⚠️ Make sure to backup your notes before trying this, or just try it in test mode.- 📅 Running this script will change modification dates of all modified notes (I would like to prevent this, but for now I can't and asked for help here).
- 💻 Install scripts are mainly disgned for non-developer users, if you are confortable with git/python it may be more confortable for you to proceed with the manual installation.
Back references to notes
BEAR_BR_SECTIONS=false \
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cglacet/bear/master/install.sh)"Back references to sections
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cglacet/bear/master/install.sh)"How to run a bash command on OSX:
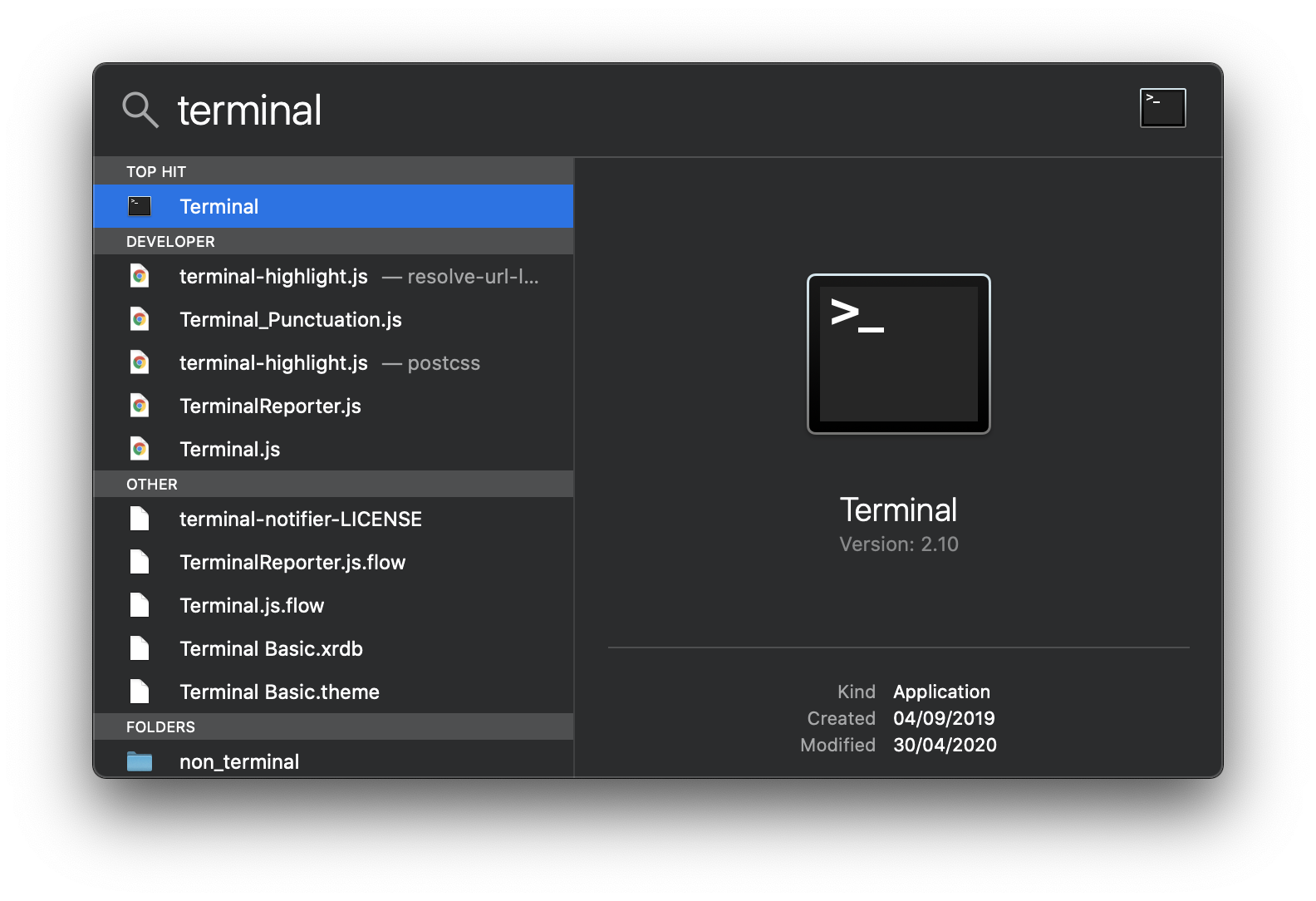
Bring spotlight search in by hitting ⌘ + space,
search for terminal
and validate you search with ↵ enter.
A terminal window shows up,
copy paste any of the previous command /bin/bash -c "..." in the terminal
then hit ↵ enter to run the bash script.
The suggestion comes from this question on reddit:
There has been interest in this feature already with previous posts:
https://www.reddit.com/r/bearapp/comments/9sbx6h/feature_request_reverse_links_a_note_shows_all/
https://www.reddit.com/r/bearapp/comments/5hn8ts/feature_request_compile_all_note_mentionlinks_in/
Is this feature on the near-future roadmap?
I would absolutely love this for the Zettelkasten tool I want to build [based on Niklas Luhmann note scheme]. There are several dedicated software tools out there implementing ZTK specifically [nvALT, The Archive], but they all have downsides. For starters they are not cross platform macOS/iOS/iPadOS...]!
Bear already supported the auto-link-complete feature with [[ notation...
Having a note at the bottom of each note indication other notes that are linking to it would make Bear for me 'the perfect Zettelkasten' tool! And probably that of many others too. No problem if this would be subscription only feature... happy to pay for it, in fact it should be, otherwise the cross platform requirement would be moot ;)
The script:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cglacet/bear/master/install.sh)"Here is what this script does, it:
- installs all shell dependencies (Git/Python/pyenv) using Homebrew,
- downloads the most recent sources from here in the repository
~/.github/bear/back-references, - sets this directory's default python interpreter to a recent version of python 3.7.
- runs the python script that actually make all the work, which is:
- finding all outgoing links from existing Bear notes
- adding back-references to existing notes.
Theses steps are also described in the manual installation section and more details on how the python script operate on Bear notes can be found here. The installation script can be found here and uses more general scripts from here.
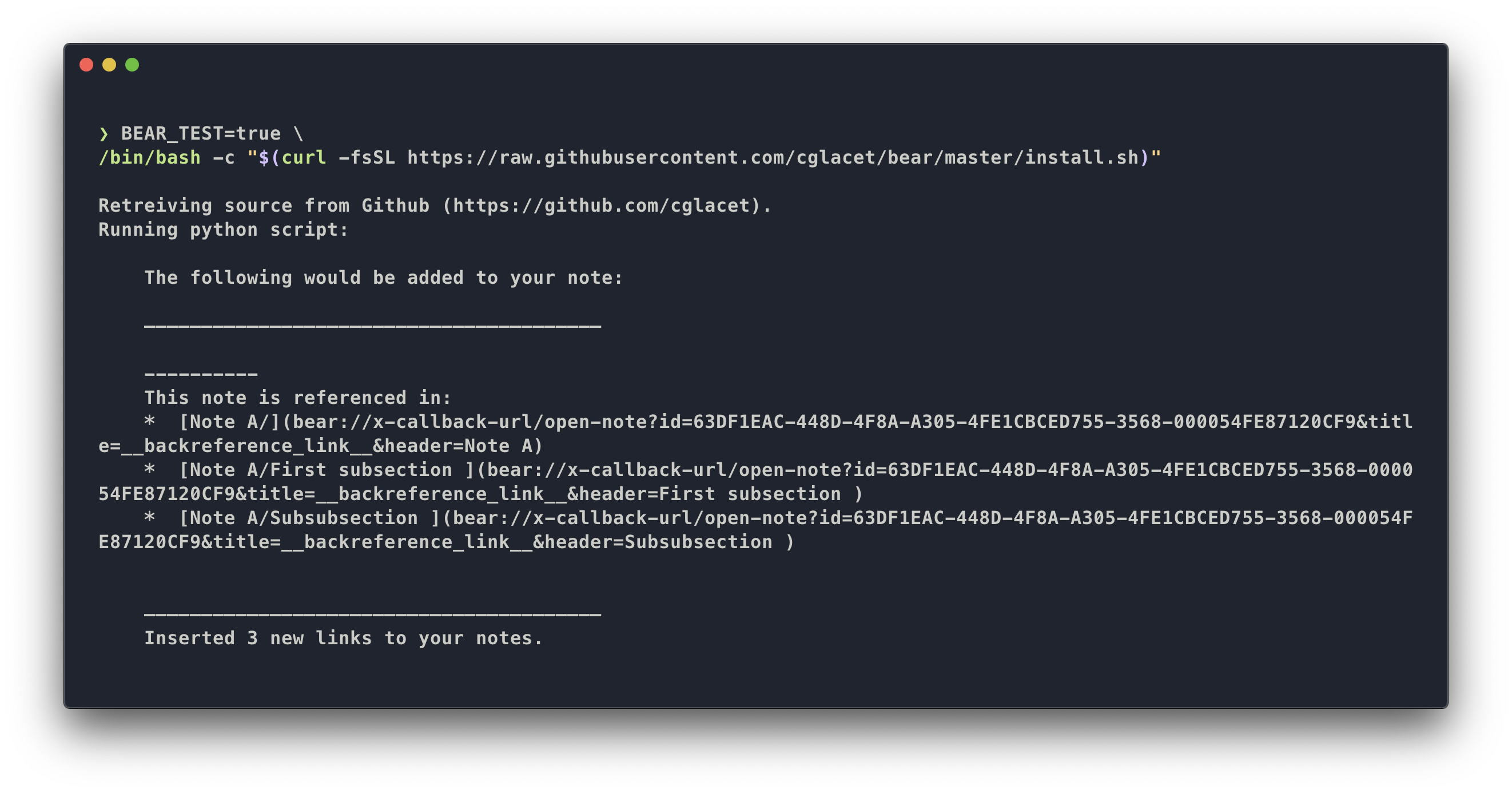
In test mode, nothing will happen to your notes. The script will only output what it would have
added to your notes directly in the terminal. To use the test mode, simply set BEAR_TEST=true
before running the script:
BEAR_TEST=true \
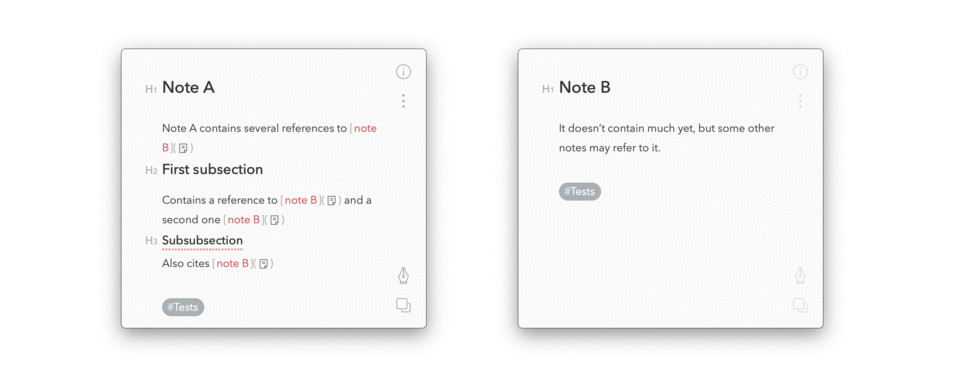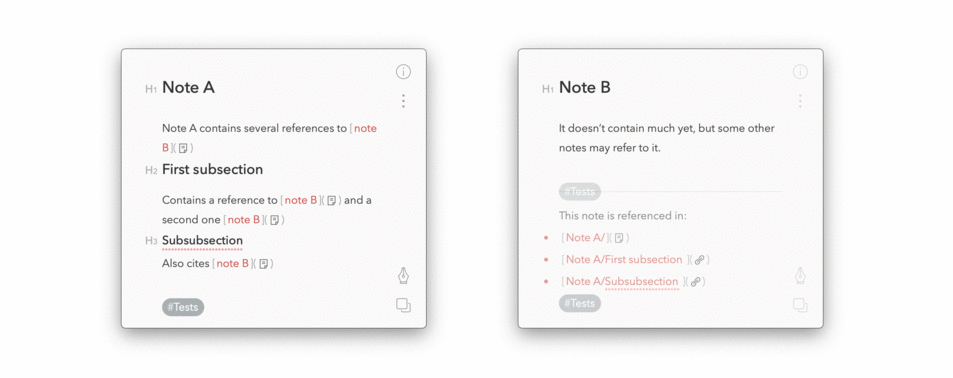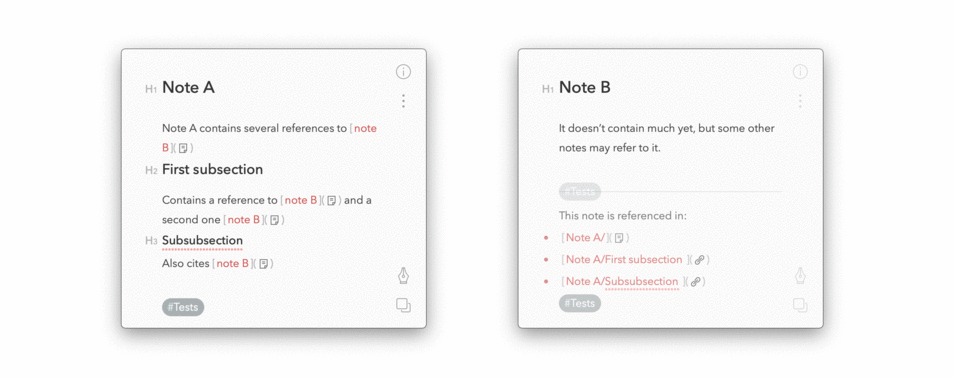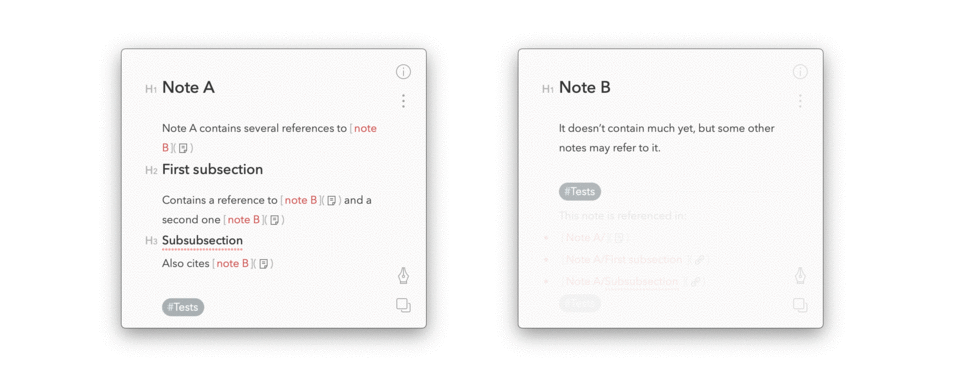
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cglacet/bear/master/install.sh)"The result will look like that:
You can set environment variables to modify the output of this program. By default the markdown produced for back-references is the following:
---
Non-referenced incoming links:
* [Title of the note](link-to-node)
* [Title of another note](link-to-another-node)For example if we need to modify the introduction text you just need to run:
BEAR_BACKREFERENCES_INTRO_TEXT="Liens entrants vers cette note :" \
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cglacet/bear/master/install.sh)"Which will render the following markdown:
---
Liens entrants vers cette note :
* [Title of the note](link-to-node)
* [Title of another note](link-to-another-node)If you need to have several options:
BEAR_BR_SECTIONS=false \
BEAR_BACKREFERENCES_INTRO_TEXT="# References" \
BEAR_BACKREFERENCES_SECTION="" \
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cglacet/bear/master/install.sh)"# References
* [Title of the note](link-to-node)
* [Title of another note](link-to-another-node)| environment variable | target/effect | default value |
|---|---|---|
BEAR_BACKREFERENCES_SEPARATOR |
separator | --- |
BEAR_BACKREFERENCES_INTRO_TEXT |
introduction text | This note is referenced in: |
BEAR_BACKREFERENCE_PREFIX |
prefix of each link | \n* |
BEAR_ROOT_SECTION_TEXT |
root section representation | / |
BEAR_BR_SECTIONS |
link back references to sections | true |
BEAR_TEST |
output text in terminal | false |
Since non developers may use this I wanted to have a single command to copy paste and make things as simple as possible for everyone. This is why this section doesn't come first. Get the latest version of this repository:
git clone git@github.com:cglacet/bear.git
cd bearIf you already cloned the repository you can just pull the latest version:
cd bear
git pull origin masterIn order to run the script you need python ≥ 3.6:
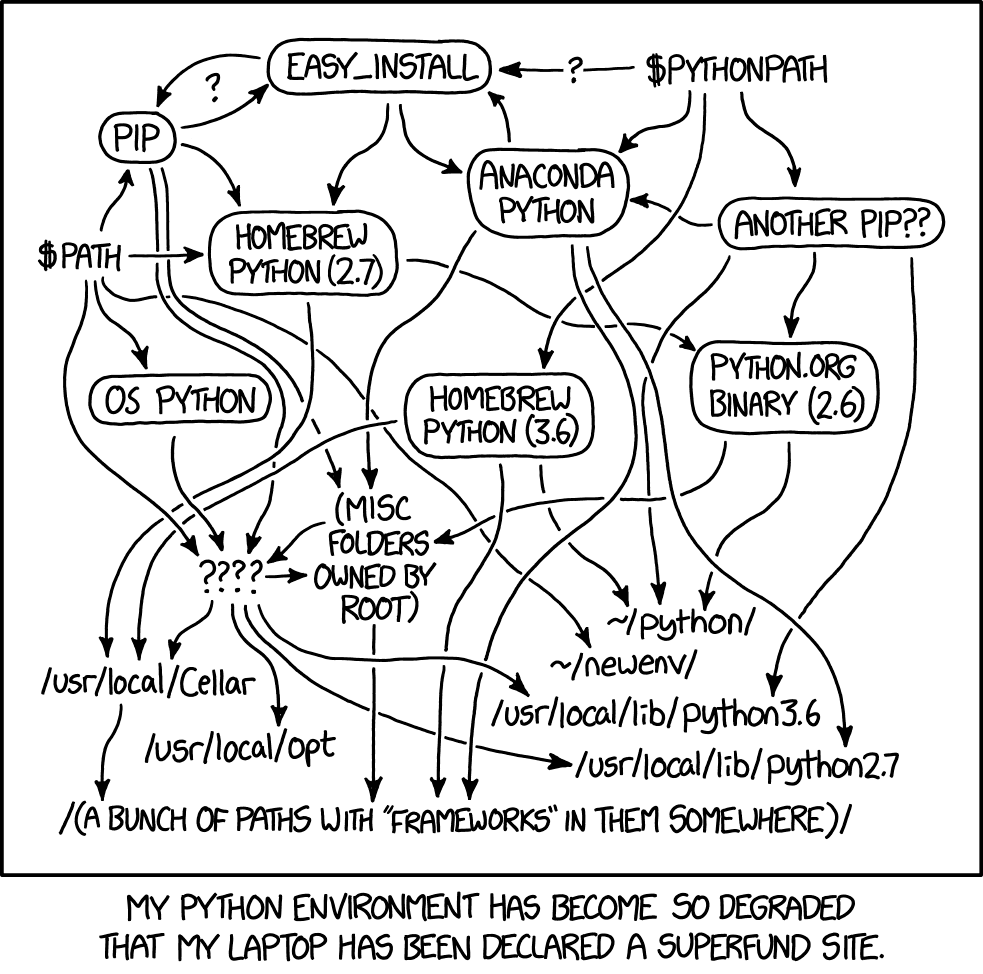
python --versionIf you version is older than 3.6 you will need to update it, and as this drawing shows, dealing with python versions is not really easy:
Therefore I would strongly advise using the amzing pyenv to deal with this mess for you:
brew install pyenv
pyenv install 3.7.7 # Install a more recent version of python (you can pick any version ≥ 3.6)
pyenv local 3.7.7 # Use that interpreter as the default one in the current directory (and only here)You can now run the script using the environment variables as documented before:
BEAR_TEST=true python insert_backreferences.pyInstead of using environement varaibles everytime, you can also directly edit the values you want to change in constants.py and config.py.
If you are a developer, maybe you can read the implementation notes. Also, any comment is welcome, feel free to open a new issue (even for discussions).