- Quick Feature Overview
- Quick Start
- Detailed Feature List
- Projects and Workspaces
- Navigation without Projects and Workspaces
- Frame Locality
- Mouse Interface
- Follow-mode
- Tag-follow-mode
- Fringe-indicator-mode
- Git-mode
- Filewatch-mode
- Session Persistence
- Terminal Compatibility
- Tag View
- Current-Directory Awareness
- Tramp Support
- Org support
- Additional Packages
- Treemacs as a Framework
- Installation
- Configuration
- Keymap
- Compatibility
- FAQ
- Contributing
- Working With The Code Base
- Dependencies
Treemacs is a file and project explorer similar to NeoTree or vim’s NerdTree, but largely inspired by the Project Explorer in Eclipse. It shows the file system outlines of your projects in a simple tree layout allowing quick navigation and exploration, while also possessing basic file management utilities. Specifically a quick feature overview looks as follows:
- Project management
- Treemacs lets you view multiple file trees - projects - at once and quickly add or remove them.
- Easy navigation
- quickly move between projects or use shortcuts to jump to parent or neighbouring nodes.
- Versatile file access
- decide exactly how and where a file will be opened, including using
ace-windowto choose a window or launching an external application. - Understanding of frames
- every frame will receive its own treemacs buffer that will live and die with that frame.
- Finding of files and tags
- Treemacs can follow along and keep in focus the currently selected file or even the tag
at point using, either manually or automatically using either
treemacs-follow-modeortreemacs-tag-follow-mode. - Git Integration
- Treemacs can use different faces for files and directories based on their git status. The git process is run asynchronously, minimizing its performance impact.
- Winum & ace-window compatibility
- The presence of treemacs will not interfere with winum’s and ace-window’s usual layouts.
- Projectile integration
- the
treemacs-projectilepackage lets you quickly add your projectile projects to the treemacs workspace. - Simple mouse interface
- Left clicks will work the same as you’re used to from with graphical applications
- Session persistence
- Treemacs automatically saves and restores your workspace.
- Dashing good looks
- Treemacs uses (optionally resizable) png images in HD 22x22 resolution for its icons (quantity is, of course, another matter). When run in a terminal a simple fallback is used.
- Tag view
- Treemacs can display files’ tags. All file types that Emacs can generate a (semantic) imenu index for are supported.
- Visual feedback
- When it would otherwise be difficult to see the message in the minibuffer success/failure is indicated with pulse.el.
- Ease of use
- Treemacs offers many configuration options, but comes with a set of (what hopefully should be) sane
defaults. Installation aside there are two obligatory pieces of setup: 1) Choosing convenient keybindings to run
treemacs and 2) If you use evil: requiring
treemacs-evilto integrate treemacs with evil and enable j/k navigation. More on both below. You can also summon a helpful hydra with?that will remind you of treemacs’ many keybindings and features.
If you don’t care about reading the full readme here’s a list of some bare bones basics to get you started:
- First of all: press
?to summon the helpful hydra: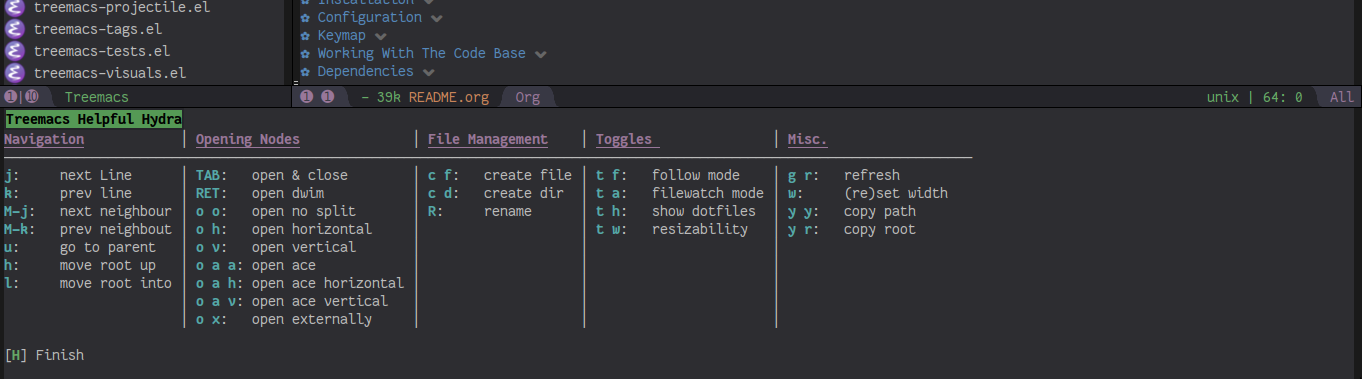
- If you use evil don’t forget to also install
treemacs-evil - If you use projectile you can install
treemacs-projectileto allow quickly add your projectile projects to treemacs. - Treemacs doesn’t bind any global keys, you need to use whatever fits you best. A full install setup can be found
below. Otherwise just add a keybind for
treemacs. - For navigation use n/p (j/k when evil), M-n/M-p to move to same-height neighbour u to go to parent, and C-n/C-k to move between projects.
- There’s half a dozen different ways to open nodes, all bound under o as prefix. Pick your favourite.
- TAB and RET are particularly configurable. See
treemacs-TAB/RET-actions-config. - Projects administration is bound under the
C-pprefix.
If you’ve previously used a different explorer like NeoTree or NerdTree - or an earlier version of treemacs for that matter - you are probably used to a display system wherein you see exactly a single file tree whose exact root you can arbitrarily change. This system makes it difficult to work on and switch between multiple projects. Treemacs used to (and still does) remedy that limitation by making every treemacs buffer unique to its frame, but it has now been redesigned to be able to display multiple file trees - projects - at once.
In treemacs a workspace is simply a (named) collection of projects, while a project consists of 2 things: its location in the file system and its display name. This is the info that you need to provide when you want to add a new project to your workspace. In the future it should be possible to switch between various workspaces and use different workspaces for different frames’ buffers, but as of now there exists only the global default workspace.
This design approach has various advantages and disadvantages. It is now no longer possible to “free roam” in the file system with treemacs, i.e. you can no longer arbitrarily switch the single file tree’s root to the directory at point or the current root’s parent. Another restriction is that the same part of the file system may not appear more than once as part of the workspace. For example it is not possible to add both /Foo and /Foo/Bar as projects, since internally treemacs heavily relies on every node having a unique natural key in its absolute path. Nonetheless the pros certainly outweigh the cons, as a multiroot setup allows to work on multiple projects with any combination concern/buffer separating frameworks, be it persp, eyebrowse, or projectile. It also opens the potential for concurrent display not only of the file system, but e.g. the currently open buffers.
If a strict workspace and project structure, as described above, is too stringent for your use-case you can, under
certain circumstances, use treemacs to freely navigate through your your file system, similar to dired: When your
workspace contains exactly a single project you can use h and l (or treemacs-root-up and treemacs-root-down) to
arbitrarily change the single project’s root. h will navigate one level upward in the file system, l will move into
the directory at point.
Treemacs buffers have a limited scope they are visible in: the frames they are created in. A treemacs buffer, once
created, lives alongside and inside its frame, and is also destroyed with that frame. Calling treemacs while inside a
new frame will create a new buffer for it, regardless how many other treemacs buffers already exist. While there can be
multiple unique treemacs buffer they will all still show the same workspace and the same projects.
A treemacs buffer that does not belong to a frame may still be made visible by manually selecting in the buffer list. This would break various assumptions in treemacs’ code base and effectively falls under undefined behaviour - a bad idea all around.
Treemacs handles left clicks in much the same way as modern graphical applications do: a single click sets the focus, a double click expands or collapses a directory or tag section node and visits a file/moves to a tag for a file/tag node.
Additionally tag sections can be expanded or collapsed by a single click on the file/tag section icon.
If you prefer to expand/collpase nodes with a single mouse click you can also use treemacs-single-click-expand-action:
(define-key treemacs-mode-map [mouse-1] #'treemacs-single-click-expand-action)treemacs-follow-mode is a global minor mode which allows the treemacs view to always move its focus to the currently
selected file. This is achieved by advising select-window, which is a ubiquitous function, often called multiple times
in a row when Emacs is working. This means two things:
treemacs-followtries to be very specific about when it is run at all.- There may be times when something slips through (
which-keyfor example would cause such a problem if treemacs
wasn’t made compatible with it by default). If you do see treemacs-follow behaving in a way it shouldn’t open up an
issue. The fix shouldn’t be more than a single bit of advice away.
treemacs-tag-follow-mode is a global minor mode which extends and effectively replaces treemacs-follow-mode. When
activated it follows not just the current file, but also the current tag. This works alongside treemacs’ integration
with imenu, so all file types providing an imenu implementation are compatible.
This mode runs on an idle timer - the exact duration of inactivity (in seconds) before a move is called is determined by
treemacs-tag-follow-delay.
Note that in order to move to a tag in treemacs the treemacs buffer’s window needs to be temporarily selected, which
will reset blink-cursor-mode’s timer if it is enabled. This will result in the cursor blinking seemingly pausing for a
short time and giving the appearance of the tag follow action lasting much longer than it really does.
treemacs-fringe-indicator-mode is a global minor mode that displays a little icon in the fringe that moves with the cursor.
It can make the selected line more visible if hl-line-mode doesn’t stand out with your theme.
treemacs-git-mode is a global minor mode which enables treemacs to check for files’ and directories’ git status
information and highlight them accordingly (see also the treemacs-git-... faces). The mode is available in 3 variants:
simple, extended and deferred:
- The simple variant starts a git status process and parses its output in elisp. The parsing is kept quick and simple, so some info is missed: this version includes git status information only for files, but not directories.
- The extended variant highlights both files and directories. This greatly increases the complexity and length of the parsing process, and is therefore done in an asynchronous python process for the sake of performance. The extended variant requires python3 to work.
- The deferred variant is the same as extended, except the tasks of rendering nodes and highlighting them are
separated. The former happens immediately, the latter after
treemacs-deferred-git-apply-delayseconds of idle time. This may be faster (if not in truth then at least in appereance) as the git process is given a much greater amount of time to finish. The downside is that the effect of nodes changing their colors may be somewhat jarring, though this effect is largely mitigated due to the use of a caching layer.
When called interactively treemacs-git-mode will ask for the variant to use. In lisp code an appropriate symbol can
be directly passed to the minor mode function:
(treemacs-git-mode 'deferred)All versions use an asynchronous git process and are optimized to not do more work than necessary, so their performance
cost should, for the most part, be the constant amount of time it takes to fork a subprocess. For repositories where
this is not the case treemacs-max-git-entries (default value 5000) will limit the number of git status entries
treemacs will process before ignoring the rest.
treemacs-filewatch-mode is a global minor mode which enables treemacs to watch the files it is displaying for changes
and automatically refresh itself when it detects a change in the file system that it decides is relevant.
A change event is relevant for treemacs if a new file has been created or deleted or a file has been changed and
treemacs-git-mode is enabled. Events caused by files that are ignored as per treemacs-ignored-file-predicates are
likewise counted as not relevant.
The refresh is not called immediately after an event was received, treemacs instead waits treemacs-file-event-delay ms
to see if any more files have changed to avoid having to refresh multiple times over a short period of time. Treemacs
will not refresh the entire view to make the detected changes visible, but will instead only make updates to the
directories where the change(s) happened. Using this mode is therefore by far not as expensive as a full refresh on
every change and save.
The mode only applies to directories opened after this mode has been activated. This means that to enable file watching in an already existing treemacs buffer it needs to be killed and rebuilt. Turning off this mode is, on the other hand, instantaneous - it will immediately turn off all existing file watch processes and outstanding refresh actions.
Known limitations:
Staging and committing changes does not produce any file change events of its own, if you use treemacs-git-mode you
still need to do a manual refresh to see your files’ faces go from ‘changed’ and ‘untracked’ to ‘unchanged’ after a
commit.
Treemacs’ sessions - your workspace and the projects it contains - are saved when Emacs shuts down and restored when
treemacs is first loaded. This persistence process is fully automatic and independant, and should therefore be fully
compatible with desktop-save-mode.
The persisted state is saved under user-emacs-directory/.cache/treemacs-persist by default. The exact file location
is saved in the variable treemacs-persist-file.
When run in a terminal treemacs will fall back to a much simpler rendering system, foregoing its usual png icons and
using simple + and - characters instead. The exact characters used are highly customizable.
Treemacs is able to display not only the file system, but also tags found in individual files. The tags list is sourced using emacs’ builtin imenu functionality, so all file types that emacs can generate an imenu index for are supported.
Imenu caches its result, so to avoid stale tag lists setting imenu-auto-rescan to t is recommended. Tags generated
with the help of semantic-mode are likewise supported.
Treemacs can show the tags produced by ggtags if you switch a buffer’s imenu index function to use ggtags:
(setq-local imenu-create-index-function #'ggtags-build-imenu-index)Treemacs always sets the default-directory variable based on the (nearest) path at the current node, falling back to
your home directory when there is no node or path at point. That means that various commands like find-file,
magit-status or helm-projectile-ag will correctly act based on the current directory or project context.
Treemacs supports projects on remote directories, e.g. /scp:remote-server:path/to/directory.
Treemacs supports storing links to its file nodes by means of org-store-link.
Next to treemacs itself you can optionally install:
Must be installed and loaded if you use evil. The keybindings and the cursor will not be setup properly otherwise. It’ll also enable navigation with j/k instead of n/p.
Allows to quickly add your projectile projects to the treemacs workspace by calling treemacs-projectile.
Allows you to use treemacs icons in dired buffers with treemacs-icons-dired-mode:
![]()
Treemacs can be extended to display arbitrary nodes as well as be used as a general rendering backend for any tree-like structures. See here for an extended tutorial and demonstration.
Treemacs is included in Spacemacs (for now only on the dev branch). If you are using the development version of
Spacemacs you can simply add treemacs to dotspacemacs-configuration-layers to replace the default NeoTree. Check SPC
h SPC treemacs for details. Otherwise you will need to add treemacs to dotspacemacs-additional-packages.
Treemacs is also available on MELPA. If you just want to quickly start using it grab the use-package example below,
and customize it as needed (remove treemacs-evil if you don’t use it, customize the keybindings to you taste, etc).
Either way keep in mind that treemacs has no default keybindings for its globally callable initialization functions. Each
user is supposed to select keybindings for functions like treemacs-find-file based on whatever they find convenient.
You can find an exhaustive overview of all functions, their keybindings and functions you need to bind yourself below.
The following use-package snippet includes a list of all of treemacs’ configuration variables in their default
setting. Setting them all yourself is not necessary, they are only listed here to encourage discoverability.
(use-package treemacs
:ensure t
:defer t
:init
(with-eval-after-load 'winum
(define-key winum-keymap (kbd "M-0") #'treemacs-select-window))
:config
(progn
(setq treemacs-collapse-dirs (if (executable-find "python") 3 0)
treemacs-deferred-git-apply-delay 0.5
treemacs-display-in-side-window t
treemacs-file-event-delay 5000
treemacs-file-follow-delay 0.2
treemacs-follow-after-init t
treemacs-follow-recenter-distance 0.1
treemacs-git-command-pipe ""
treemacs-goto-tag-strategy 'refetch-index
treemacs-indentation 2
treemacs-indentation-string " "
treemacs-is-never-other-window nil
treemacs-max-git-entries 5000
treemacs-no-png-images nil
treemacs-no-delete-other-windows t
treemacs-project-follow-cleanup nil
treemacs-persist-file (expand-file-name ".cache/treemacs-persist" user-emacs-directory)
treemacs-recenter-after-file-follow nil
treemacs-recenter-after-tag-follow nil
treemacs-show-cursor nil
treemacs-show-hidden-files t
treemacs-silent-filewatch nil
treemacs-silent-refresh nil
treemacs-sorting 'alphabetic-desc
treemacs-space-between-root-nodes t
treemacs-tag-follow-cleanup t
treemacs-tag-follow-delay 1.5
treemacs-width 35)
;; The default width and height of the icons is 22 pixels. If you are
;; using a Hi-DPI display, uncomment this to double the icon size.
;;(treemacs-resize-icons 44)
(treemacs-follow-mode t)
(treemacs-filewatch-mode t)
(treemacs-fringe-indicator-mode t)
(pcase (cons (not (null (executable-find "git")))
(not (null (executable-find "python3"))))
(`(t . t)
(treemacs-git-mode 'deferred))
(`(t . _)
(treemacs-git-mode 'simple))))
:bind
(:map global-map
("M-0" . treemacs-select-window)
("C-x t 1" . treemacs-delete-other-windows)
("C-x t t" . treemacs)
("C-x t B" . treemacs-bookmark)
("C-x t C-t" . treemacs-find-file)
("C-x t M-t" . treemacs-find-tag)))
(use-package treemacs-evil
:after treemacs evil
:ensure t)
(use-package treemacs-projectile
:after treemacs projectile
:ensure t)
(use-package treemacs-icons-dired
:after treemacs dired
:ensure t
:config (treemacs-icons-dired-mode))Treemacs offers the following configuration options (describe-variable will usually offers more details):
| Variable | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| treemacs-indentation | 2 | The number of times each level is indented in the file tree. |
| treemacs-indentation-string | ” ” | The string that is used to create indentation. |
| treemacs-width | 35 | Width of the treemacs window. |
| treemacs-show-hidden-files | t | Dotfiles will be shown if this is set to t and be hidden otherwise. |
| treemacs-follow-after-init | nil | When t follow the currently selected file after initializing the treemacs buffer, regardless of treemacs-follow-mode setting. |
| treemacs-sorting | alphabetic-asc | Indicates how treemacs will sort its files and directories. (Files will always be shown after directories.) |
| treemacs-ignored-file-predicates | (treemacs–std-ignore-file-predicate) | List of predicates to test for files and directories ignored by Emacs. Ignored files will never be shown in the treemacs buffer. |
| treemacs-pre-file-insert-predicates | nil | List of predicates to test for files and directories not to be rendered. Unlike treemacs-ignored-file-predicates these predicates apply when files’ git status information is available. |
| treemacs-file-event-delay | 5000 | How long (in milliseconds) to collect file events before refreshing. See also treemacs-filewatch-mode. |
| treemacs-goto-tag-strategy | refetch-index | Indicates how to move to a tag when its buffer is dead. |
| treemacs-RET-actions-config | Prefers visiting nodes over closing/opening | Alist defining the behaviour of treemacs-RET-action. |
| treemacs-TAB-actions-config | Prefers closing/opening nodes over visiting | Alist defining the behaviour of treemacs-TAB-action. |
| treemacs-collapse-dirs | 0 | Collapse this many directories into one, when possible. A directory is collapsible when its content consists of nothing but another directory. |
| treemacs-silent-refresh | nil | When non-nil a completed refresh will not be announced with a log message. This applies both to manual refreshing as well as automatic (due to treemacs-filewatch-mode). |
| treemacs-silent-filewatch | nil | When non-nil a refresh due to filewatch-mode will cause no log message. |
| treemacs-is-never-other-window | nil | Prevents treemacs from being selected with other-window. |
| treemacs-position | left | Position of treemacs buffer. Valid values are left, right. |
| treemacs-tag-follow-delay | 1.5 | Delay in seconds of inactivity for treemacs-tag-follow-mode to trigger. |
| treemacs-tag-follow-cleanup | t | When non-nil treemacs-tag-follow-mode will keep only the current file’s tags visible. |
| treemacs-project-follow-cleanup | nil | When non-nil treemacs-follow-mode will keep only the current project expanded and all others closed. |
| treemacs-no-png-images | nil | When non-nil treemacs will use TUI string icons even when running in a GUI. |
| treemacs-python-executable | (executable-find “python”) | Python binary used by treemacs. Should only need changing if python2 is the default and you want treemacs to use python3 for the extended version of treemacs-git-mode. |
| treemacs-recenter-after-file-follow | nil | When non-nil recenter will be called when treemacs-follow-mode moves to a new file. |
| treemacs-recenter-after-tag-follow | nil | When non-nil recenter will be called when treemacs-tag-follow-mode moves to a new tag. |
| treemacs-follow-recenter-distance | 0.1 | Minimum distance from window top/bottom (0.1 = 10%) before treemacs calls recenter in tag/file-follow-mode. |
| treemacs-pulse-on-success | t | When non-nil treemacs will pulse the current line as a success indicator, e.g. when creating a file. |
| treemacs-pulse-on-failure | t | When non-nil treemacs will pulse the current line as a failure indicator, e.g. when failing to find a file’s tags. |
| treemacs-elisp-imenu-expression | [too large to list] | The imenu expression treemacs uses in elisp buffers. |
| treemacs-persist-file | ”~/.emacs.d/.cache/treemacs-persist” | Path to the file treemacs uses to persist its state. |
| treemacs-space-between-root-nodes | t | When non-nil treemacs will separate root nodes with an empty line. |
| treemacs–fringe-indicator-bitmap | [vertical bar] | The fringe bitmap used by the fringe-indicator minor mode. |
| treemacs-deferred-git-apply-delay | 0.5 | Seconds of idle time for git highlighting to apply when using the deferred treemacs-git-mode. |
| treemacs-file-follow-delay | 0.2 | Delay in seconds of idle time for treemacs to follow the selected window. |
| treemacs-display-in-side-window | t | When non-nil treemacs will use a dedicated side-window. |
| treemacs-max-git-entries | 5000 | Maximum number of git status entries treemacs will process. Anything above that number will be ignored. |
| treemacs-show-cursor | nil | When non-nil the cursor will stay visible in the treemacs buffer. |
| treemacs-git-command-pipe | ”” | Text to be appended to treemacs’ git command. Useful for filtering with something like grep. |
| treemacs-no-delete-other-windows | t | Prevents the treemacs window from being deleted by commands like delete-other-windows and magit-status. |
Treemacs defines and uses the following faces:
| Face | Based on | Description |
|---|---|---|
| treemacs-directory-face | font-lock-function-name-face | Face used for directories. |
| treemacs-directory-collapsed-face | treemacs-directory-face | Face used for collapsed part of directories. |
| treemacs-file-face | default | Face used for files. |
| treemacs-root-face | font-lock-constant-face | Face used for project roots. |
| treemacs-tags-face | font-lock-builtin-face | Face used for tags. |
| treemacs-help-title-face | font-lock-constant-face | Face used for the title of the helpful hydra. |
| treemacs-help-column-face | font-lock-keyword-face | Face used for the column headers of the helpful hydra. |
| treemacs-git-*-face | various font lock faces | Faces used by treemacs for various git states. |
| treemacs-term-node-face | font-lock-string-face | Face for directory node symbols used by treemacs when it runs in a terminal. |
| treemacs-on-success-pulse-face | :fg #111111 :bg #669966 | Pulse face used when pulsing on a successful action. |
| treemacs-on-failure-puse-face | :fg #111111 :bg #ab3737 | Pulse face used when pulsing on a failed action. |
To make treemacs get along with evil-mode you need to install and load treemacs-evil. It does not define any functions
or offer any configuration options, making sure it is loaded is sufficient.
The icons treemacs uses can be roughly divided into the following 3 groups (with the first 2 behaving identically). Each
group also makes further adjustments depending on whether treemacs is shown in a GUI or terminal frame. Changes to
icons, as described below, will takes place when a treemacs buffer is killed and rebuilt. Changes to icons can be
reverted by calling treemacs-reset-icons.
Important: There is a restriction that all icons must must be exactly 2 characters long. That’s including the space that will separate an icon from the filename.
These are the 2 icons used for expanded or closed directory nodes. They are stored in the variables treemacs-icop-open
and treemacs-icon-closed. Depending on whether the treemacs instance runs in a GUI or TUI they’ll assume different
values stored in other variables:
| Variable | Value in GUI | Value in TUI |
|---|---|---|
treemacs-icop-open | treemacs-icon-open-png | treemacs-icon-open-text |
treemacs-icon-closed | treemacs-icon-closed-png | treemacs-icon-closed-text |
To change the display of directory nodes you need to overwrite the values of the png/text variables. For example the code to use Unicode icons to display directories in gui mode could look like this:
(with-eval-after-load "treemacs"
(setq treemacs-icon-open-png (propertize "⊖ " 'face 'treemacs-directory-face)
treemacs-icon-closed-png (propertize "⊕ " 'face 'treemacs-directory-face)))Tag icons behave just like directory icons, except there’s 3 of them: one for closed tag sections, one for open tag sections and one for the tags proper:
| Variable | Value in GUI | Value in TUI |
|---|---|---|
treemacs-icop-tag-node-open | treemacs-icop-tag-node-open-png | treemacs-icop-tag-node-open-txt |
treemacs-icon-tag-node-closed | treemacs-icon-tag-node-closed-png | treemacs-icon-tag-node-closed-txt |
treemacs-icon-tag-leaf | treemacs-icon-tag-leaf-png | treemacs-icon-tag-leaf-txt |
Same as above, to change the display of tag nodes you need to overwrite the values of the png/text variables. For example the code to use textual icons to display tags in gui mode could look like this:
(with-eval-after-load "treemacs"
(setq treemacs-icon-tag-node-open-png (propertize "− " 'face 'font-lock-keyword-face)
treemacs-icon-tag-node-closed-png (propertize "+ " 'face 'font-lock-keyword-face)
treemacs-icon-tag-leaf-png (propertize "🞄 " 'face 'font-lock-keyword-face)))First of all if you have an icon you’d like to make use of in treemacs my preferred solution is very much for you to open a pull request (adding a new icon is a one-liner in treemacs-visuals.el, see the last part of the Contributing section) or an issue to let me know about a good icon I can add.
If that’s not possible or if you’d like to use something like all-the-icons.el (which isn’t used in treemacs by
default due to iconic fonts not being monospaced and therefore oftentimes looking uneven) treemacs offers the option to
use your own custom file icons.
File icons are implemented differently than the other icon groups. They too exist as variables, usually named like
treemacs-icon-html, but the selection process happens through a hashtable - treemacs-icons-hash - which maps file
extensions to their icons. Note that treemacs has a very loose definition of what constitutes a file extension - it’s
either everything past the last period, or just the file’s full name if there is no period. This makes it possible to
match file names like ‘.gitignore’ and ‘Makefile’. Extensions are not case-sensitive and will be downcased when their
icons is to be retrieved.
There is also the special case of treemacs-icon-fallback, which is used when a file extension has no specific icon
assigned to it. It takes the value treemacs-icon-text in a GUI and treemacs-icon-fallback-text in a TUI.
While it is possible to directly push a mapping to treemacs-icons-hash treemacs also offers the utility function
treemacs-define-custom-icon. It takes as its arguments an icon (a string) and as &rest a list of file extension to
use the icon for. Already present icons for the given extensions will be overwritten.
Using it would look like this:
(with-eval-after-load "treemacs"
(defvar treemacs-custom-html-icon (all-the-icons-icon-for-file "name.html"))
(treemacs-define-custom-icon treemacs-custom-html-icon "html" "htm"))For some file extensions, like “.cc” or “.hh”, it is not immediately obvious which major mode will open these files, and
thus which icon they should be assigned. Treemacs offers the option that automate this decision based on
auto-mode-alist. You can use the function treemacs-map-icons-with-auto-mode-alist to change the assigned icons for a
list of file extensions based on the major mode the icons are mapped to in auto-mode-alist.
treemacs-map-icons-with-auto-mode-alist takes 2 arguments: first a list of file extensions, then an alist that decides
which icon should be used for which mapped major mode. For example the code to decide the icons for “.hh” and “.cc”
files with auto-mode-alist would look like this:
(with-eval-after-load "treemacs"
(treemacs-map-icons-with-auto-mode-alist
'(".cc" ".hh")
'((c-mode . treemacs-icon-c)
(c++-mode . treemacs-icon-cpp))))It is possible to force treemacs to use the simple TUI icons in GUI mode by setting treemacs-no-png-images to t.
If your emacs has been compiled with imagemagick support you can arbitrarily change the size of treemacs’ icons by
(interactively) calling treemacs-resize-icons.
Not really part of the icons, but a useful visual feature nonetheless: An indent guide like effect can be created by
selecting appropriate values for treemacs-indentation and treemacs-indentation-string:
(setq treemacs-indentation-string (propertize " ⫶ " 'face 'font-lock-comment-face)
treemacs-indentation 1)These functions are not bound to any keys by default. It’s left up to users to find the most convenient key binds.
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| treemacs | Show/Hide/Initialize treemacs. |
| treemacs-bookmark | Find a bookmark in treemacs. |
| treemacs-find-file | Find and focus the current file in treemacs. |
| treemacs-find-tag | Find and focus the current tag in treemacs. |
| treemacs-select-window | Select the treemacs window if it is visible. Call treemacs if it is not. |
| treemacs-delete-other-windows | Same as delete-other-windows, but will not delete the treemacs window. |
| treemacs-show-changelog | Opens a buffer showing the changelog. |
By default Treemacs’s keymap looks as follows:
| Key | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ? | treemacs-helpful-hydra | Summon the helpful hydra to show you the treemacs keymap. |
| j/n | treemacs-next-line | Go to the next line. |
| k/p | treemacs-previous-line | Go to the previous line. |
| M-J/N | treemacs-next-line-other-window | Go to the next line in next-window. |
| M-K/P | treemacs-previous-line-other-window | Go to the previous line in next-window.. |
| <PgUp> | treemacs-next-page-other-window | Go to the next page in next-window. |
| <PgDn> | treemacs-previous-page-other-window | Go to the previous page in next-window.. |
| M-j/M-n | treemacs-next-neighbour | Go to the next same-level neighbour of the current node. |
| M-k/M-p | treemacs-previous-neighbour | Go to the previous same-level neighbour of the current node. |
| u | treemacs-goto-parent-node | Go to parent of node at point, if possible. |
| C-p a | treemacs-add-project-to-workspace | Select a new project to add to the treemacs workspace. |
| C-p p | treemacs-projectile | Select a projectile project to add to the workspace. |
| C-p d | treemacs-remove-project-from-workspace | Remove project at point from the workspace. |
| C-p r | treemacs-rename-project | Rename project at point. |
| C-p c c | treemacs-collapse-project | Collapse project at point. |
| C-p c o/S-TAB | treemacs-collapse-all-projects | Collapse all projects. |
| C-p c o | treemacs-collapse-all-projects | Collapse all projects except the project at point. |
| <M-Up> | treemacs-move-project-up | Switch positions of project at point and the one above it. |
| <M-Down> | treemacs-move-project-down | Switch positions of project at point and the one below it. |
| th | treemacs-toggle-show-dotfiles | Toggle the hiding and displaying of dotfiles. |
| tw | treemacs-toggle-fixed-width | Toggle whether the treemacs window should have a fixed width. See also treemacs-width. |
| tf | treemacs-follow-mode | Toggle treemacs-follow-mode. |
| ta | treemacs-filewatch-mode | Toggle treemacs-filewatch-mode. |
| tv | treemacs-fringe-indicator-mode | Toggle treemacs-fringe-indicator-mode. |
| w | treemacs-set-width | Set a new value for the width of the treemacs window. |
| RET | treemacs-RET-action | Run the action defined in treemacs-RET-actions-config for the current node. |
| TAB | treemacs-TAB-action | Run the action defined in treemacs-TAB-actions-config for the current node. |
| g/r/gr | treemacs-refresh | Refresh the project at point. |
| d | treemacs-delete | Delete node at point. |
| R | treemacs-rename | Rename node at point. |
| cf | treemacs-create-file | Create a file. |
| cd | treemacs-create-dir | Create a directory. |
| q | bury-buffer | Hide the treemacs buffer. |
| Q | treemacs-kill-buffer | Delete the treemacs buffer. |
| ov | treemacs-visit-node-vertical-split | Open current file or tag by vertically splitting next-window. |
| oh | treemacs-visit-node-horizontal-split | Open current file or tag by horizontally splitting next-window. |
| oo/RET | treemacs-visit-node-no-split | Open current file or tag, performing no split and using next-window directly. |
| oaa | treemacs-visit-node-ace | Open current file or tag, using ace-window to decide which window to open the file in. |
| oah | treemacs-visit-node-ace-horizontal-split | Open current file or tag by horizontally splitting a window selected by ace-window. |
| oav | treemacs-visit-node-ace-vertical-split | Open current file or tag by vertically splitting a window selected by ace-window. |
| ox | treemacs-visit-node-in-external-application | Open current file according to its mime type in an external application. Linux, Windows and Mac are supported. |
| P | treemacs-peek | Peek at the file (or tag) at point without fully opening it. |
| yy | treemacs-copy-path-at-point | Copy the absolute path of the node at point. |
| yr | treemacs-copy-project-root | Copy the absolute path of the project root for the node at point. |
| s | treemacs-resort | Set a new value for treemacs-sorting. |
| b | treemacs-add-bookmark | Bookmark the currently selected files’s, dir’s or tag’s location. |
| h | treemacs-root-up | Move treemacs’ root one level upward. Only works with a single project in the workspace. |
| l | treemacs-root-down | Move treemacs’ root into the directory at point. Only works with a single project in the workspace. |
The correctness of treemacs’ display behaviour is, to a large degree, ensured through window properties and reacting to changes in the window configuration. The packages most likely to cause trouble for treemacs are therefore those that interfere with Emacs’ buffer spawning and window splitting behaviour. Treemacs is included in Spacemacs and I am a Spacemacs user, therefore treemacs guarantees first-class support & compatibility for window-managing packages used in Spacemacs, namely persp, eyebrowse, popwin and window-purpose, as well as shackle. For everything else there may be issues and, depending on the complexity of the problem, I may decide it is not worth fixing.
Aside from this there are the following known incompatibilities:
- Any package invoking
font-lock-ensurein the treemacs buffer. This will reset the faces of treemacs’ buttons (once) and is a known emacs bug. - A possible cause of this issue using an old version of swiper.
- Rainbow mode activated in treemacs will likewise produce this behaviour. Make sure not to include rainbow-mode as
part of
special-mode-hook, since this is the modetreemacs-modeis derived from.
- How do I keep treemacs from showing files that are ignored by git?
Short answer:
(add-to-list 'treemacs-pre-file-insert-predicates #'treemacs-is-file-git-ignored?)
A slightly longer explanation about how you can hook into the render process can be found in the documentation string of
treemacs-pre-file-insert-predicates. - Why am I seeing no file icons and only +/- for directories?
Treemacs will permanently fall back on its simple TUI icons if it detects that the emacs instance it is run in cannot create images. You can test this by evaluating
(create-image "" 'png). If this code returns an error like “Invalid image type ´png´” your emacs does not support images. - How do I get treemacs to stop telling me when it’s been refreshed, especially with filewatch-mode?
See
treemacs-silent-refreshandtreemacs-silent-filewatch. - ENOSPC / No space left on device
You may run into this error when you use filewatch-mode. The solution is to increase the number of allowed user watches, as described in this link. You’ll also want to see what’s responsible for setting all those file watches in the first place, since treemacs only watches the directories it is displaying and so won’t produce more than a couple dozen watches at best.
- Why is treemacs warning me about not being able to find some background colors and falling back to something else?
Treemacs needs those colors to make sure that background colors of its icons correctly align with hl-line-mode. Png images’ backgrounds are not highlighted by hl-line-mode by default, treemacs is manually correcting this every time hl-line’s overlay is moved. To make that correction work it needs to know two colors: the current theme’s
defaultbackground, and itshl-linebackground color. If treemacs cannot find hl-lines’s background color it falls back to the default background color. If it cannot even find the default background it will fall back to #2d2d31. The warnings serve to inform you of that fallback.If your theme does not define a required color you can set it yourself before treemacs loads like this:
(set-face-attribute 'hl-line nil :background "#333333")
If you just want to disable the warnings you can do so by defining the variable
treemacs-no-load-time-warnings. Its exact value is irrelevant, all that matters is that it exists at all. Since the warnings are issues when treemacs is first being loaded the variable must be defined before treemacs is initialized. This is best achieved by adding the line(defvar treemacs-no-load-time-warnings t)to treemacs’ use-package:initblock. - Can I expand everything under a node?
Yes, you just need to expand it with a prefix argument. Closing nodes with a prefix argument works as well. In this case treemacs will forget about the nodes opened below the one that was closed and not reopen them automatically.
Contributions are very much welcome, but should fit the general scope and style of treemacs. The following is a list of guidelines that should be met (exceptions confirm the rule):
- There should be one commit per feature.
- Commit messages should start with a note in brackets that roughly describes the area the commit relates to, for
example
[Icons]if you add an icon. - Code must be in the right place (what with the codebase being split in many small files). If there is no right place it probably goes into treemacs-impl.el which is where all the general implementation details go.
- New features must be documented in the readme (for example mentioning new config options in the Config Table).
- There must not be any compiler warnings.
- The test suite must pass.
Treemacs uses cask to setup a local testing environment and a Makefile that simplifies compiling and testing the
codebase. First run cask install to locally pull treemacs’ dependencies. Then you can use the following Makefile
targets:
- make prepare
- Downloads and updates Cask’s dependencies. Is a dependency of the
testandcompiletargets. - make compile
- Compiles the code base (and treats compiler warnings as errors).
- make clean
- Removes the generated .elc files.
- make lint
- Runs first
compilethenclean, even if the former fails. - make test
- Runs the testsuite, once in a graphical environment and once in the terminal.
Finally if you want to just add an icon you can take this commit as an example (though the icons have since been moved
into their own module in treemacs-icons.el).
If you want to delve into the treemacs’ code base, check out the wiki for some general pointers.
- emacs >= 25.2
- f.el
- s.el
- dash
- cl-lib
- ace-window
- pfuture
- ht
- hydra
- (optionally) evil
- (optionally) projectile
- (optionally) winum
- (optionally) python(3)