long long time ago"
You can also prompt the model with some text from a file prefixing its path with FILE:, example:
$ python sample.py \
--config="./config/train_1B.json" \
--max_new_tokens=100 \
--temperature=0.7 \
--top_k=200 \
--num_samples=5 \
--prompt="FILE:prompt.txt"
Specify the tokenizer using --tiktoken_tokenizer_name for Tiktoken (e.g. cl100k_base), or thanks to HuggingFace Transformers, you can easily use your own pretrained tokenizer using --custom_tokenizer_path to provide your tokenizer's JSON config file.
Use the script 'sample_api.py' to expose 3 API endpoints. Then you will be able to query a pretrained model for text embeddings and completions.
To run the API with a pretrained model, example:
$ python sample_api.py \
--config="./config/train_1B.json" \
--max_new_tokens=10 \
--temperature=0.7 \
--top_k=200 \
--num_samples=5
- Query for text embeddings, example:
$ curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:5000/embeddings -d '{"prompt": "Long long time ago"}'
- Query for text completions, example:
$ curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:5000/completions -d '{"prompt": "Long long time ago", "num_samples": 3}'
- Query for tokens to see how your prompt is tokenized, example:
$ curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" http://localhost:5000/tokens -d '{"prompt": "Long long time ago"}'
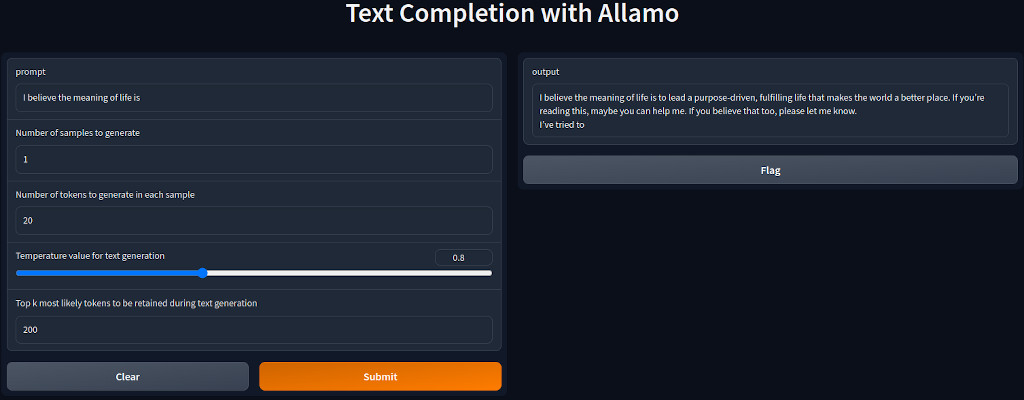
To run the UI at top of the API, example:
$ python sample_u.py
Running LLaMA 7B on CPU
You can reach a point where you intend to run an LLaMA model, but your GPU does not have sufficient memory, and you encounter the OOM error. The easiest and quickest way to handle, or rather work around, this issue is to run the model on the CPU using your RAM. You can easily do this by specifying the device in the arguments. Here is an example:
$ python sample_api.py \
--checkpoint_path="../data/llama-7b/import_ckpt.pt" \
--llama_tokenizer_path="../data/llama-7b/" \
--device=cpu
Note: in order to run the 7B model, you will need ~14GB of RAM.
Efficiency
With PyTorch 2.0 and torch.compile(), you can see significant speedup. Using the fused AdamW optimizer and compile(), my training ran 30% faster than without these two modes enabled.
Citation
Please cite this repo if you use it.
@misc{allamo,
author = {Krzysztof Ociepa},
title = {ALLaMo: Simple, hackable and fast implementation for medium-sized LLaMA-based models},
year = {2023},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/chrisociepa/allamo}},
}