Adversarial Threat Detector makes AI development Secure.
In recent years, deep learning technology has been developing, and various systems using deep learning are spreading in our society, such as face recognition, security cameras (anomaly detection), and ADAS (Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems).
On the other hand, there are many attacks that exploit vulnerabilities in deep learning algorithms. For example, the Evasion Attacks are an attack that causes the target classifier to misclassify the Adversarial Examples into the class intended by the adversary. the Exfiltration Attacks are an attack that steals the parameters and train data of a target classifier. If your system is vulnerable to these attacks, it can lead to serious incidents such as face recognition being breached, allowing unauthorized intrusion, or information leakage due to inference of train data.
So we released a vulnerability scanner called "Adversarial Threat Detector" (a.k.a. ATD), which automatically detects vulnerabilities in deep learning based classifiers.
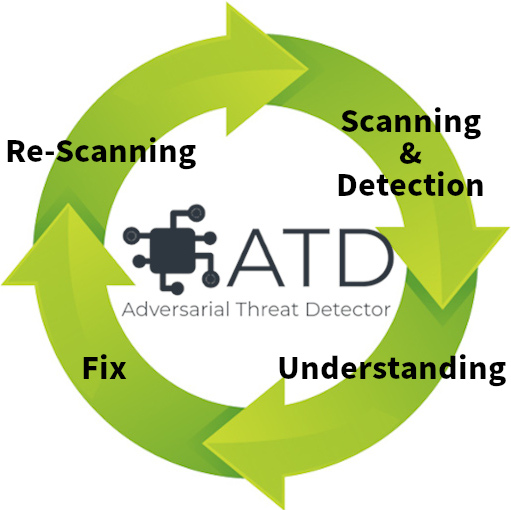
ATD contributes to the security of your classifier by executing the four cycles of "Detecting vulnerabilities (Scanning & Detection)", "Understanding vulnerabilities (Understanding)", "Fixing vulnerabilities (Fix)", and "Check fixed vulnerabilities (Re-Scanning)".
ATD is following the Adversarial Threat Matrix, which summarizes threats to machine learning systems. And currently, ATD uses the Adversarial Robustness Toolbox (ART), a security library for machine learning, as its core engine. Currently ATD is beta version, but we will release new functions once a month, so please check our release information.
ATD automatically executes a variety of attacks against the classifier and detects vulnerabilities.
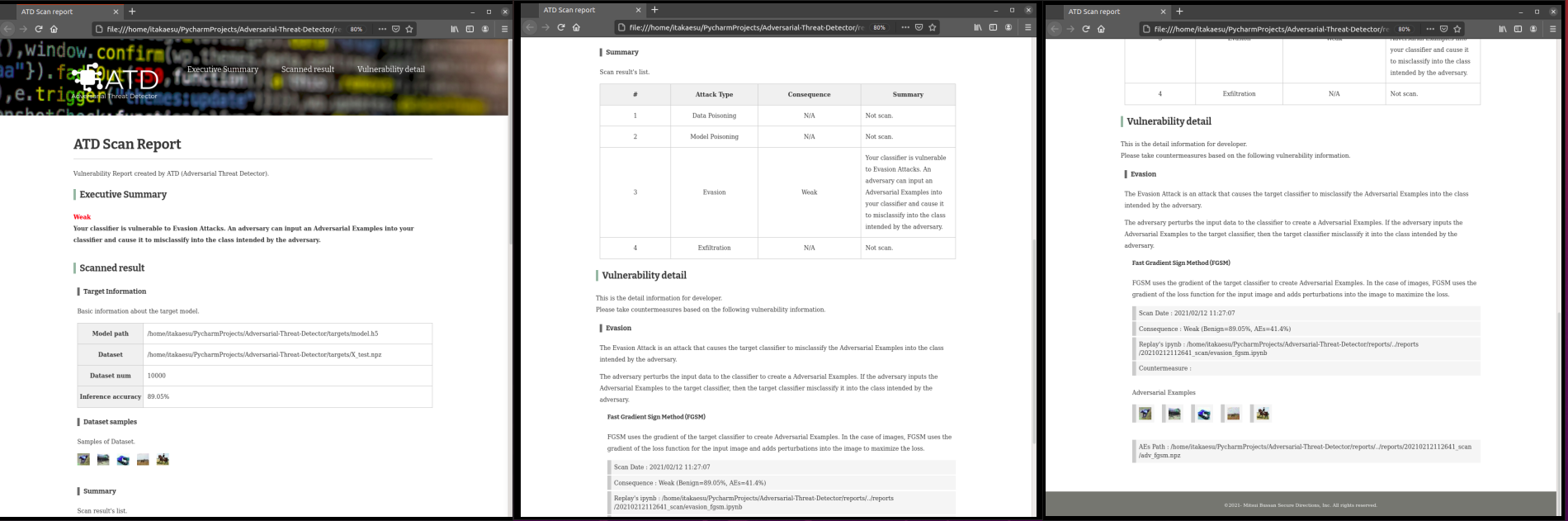
When a vulnerability is detected, ATD will generate a countermeasure report (HTML style) and a replay environment (ipynb style) of the vulnerabilities. Developers can understand the vulnerabilities by referring to the countermeasure report and the replay environment.
- Countermeasure report (HTML style)
Developers can fix the vulnerabilities by referring to the vulnerability overview and countermeasures.
Sample report is here.
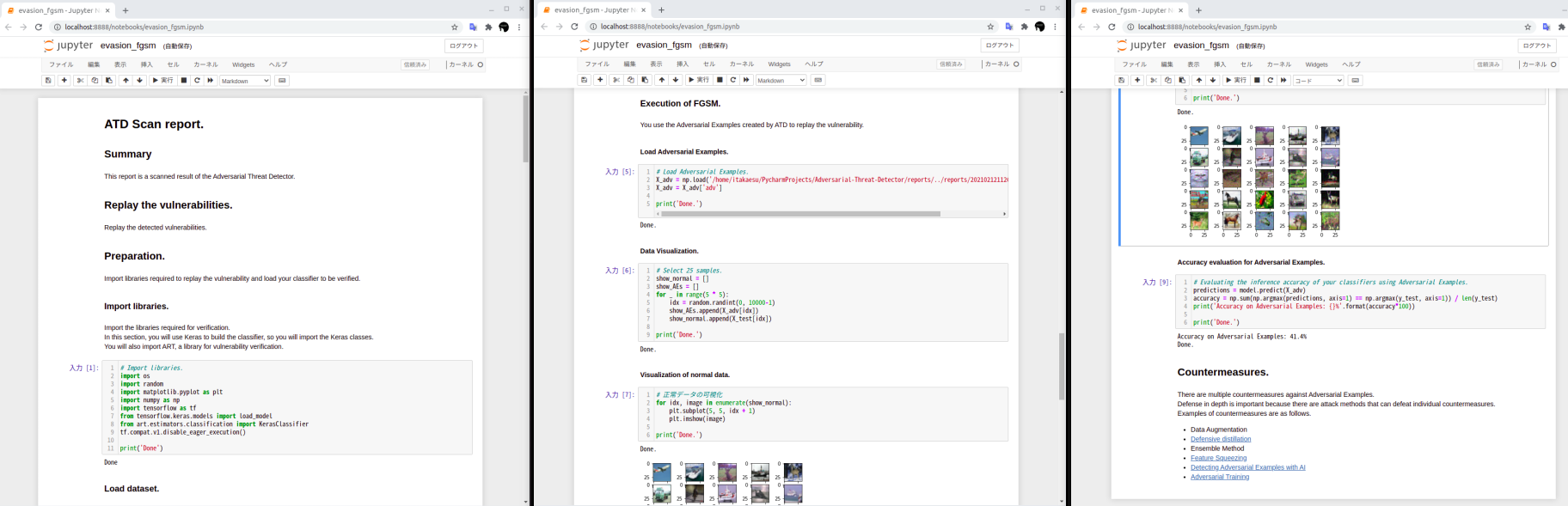
- Vulnerabilities Replay environment (ipynb style)
By opening the ipynb automatically generated by ATD in Jupyter Notebook so on, developers can replay the attack against the classifier. Developers can understand the vulnerabilities.
Sample notebook is here.
ATD automatically fixes detected vulnerabilities.
* This feature will be supported in the next release.
The ATD checks fixed vulnerabilities of the fixed classifier.
* This feature will be supported in the next release.
The current version of ATD supports only image classifier built with tf.keras.
Other classifiers will be supported in the future.
| Estimators | Image classifier | Text classifier | Other classifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keras | supported | - | - |
| TensorFlow | - | - | - |
| TensorFlow v2 | - | - | - |
| PyTorch | - | - | - |
| Scikit-learn | - | - | - |
ATD supports only Evasion Attack.
Other attacks will be supported in the future.
| Attack type | Image classifier | Text classifier | Other classifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Poisoning | - | - | - |
| Model Poisoning | - | - | - |
| Evasion | supported | - | - |
| Exfiltration | - | - | - |
We will be releasing new features of ATD every other month.
The roadmap for ATD is as follows.
- 01.2021: Implementation of Evasion Attacks (completed).
- 02.2021: Implementation of "Fix" and "Re-Scanning" functions.
- 03.2021: Implementation of Exfiltration Attacks.
- 04.2021: Implementation of Detecting Model Poisoning.
- 05.2021: Implementation of Detecting Data Poisoning.
- 06.2021: Support for classifiers other than Keras.
- 07.2021: Support for non-image classifiers.
- git clone ATD's repository.
root@kali:~# git clone https://github.com/gyoisamurai/Adversarial-Threat-Detector
- Get python3-pip.
root@kali:~# apt-get update
root@kali:~# apt-get install python3-pip
- Install required python packages for ATD.
root@kali:~# cd Adversarial-Threat-Detector
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# pip3 install -r requirements.txt
You can execute various vulnerability scans by changing the arguments to the ATD.
| Note |
|---|
| The current version of ATD only supports Evasion Attacks. Other attack methods will be supported in the future. |
usage: atd.py [-h] [--model_name MODEL_NAME] [--dataset_name DATASET_NAME] [--use_dataset_num USE_DATASET_NUM] [--label_name LABEL_NAME]
[--attack_type {all,data_poisoning,model_poisoning,evasion,exfiltration}] [--data_poisoning_method {fc,cp}] [--model_poisoning_method {node_injection,layer_injection}]
[--evasion_method {all,fgsm,cnw,jsma}] [--exfiltration_method {mi,label_only,inversion}] [--lang {en,ja}]
Adversarial Threat Detector.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--model_name MODEL_NAME
Target model name.
--dataset_name DATASET_NAME
Dataset name.
--use_dataset_num USE_DATASET_NUM
Dataset number for test.
--label_name LABEL_NAME
Label name.
--attack_type {all,data_poisoning,model_poisoning,evasion,exfiltration}
Specify attack type.
--data_poisoning_method {fc,cp}
Specify method of Data Poisoning Attack.
--model_poisoning_method {node_injection,layer_injection}
Specify method of Poisoning Attack.
--evasion_method {all,fgsm,cnw,jsma}
Specify method of Evasion Attack.
--exfiltration_method {mi,label_only,inversion}
Specify method of Exfiltration Attack.
--lang {en,ja} Specify language of report.
| Parameter | Overview |
|---|---|
| model_name | Specify the file name of the trained model to be scanned for vulnerabilities. You need to put the model in HDF5 format in the targets directory. |
| dataset_name | Specify the file name of the dataset that can be inferred by the classifier specified by model_name. You need to put the files in npz format in the targets directory. Also, the dataset should contain at least 100 data. |
| use_dataset_num | Specify the number of data to be used for vulnerability scanning from dataset_name. |
| label_name | Specify the file name of the label of the dataset specified by dataset_name. You need to put the files in npz format in the targets directory. |
| attack_type | Specifies the attack type for the classifier specified by model_name. Currently only evasion is supported. |
| evasion_method | Specifies the method of evasion attack (If evasion is specified for attack_type). |
| lang | Specify the language of the report. Default is en. |
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# python3 atd.py --model_name target_model.h5 --dataset_name X_test.npz --label_name y_test.npz --use_dataset_num 100 --attack_type evasion --evasion_method fgsm
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# python3 atd.py --model_name target_model.h5 --dataset_name X_test.npz --label_name y_test.npz --use_dataset_num 100 --attack_type evasion --evasion_method cnw
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# python3 atd.py --model_name target_model.h5 --dataset_name X_test.npz --label_name y_test.npz --use_dataset_num 100 --attack_type evasion --evasion_method jsma
You can run ATD by using trained model and dataset we have prepared.
- Download the trained image classifier built in
tf.keras.
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# wget "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1zFNn8EBHR_xewFW3-IhXkfdEop0gYUbu" -O demo_model.h5
- Download the lightweight CIFAR10 which reduces the data to 1000.
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# wget "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1AVtPVe2Z4UNVcIJlnO-Lbg0zVMQPS17Z" -O X_test.npz
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# wget "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1JFEJPrwblgLn_alkzTR_ZKG7sEOp4Mom" -O y_test.npz
- Move
demo_model.h5,X_test.npz,y_test.npztotargetsdirectory.
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# mv demo_model.h5 X_test.npz y -O X_test.npz y_test.npz ./targets/
- Run ATD.
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# python3 atd.py --model_name demo_model.h5 --dataset_name X_test.npz --label_name y_test.npz --use_dataset_num 100 --attack_type evasion --evasion_method fgsm
..snip..
[!] Created report: ~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector/reports/../reports/20210217151416_scan/scan_report.html
atd.py Done!!
- Check scan report (html and ipynb).
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# firefox reports/20210217151416_scan/scan_report.html
root@kali:~/Adversarial-Threat-Detector# jupyter notebook reports/20210217151416_scan/evasion_fgsm.ipynb
- Email
gyoiler3@gmail.com