There is this Beat Sage map generator powered by AI that seems to be working well. The results looks fun.
Still, I was curious to see if it would be possible to generate maps through probabilities, based on observed patterns from existing maps.
The strategy was to take existing maps, break them into sequences (2 beats per sequence seems like a good balance), take note of which sequence follows which ones, and then randomly generate new maps based on these known patterns.
That worked well, kind of. What I noticed was that unless mappers reuses the same sequences of blocks, options for the "next sequence" will be quite limited to... the next sequence from that song.
This script end up actually reskining existing maps to new songs, which is still fun, but is far from original new sequences of beats.
The following code demonstrates the approach I took. The result is fun, and was an interesting exercise to understand how maps can be rendered.
In this example, I will use maps created by multipe mappers that I like to play and mainly because their maps tend to have a nice flow:
- Dee-Dee
- Nixie.Korten
- misterlihao
- Joetastic
- ... and some more.
Depending on the tracks that I downloaded from these mappers in my customLevels folder, the results will tend to be quite different. It's possible to train sequences on all maps in the customLevels by adding "" to the filtering list, but this will render inconsistent songs when there is a wide range of music style. Focusing on specific styles seems to work better.
Here are two examples of songs produced by this code:
- Big In Japan by Alphaville (first version, without lighting effects)
- Maria - I Like It Loud by Scooter
Beastsaber has excellent instructions explaining how to prepare an audio file for mapping.
At a high level, the following steps are necessary:
-
Software Setup: Download the necessary tools for mapping: an audio editor and a map editor.
-
Audio Setup: Set up your audio file, find and confirm the BPM, and export in OGG format.
- Adding 8 full beat before the song starts gives some time to see the first blocks comming
-
Editor Setup & Mapping: Set up your song in your mapping editor (we recommend MMA2) and get mapping! Review basic mapping practices before you start. Playtest your own work early and often.
<- This is where we can insert ourselves in the creation process
- Lighting: Review basic lighting information. Simple manual lighting is easier than you think!
Playtesting: Third-party playtesting via the BSMG Discord is highly recommended to get constructive feedback and to get past your own “map blindness.Release Your Map: Once your song has been mapped, lighted, and playtested you’re ready to release your song to the world on BeatSaver (it will mirror here to BeastSaber in a few minutes).
^ About the two last steps: the result will be quite random, and not worthy of standing along all the great work from real mappers.
# pip install -r requirements.txt
import json
import random
from os.path import exists
import os
import time
import copy
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.io.wavfile as wavfile
import math
import soundfile as sf
start_time = time.time()Location of the customeLevels and WIP levels, as well as the difficulty used for training
customLevels_folder = "/mnt/c/Program Files/Oculus/Software/Software/hyperbolic-magnetism-beat-saber/Beat Saber_Data/CustomLevels/"
customWIPLevels_folder = "/mnt/c/Program Files/Oculus/Software/Software/hyperbolic-magnetism-beat-saber/Beat Saber_Data/CustomWIPLevels"
assert exists(customLevels_folder) == True, f"customLevels folder {customLevels_folder} should exists"
assert exists(customWIPLevels_folder) == True, f"customWIPLevels folder {customWIPLevels_folder} should exists"For this, I am searching for folders in the customeLevels folder, and uses any song matching one of listed keywords
# MODIFY ME
difficulty = "ExpertStandard.dat"
# This is where I define filters for songs. Using the mapper's name works well
filters = ["dee", "nixie", "joetastic", "faded", "ge2toro", "nitronik", "misterlihao", "majorpickle"]While I define each functions used by this code, I will be using the first entry of the song queue for testing and demonstratation.
In reality, the mapping is done in two parts:
- Training on existing maps. This only needs to be done once
- Mapping of new songs.
For this last part, the code will be going through the song_queues variable defined in the next cell, and will map each of them.
The reason why I am doing this is that it makes it easier to add a new song to map, while still keeping the parameters of the files I mapped previously.
The difficulty is defined only once, so are the song used for training. Otherwise the code would need to retrain for each songs, which might be suitable if I want to use different style of maps as a template, but is quite time consuming if I am going to try to find the best match against the output audio.
The inconvenient of the current method is that if I train on maps that are inconsistent, so will be the output maps. It's likely that there will be super slow portions, followed by crazy fast sequences because of the sequences used for training.
# MODIFY ME
song_queues = [
{ "folder": "Alphaville - Big In Japan - 97.79", "first_beat": 16, "last_beat": 368 },
{ "folder": "Scooter - Maria (I Like It Loud)", "first_beat": 8, "last_beat": 510 },
{ "folder": "Vanilla Ice - Ice Ice Baby", "first_beat": 8, "last_beat": 505 },
{ "folder": "Les Rita Mitsouko - C'est comme ça", "first_beat": 8, "last_beat": 848 },
{ "folder": "Ramasutra - Marder", "first_beat": 34, "last_beat": 602 },
{ "folder": "Les Trois Accords - Bamboula", "first_beat": 8,"last_beat": 540},
]# probably ok to leave me unmodified
# uses two beats for one sequence of blocks
# longer sequences (ex.: 4) reduces the randomness since it reduces the potential possibility of
# chaining sequences
sequence_length = 2
# precision: break each beat in 8 parts. 1/8 of a beat. necessary for fast songs.
# having this too low could cause block overlay
precision = 16def get_list_map_files(customLevels_folder, filters):
filters_lower = [x.lower() for x in filters]
return sorted(list(set([
x for x in os.listdir(customLevels_folder)
if any(y in x.lower() for y in filters_lower)
])))
notes_files = get_list_map_files(customLevels_folder, filters)
assert len(notes_files) > 0, "There are no training files. check your `customerLevels_folder`, or your `filters` variable"
print('Number of songs used for training:', len(notes_files))
# notes_filesNumber of songs used for training: 78
def open_file_info(current, customWIPLevels_folder):
output_file = "{}/{}/{}".format(customWIPLevels_folder, current['folder'], difficulty)
output_info_dat_file = "{}/{}/Info.dat".format(customWIPLevels_folder, current['folder'])
assert exists(output_info_dat_file), f"info file should exists in the song_output_folder"
assert exists(output_file), f"output file {current['folder']}/{difficulty} should exist"
new_config = copy.copy(current)
with open(output_info_dat_file) as f:
song_key = "_songFilename"
bpm_key = "_beatsPerMinute"
song_file_key = "_songFilename"
info_dat = json.load(f)
song_file_name = info_dat[song_file_key]
audio_file = "{}/{}/{}".format(customWIPLevels_folder, current['folder'], song_file_name)
new_config['config'] = {
'output_file': output_file,
'output_info_dat_file': output_info_dat_file,
'info_dat': info_dat,
'song_key': song_key,
'bpm_key': bpm_key,
'song_file_key': song_file_key,
'song_file_name': song_file_name,
'audio_file': audio_file
}
return new_config
current1 = open_file_info(song_queues[0], customWIPLevels_folder)
# print("* checking that the song file exists in the song_output_folder")
assert exists(current1['config']['audio_file']), f"song file {current1['config']['info_dat']['song_file_key']} should exist"
# print("* checking that the _beatsPerMinute value is configured")
assert current1['config']['bpm_key'] in current1['config']['info_dat'].keys(), f"key {current1['config']['bpm_key']} should be in current1['config']['info_dat'].keys(): {current1['config']['bpm_key'] in current1['config']['info_dat'].keys()}"
assert current1['config']['info_dat']["_beatsPerMinute"] > 0.0, f"{current1['config']['bpm_key']} should have a value greater than zero: {info_dat[bpm_key]}"
# the info.dat file looks like this
current1['config']['info_dat']{'_version': '2.0.0',
'_songName': 'Big In Japan',
'_songSubName': '',
'_songAuthorName': 'Alphaville',
'_levelAuthorName': 'unknow',
'_beatsPerMinute': 97.79000091552734,
'_shuffle': 0,
'_shufflePeriod': 0.5,
'_previewStartTime': 12,
'_previewDuration': 10,
'_songFilename': 'song.ogg',
'_coverImageFilename': 'cover.jpg',
'_environmentName': 'PanicEnvironment',
'_songTimeOffset': 0,
'_customData': {'_contributors': [],
'_editors': {'MMA2': {'version': '4.8.4'}, '_lastEditedBy': 'MMA2'}},
'_difficultyBeatmapSets': [{'_beatmapCharacteristicName': 'Standard',
'_difficultyBeatmaps': [{'_difficulty': 'Expert',
'_difficultyRank': 7,
'_beatmapFilename': 'ExpertStandard.dat',
'_noteJumpMovementSpeed': 16,
'_noteJumpStartBeatOffset': 0,
'_customData': {'_editorOffset': 0,
'_editorOldOffset': 0,
'_warnings': [],
'_information': [],
'_suggestions': [],
'_requirements': []}}]}]}
ExpertStandard.dat is a JSON file, and contains multiple sections. The one that is interesting is the "_notes" section, which contains a long series of entries like the folowing:
sample_block = {
"_time" : 25.5,
"_lineIndex" : 3,
"_lineLayer" : 1,
"_type" : 1,
"_cutDirection" : 0
}The _time key identifies the beat where that specific entry will show up.
The following lines are a bit more cryptic, but here is a lookup table, and with which charactor I translate them when I flatten each block for processing.
Columns. translated by the idx directly
- _lineIndex: 0 "far left column"
- _lineIndex: 1 "center left column"
- _lineIndex: 2 "center right column"
- _lineIndex: 3 "far right column"
Layer. translated by the first column of letters on my keyboard
- _lineLayer: 0 "bottom" "z"
- _lineLayer: 1 "middle" "a"
- _lineLayer: 2 "top" "q"
Block type.
- _type: 0 "red" "r"
- _type: 1 "blue" "b"
- _type: 3 "bomb" "x"
Cut Direction. I don't have a numeric keypad on my keyboard, so I used the left secton to represent them.
- _cutDirection: 0 "up" w
- _cutDirection: 1 "down" x
- _cutDirection: 2 "left" a
- _cutDirection: 3 "right" d
- _cutDirection: 4 "up left" q
- _cutDirection: 5 "up right" e
- _cutDirection: 6 "down left" z
- _cutDirection: 7 "down right" c
- _cutDirection: 8 "all" s
The lighting track (_events key in the ExpertStandard.dat JSON file) is a lot more complex than the _notes track.
A single lighting event looks like this:
sample_light = {
"_time": 52.5,
"_type": 1,
"_value": 5,
}The pairs of _type and _value maps to specific conditions, which looks like this
A major difference with the blocks is that some of these lights are toggles. They will go on, and stay on until they are turned off, which makes it harder train on since a certain light might be turned off a few sequences later, completely out of context with when it was activated.
layer = "zaq"
colour = "rb?x"
cut_dir = "wxadqezcs"
lighting_type = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz1234567890ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
lighting_value = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz1234567890ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
def encode_block(note, light):
global layer, colour, cut_dir, lighting_type, lighting_value
seq = (
str(note["_lineIndex"])
+ layer[note["_lineLayer"]]
+ colour[note["_type"]]
+ cut_dir[note["_cutDirection"]]
)
if light != False:
seq = seq + lighting_type[light['_type']] + lighting_value[min(light['_value'], len(lighting_value)-1)]
else:
seq = seq + lighting_type[random.randint(0,5)] + lighting_value[0]
return seq
def decode_pattern(base, precision, seq):
global layer, colour, cut_dir
seqs = json.loads(seq)
outputs = []
for i in range(len(seqs)):
for j in range(len(seqs[i])):
outputs.append({
"_time": base+(i/precision),
"_lineIndex": int(seqs[i][j][0]),
"_lineLayer": layer.index(seqs[i][j][1]),
"_type": colour.index(seqs[i][j][2]),
"_cutDirection": cut_dir.index(seqs[i][j][3])
})
return outputs
def decode_lighting(base, precision, seq):
global lighting_type, lighting_value
seqs = json.loads(seq)
lights = []
for i in range(len(seqs)):
for j in range(len(seqs[i])):
lights.append({
"_time": base+(i/precision),
"_type": lighting_type.index(seqs[i][j][4]),
"_value": lighting_value.index(seqs[i][j][5])
})
return lights
assert encode_block(sample_block, sample_light) == "3abwbf", f"the output from encoding isn't matching expectations"
assert json.dumps(decode_pattern(sample_block['_time'], precision, '[["3abwbf"]]')) == json.dumps([sample_block]), f"decoded pattern isn't matching the original block"
assert json.dumps(decode_lighting(sample_light['_time'], precision, '[["3abwbf"]]')) == json.dumps([sample_light]), f"decoded pattern isn't matching the original block"def turnoff_lights(beat):
sequences = []
for i in [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 12, 13]:
sequences.append(
{
"_time": beat,
"_type": i,
"_value": 0
}
)
return sequencesdef count_patterns(sequence):
blocks = 0
for i in sequence:
blocks += len(i)
return blocks
def check_integrity(current):
global sequence_length
global precision
if len(current) == sequence_length * precision:
return True
print(f"failed: {len(current)} vs {sequence_length * precision}")
return False
def remember_patterns(track, sequence_length, precision, track_name = ""):
global following
global encoded_song
previous_pattern = ""
for i in range(len(track)):
if check_integrity(track[i]):
current_pattern = json.dumps(track[i])
if file not in encoded_song.keys():
encoded_song[file] = []
encoded_song[file].append(current_pattern)
if previous_pattern not in following.keys():
following[previous_pattern] = []
if count_patterns(track[i]) > 0:
following[previous_pattern].append(current_pattern)
previous_pattern = current_pattern
else:
print("current pattern failed the integrity test:", current_pattern)
raisedef read_track_file(base_folder, song_output_folder, difficulty_file):
filename = "{}/{}/{}".format(base_folder, song_output_folder, difficulty_file)
if exists(filename):
with open(filename) as f:
return json.load(f)
# print("( ) file '{}/{}' not found. skipping folder".format(song_output_folder, difficulty_file))
return False
def find_lighting_for_note(lightings, t):
for event in lightings:
if event['_time'] > t:
return False
elif event['_time'] == t:
return event
return False
def convert_json_to_patterns(file, sequence_length, precision, content):
if "_notes" not in content.keys() or "_events" not in content.keys():
# print("( ) this is a new song with arks:", file)
return False
first_note = math.floor(content["_notes"][0]["_time"])
last_note = content["_notes"][-1]["_time"]
nb_sequence = int(((last_note - first_note)) / sequence_length)+1
# print("(+) file: {}, first_note: {}, last_note: {}, precision: {}, nb_sequences: {}".format(
# file, first_note, last_note, precision, nb_sequence
# ))
# initializing an empty list that will keep track of the notes
track = [[[] for y in range(sequence_length * precision)] for x in range(int(nb_sequence))]
for note, block in enumerate(content["_notes"]):
index = int(block["_time"])
subindex = int((block["_time"] - index) * precision)
idx = (index - first_note) * precision + subindex
seq = idx//(sequence_length*precision)
pos = idx%(sequence_length*precision)
encoded = encode_block(block, find_lighting_for_note(content["_events"], block["_time"]))
try:
track[seq][pos].append(encoded)
except:
print(filename, note, seq, pos, idx, block)
raise
return track
def process_file(folder, file, difficulty, precision, sequence_length):
notes_json = read_track_file(folder, file, difficulty)
if notes_json != False:
track = convert_json_to_patterns(file, sequence_length, precision, notes_json)
if track != False:
remember_patterns(track, sequence_length, precision, file)This section goes through all training files and register transitions in the following global variable.
The encoded_song variable will contain the complete encoded songs. This is useful to find out which sequence comes from what maps later on.
following = {}
encoded_song = {}
for file in notes_files:
process_file(customLevels_folder, file, difficulty, precision, sequence_length)This sections is an attempt to naively detect variations in the song. Using these variations, we can compare them against potential following sequences of blocks, and see which one might be a better fit given the density of the noise.
def load_audio(audio_file):
audio_file_wav = audio_file + ".wav"
data, samplerate = sf.read(audio_file)
if not exists(audio_file_wav):
sf.write(audio_file_wav, data, samplerate)
Fs, aud = wavfile.read(audio_file_wav)
# once the audio file is processed, we don't need the wave file anymore.
if exists(audio_file_wav):
os.remove(audio_file_wav)
return (Fs, aud)
Fs, aud = load_audio(current1['config']['audio_file'])
assert Fs == 44100, f"Audio File ${current1['config']['audio_file']} converted to wave is not 44100hz"
assert len(aud) > 0, f"Audio extract is empty"
print(Fs, len(aud))44100 10313147
def get_rythme(current, Fs, aud):
song_bpm = current["_beatsPerMinute"]
rythme = {
'song_bpm': song_bpm,
'song_bps': song_bpm/60,
'song_spb': 60/song_bpm,
'sample_per_beat': int(Fs * 60/song_bpm),
'audio': aud[:,0] # select left channel only
}
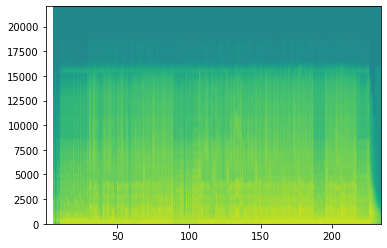
powerSpectrum, frequenciesFound, time_val, imageAxis = plt.specgram(rythme['audio'], Fs=Fs)
plt.show()
return rythme
rythme = get_rythme(current1['config']['info_dat'], Fs, aud)
assert rythme['song_bpm'] > 0, "Song bpm should be greater than 0"
assert rythme['sample_per_beat'] > 0, "sample_per_beat should be greater than 0"
assert len(rythme['audio']) > 0, "rythme['audio'] should contain the decoded audio track"
print(f"Folder: {current1['folder']}")
print(f"file: {current1['config']['song_file_name']}")
print(f"bpm: {rythme['song_bpm']}")
print(f"bps: {rythme['song_bps']}")
print(f"seconds per beat: {rythme['song_spb']}")
print(f"audio samples per beat: {rythme['sample_per_beat']}")/home/simon/.virtualenvs/py38/lib/python3.8/site-packages/matplotlib/axes/_axes.py:7553: RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in log10
Z = 10. * np.log10(spec)
Folder: Alphaville - Big In Japan - 97.79
file: song.ogg
bpm: 97.79000091552734
bps: 1.6298333485921224
seconds per beat: 0.6135596629335244
audio samples per beat: 27057
def get_audio_ranges(aud_left, sample_per_beat, precision):
positive_aud_left = [abs(x) for x in aud_left]
range3 = max(positive_aud_left)
range0 = range3 // 10
break_down = []
for beat in range(int(len(positive_aud_left)/sample_per_beat)):
for p in range(precision):
boundary_left = int((beat * sample_per_beat) + (p * (sample_per_beat/precision)))
boundary_right = int(boundary_left + ((p+1) * (sample_per_beat/precision)))
noise_left = int(np.mean(positive_aud_left[boundary_left:boundary_right]))
break_down.append(int(noise_left//range0))
return range0, range3, break_down
range0, range3, break_down = get_audio_ranges(rythme['audio'], rythme['sample_per_beat'], precision)
assert range0 > 0, "range0 should be greater than 0"
assert range3 > 0, "range3 should be greater than 0"
assert len(break_down) > 0, "the break_down variable should not be empty"def trim_audio(current, precision, Fs, aud):
rythme = get_rythme(current['config']['info_dat'], Fs, aud)
range0, range3, break_down = get_audio_ranges(rythme['audio'], rythme['sample_per_beat'], precision)
return break_down[current['first_beat']*precision:]
trimmed_intensity = trim_audio(current1, precision, Fs, aud)
assert len(trimmed_intensity) < len(break_down), "trimmed_intensity should be smaller than break_down"print('beginning...')
print(break_down[:current1['first_beat']*(precision)], '*', break_down[current1['first_beat']*precision:(current1['first_beat']*sequence_length*precision)])
print('...end')
print(break_down[-(current1['last_beat']*precision):current1['last_beat']], '*', break_down[-current1['last_beat']:])beginning...
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1] * [2, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 2, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
...end
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1] * [1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
The method used is trying to generate collisions between the audio intensity and potential candidates. The higher the number of collisions, the more likely the intensity should match.
At the same moment, we should be trying to find the sequence that better match the intensity of the audio, so the difference between the candidate and the intensity should be the lowest as possible.
Here is an example of audio intensity calculated earlier.
[3, 4, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2]
The candidate sequences are converted in number of blocks per step. One block = 1, 2 blocks (blue or red) = 2, etc.
[1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0]
[1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0]
[1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0]
[1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0]
[2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0]
[1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0]
By multiplying one array by the other, and calculating the sum of the results, we can get a amplitude value. By substracting the amplitude to the sequences from a candidate, we get a proximity score
The higher the value of sum(amplitude) - sum(proximity) should indicate a good match.
Here are three examples:
audio_sequence = [3, 4, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 2, 2]
bad_candidate = [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
best_candidate = [1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0]
good_candidate = [2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
def test_selection(audio_sequence, candidate):
a = np.array(audio_sequence)
c = np.array(candidate)
r = a * c
p = c - a
print('audio intensity:', a)
print('* candidate:', c)
print('* amplification of the result:', r)
print('* proximity of the amplitude:', p)
print('* sum of the results (score):', sum(r) - sum(p))
print('\n')
test_selection(audio_sequence, bad_candidate)
test_selection(audio_sequence, good_candidate)
test_selection(audio_sequence, best_candidate)
audio intensity: [3 4 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 2 2]
* candidate: [1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
* amplification of the result: [3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
* proximity of the amplitude: [-2 -4 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -1 -2 -2 -3 -3 -3 -2 -2]
* sum of the results (score): 41
audio intensity: [3 4 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 2 2]
* candidate: [2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
* amplification of the result: [6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
* proximity of the amplitude: [-1 -4 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -2 -3 -3 -3 -2 -2]
* sum of the results (score): 42
audio intensity: [3 4 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 3 3 2 2]
* candidate: [1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0]
* amplification of the result: [3 0 0 0 2 0 2 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 2 0]
* proximity of the amplitude: [-2 -4 -2 -2 -1 -2 -1 -2 -2 -2 -1 -3 -3 -3 -1 -2]
* sum of the results (score): 44
def find_origins(selected):
sources = []
for key in encoded_song.keys():
c = encoded_song[key].count(selected)
if c > 0:
if key not in sources:
sources.append(key)
return sources
def number_successors(candidates, array):
global following
counts = [0] * len(candidates)
for i, s in enumerate(candidates):
if array[s] in following.keys():
counts[i] = len(following[array[s]])
return counts
def add_bookmark(song, beat):
return {
"_time": beat,
"_name": song
}
def guess_origin(last_source, sources, known_sources):
if last_source not in sources:
most_likely_song = ""
most_likely_count = -1
for s in sources:
c = known_sources.count(s)
if c > most_likely_count:
most_likely_count = c
most_likely_song = s
return most_likely_songdef select(array, audio_sample):
best_fits = []
np_audio_sample = np.array(audio_sample)
for i, a in enumerate(array):
decoded = json.loads(a)
candidates = np.array([len(x) for x in decoded])
amplification = candidates[:len(np_audio_sample)] * np_audio_sample
proximity = candidates[:len(np_audio_sample)] - np_audio_sample
best_fits.append(sum(amplification) - sum(proximity))
candidates = [i for i in range(len(best_fits)) if best_fits[i] == max(best_fits)]
forward_checks = number_successors(candidates, array)
electables = [candidates[i] for i in range(len(candidates)) if forward_checks[i] > 0]
if len(electables) == 0:
elected = random.choice(candidates)
else: # this case happens when there is no candidate with a following sequence. the code will recover later
elected = random.choice(electables)
if False:
print(audio_sample)
print(elected)
print(len(array), max(best_fits), len(candidates), 'elected:', elected)
return array[elected]If it crashes here because the output file does not exists, you might need to generate it by added on random block to the level in MMA2, then save. The file isn't created until something is added to it.
def save_output(output_file, new_track, new_lights, new_bookmarks):
with open(output_file) as f:
output_song = json.load(f)
output_song["_notes"] = new_track
output_song["_events"] = new_lights
if "_customData" not in output_song.keys():
output_song[_customData] = {}
output_song["_customData"]["_bookmarks"] = new_bookmarks
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
f.write(json.dumps(output_song))This is where we generate the sequence of blocks.
The base is the first_beat, and it will continue to select sequences of blocks until it reaches the last_beat.
These two variables are defined at the top of the notebook, and need to be configured manually. They can be found by matching the beats to the audio in Mediocre Map Assistant 2 (MMA2). Since the loop generates sequences of sequence_length (normally 2 beats), it might be necessary to manually add or delete blocks at the end.
The loop starts by setting the current_pattern to blank, the code will select the opening sequences (based on the training songs) that better matches the current audio intensity.
The selected sequence will be checked against potential following sequences (variable following trained earlier). If somehow there is no known following sequence to the current_pattern, then the code will recover by selecting a new pattern from the opening ones.
print("Total Training Time: {:0.2f} seconds".format(time.time() - start_time))
def generate_seed(aud, filename, sample_per_beat):
seed = np.array(aud[len(aud)//len(filename)-sample_per_beat:len(aud)//len(filename)+sample_per_beat]).sum()
print(f"\trandom seed: {sample_per_beat} {seed}")
return seed
def extract_audio_sample(beat, precision, sequence_length, trimmed_intensity):
l = beat * precision * sequence_length
r = (beat+1) * precision * sequence_length
return trimmed_intensity[l:r]
for song in song_queues:
start_time = time.time()
match_stats = []
last_source = False
current_song = open_file_info(song, customWIPLevels_folder)
print(f"{current_song['folder']}")
Fs, aud = load_audio(current_song['config']['audio_file'])
trimmed_intensity = trim_audio(current_song, precision, Fs, aud)
random.seed(generate_seed(aud, current_song['folder'], rythme['sample_per_beat']))
base = current_song['first_beat']
current_pattern = ""
beat = 0
new_track = []
new_lights = []
new_bookmarks = []
while base < current_song['last_beat']:
audio_sample = extract_audio_sample(beat, precision, sequence_length, trimmed_intensity)
if current_pattern in following.keys():
pattern = select(following[current_pattern], audio_sample)
else:
pattern = select(following[""], audio_sample)
sources = find_origins(pattern)
if last_source not in sources:
most_likely_song = guess_origin(last_source, sources, match_stats)
new_bookmarks.append(add_bookmark(most_likely_song, base))
last_source = most_likely_song
match_stats = match_stats + sources
# add block patern to the new track
decoded = decode_pattern(base, precision, pattern)
new_track = new_track + decoded
# add the light pattern to the light track
decoded_light = decode_lighting(base, precision, pattern)
new_lights = new_lights + decoded_light
# update the current pattern
current_pattern = pattern
base += sequence_length
beat+=1
new_lights = new_lights + turnoff_lights(base)
new_bookmarks.append(add_bookmark("FIN", base))
save_output(current_song['config']['output_file'], new_track, new_lights, new_bookmarks)
print("\tOrigin of the sequences:")
for song in encoded_song.keys():
c = match_stats.count(song)
if c > 0:
print("\t\t{:3.1f}%: {}".format(c / len(match_stats) * 100, song))
print("\tBookmarks")
for b in new_bookmarks:
print('\t\tbeat {}: {}'.format(b['_time'], b['_name']))
print("\tSong rendering time: {:0.2f} seconds".format(time.time() - start_time))
Total Training Time: 23.43 seconds
Alphaville - Big In Japan - 97.79
random seed: 27057 -61481
Origin of the sequences:
52.5%: 22e63 (くうになる - misterlihao)
0.6%: 260d1 (えすけーぷ - misterlihao)
46.9%: 27ca5 (No Time - nitronik.exe)
Bookmarks
beat 16: 27ca5 (No Time - nitronik.exe)
beat 182: 22e63 (くうになる - misterlihao)
beat 368: FIN
Song rendering time: 7.32 seconds
Scooter - Maria (I Like It Loud)
random seed: 27057 11787999
Origin of the sequences:
42.6%: 27a7d (Calabria - DeeDee)
57.4%: 65c9 (Sweet Dreams (Are Made Of This) - Joetastic)
Bookmarks
beat 8: 65c9 (Sweet Dreams (Are Made Of This) - Joetastic)
beat 296: 27a7d (Calabria - DeeDee)
beat 510: FIN
Song rendering time: 6.84 seconds
Vanilla Ice - Ice Ice Baby
random seed: 27057 -344288
Origin of the sequences:
100.0%: 28efd (Contigo - Faded 99)
Bookmarks
beat 8: 28efd (Contigo - Faded 99)
beat 506: FIN
Song rendering time: 8.22 seconds
Les Rita Mitsouko - C'est comme ça
random seed: 27057 996495
Origin of the sequences:
8.1%: 1f767 (アリスブルー - misterlihao)
6.3%: 20fc6 (Horizon - Ge2toro)
1.6%: 21307 (ただ声一つ - misterlihao)
0.4%: 21333 (全部君のせいだ - misterlihao)
0.2%: 2142b (Graveyard Shift - Ge2toro)
0.2%: 21979 (フクロウさん - misterlihao)
24.4%: 250af (うらたねこ♀ - misterlihao)
0.4%: 2528b (おにけもだんす - misterlihao)
0.7%: 254a8 (感情ディシーブ - misterlihao)
24.6%: 27593 (推し変なんて許さない! - misterlihao)
19.7%: 27ca5 (No Time - nitronik.exe)
0.2%: 28c6b (Lean On Me - Faded 99)
1.3%: 28dfe (愛のモンスター - misterlihao)
11.9%: 65c9 (Sweet Dreams (Are Made Of This) - Joetastic)
Bookmarks
beat 8: 27593 (推し変なんて許さない! - misterlihao)
beat 228: 20fc6 (Horizon - Ge2toro)
beat 276: 1f767 (アリスブルー - misterlihao)
beat 278: 28dfe (愛のモンスター - misterlihao)
beat 286: 1f767 (アリスブルー - misterlihao)
beat 324: 27ca5 (No Time - nitronik.exe)
beat 500: 1f767 (アリスブルー - misterlihao)
beat 526: 250af (うらたねこ♀ - misterlihao)
beat 742: 65c9 (Sweet Dreams (Are Made Of This) - Joetastic)
beat 848: FIN
Song rendering time: 9.30 seconds
Ramasutra - Marder
random seed: 27057 -347426
Origin of the sequences:
0.3%: 205d1 (くうになる - misterlihao)
1.9%: 20fc6 (Horizon - Ge2toro)
1.0%: 21307 (ただ声一つ - misterlihao)
0.6%: 22846 (バニー - misterlihao)
0.3%: 22ee8 (Bones - Faded 99)
0.3%: 240f4 (Loco - Dee-Dee)
0.6%: 250af (うらたねこ♀ - misterlihao)
29.2%: 2528b (おにけもだんす - misterlihao)
1.3%: 254a8 (感情ディシーブ - misterlihao)
32.4%: 259b9 (La Funka - Majorpickle)
1.3%: 25a6b (Supersonic - Dee-Dee)
20.2%: 26408 (Grime Thing - nitronik.exe)
10.6%: 2923d (あの夏の旋律へ - misterlihao)
Bookmarks
beat 34: 22846 (バニー - misterlihao)
beat 36: 26408 (Grime Thing - nitronik.exe)
beat 160: 2528b (おにけもだんす - misterlihao)
beat 338: 259b9 (La Funka - Majorpickle)
beat 532: 2923d (あの夏の旋律へ - misterlihao)
beat 596: 20fc6 (Horizon - Ge2toro)
beat 602: FIN
Song rendering time: 9.27 seconds
Les Trois Accords - Bamboula
random seed: 27057 1304484
Origin of the sequences:
0.4%: 21333 (全部君のせいだ - misterlihao)
82.6%: 22e63 (くうになる - misterlihao)
0.4%: 24f18 (和音 - misterlihao)
0.7%: 260d1 (えすけーぷ - misterlihao)
15.9%: 270ed (WOW BB - DeeDee)
Bookmarks
beat 8: 22e63 (くうになる - misterlihao)
beat 454: 270ed (WOW BB - DeeDee)
beat 540: FIN
Song rendering time: 6.45 seconds
Obviously it will never match the quality of a talented mapper. Still, it's playable. More than everything, it was fun to code.