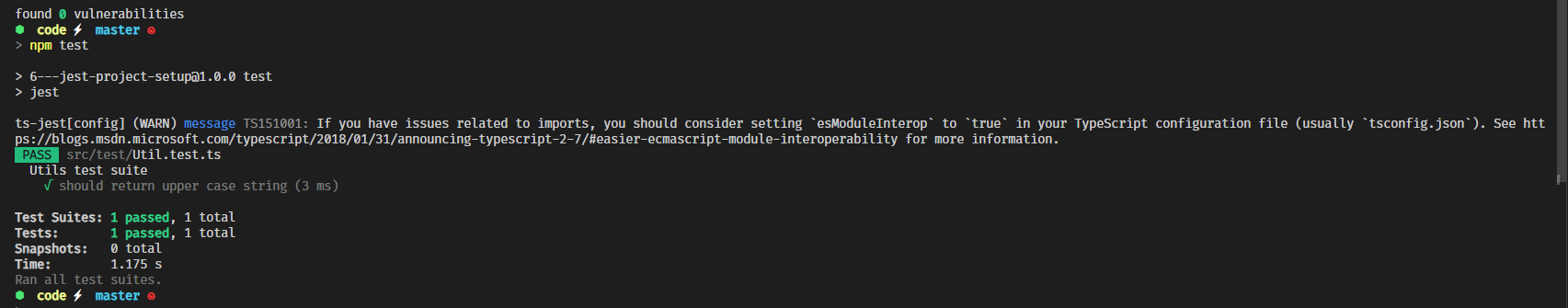
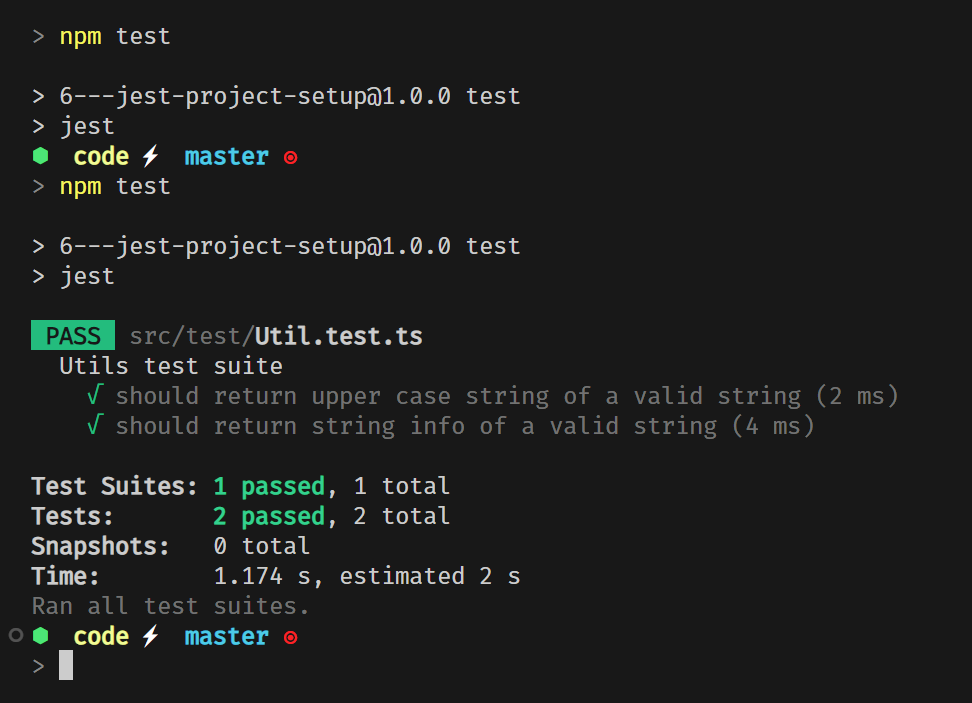
initiailize a project
npm init -yit will create a package.json file
{
"name": "6---jest-project-setup",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
let's install dev dependencies
npm i -D typescript jest ts-jest @types/jest ts-node
let's create the jest config file
npx ts-jest config:initlet's create a jest config file jest.config.ts
import type { Config } from '@jest/types';
const Config: Config.InitialOptions = {
preset: 'ts-jest',
testEnvironment: 'node',
verbose: true
};
export default Config;let's make a simple folder structure
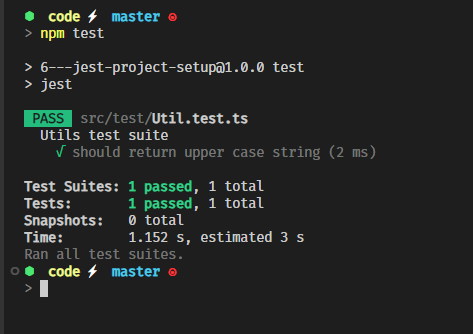
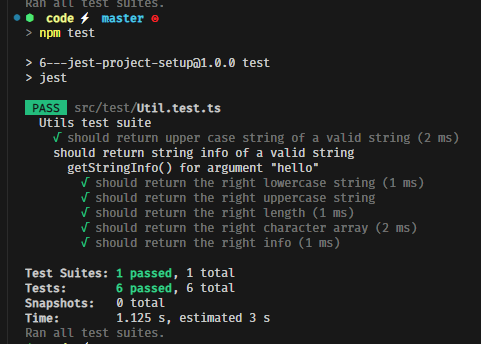
let's write a simple test
import { toUpperCase } from '../app/Util';
describe('Utils test suite', () => {
test('should return upper case string', () => {
const result = toUpperCase('hello');
expect(result).toBe('HELLO');
});
});and add the test script to package.json
"scripts": {
"test": "jest"
},we are getting a warning let's fix it
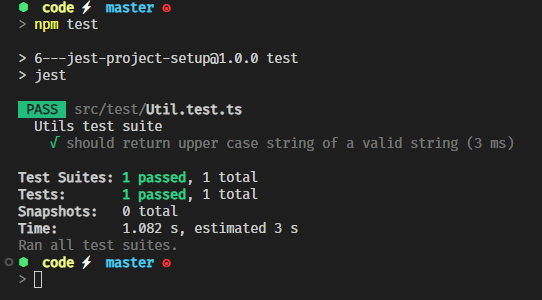
let's add typescript config file tsconfig.json
tsc --initnow the warning is gone
import { toUpperCase } from '../app/Util';
describe('Utils test suite', () => {
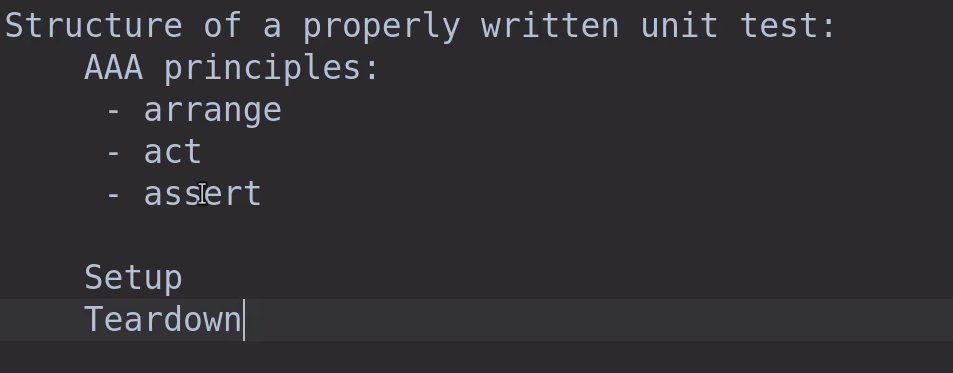
it('should return upper case string of a valid string', () => {
// arrange
const sut = toUpperCase;
const expected = 'HELLO';
// act
const actual = sut('hello');
// assert
expect(actual).toBe(expected);
});
});output
let's create a new function to test
export type TStringInfo = {
loweCase: string;
upperCase: string;
length: number;
character: string[];
extraInfo?: object;
};
export function getStringInfo(s: string): TStringInfo {
return {
loweCase: s.toLowerCase(),
upperCase: s.toUpperCase(),
length: s.length,
character: s.split('')
};
}to compare objects we can use toEqual matcher
to compare primitive types we can use toBe matcher
it('should return string info of a valid string', () => {
// arrange
const sut = getStringInfo;
const expected = {
loweCase: 'hello',
upperCase: 'HELLO',
length: 5,
character: ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']
};
// act
const actual = sut('hello');
// assert
expect(actual).toEqual(expected);
expect(actual.loweCase).toBe(expected.loweCase);
expect(actual.loweCase).toHaveLength(expected.length);
expect(actual.loweCase).toContain<string>('h');
// array
expect(actual.character).toEqual(expected.character);
expect(actual.character).toHaveLength(expected.length);
expect(actual.character).toContain<string>('h');
// when u don't know the order
expect(actual.character).toEqual(
expect.arrayContaining(['l', 'l', 'o', 'h', 'e'])
);
// object
expect(actual).toMatchObject({
loweCase: 'hello',
upperCase: 'HELLO',
length: 5,
character: ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']
});
expect(actual).toHaveProperty('length', 5);
expect(actual).toHaveProperty('character', ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']);
expect(actual).toHaveProperty('character', expect.arrayContaining(['h']));
expect(actual).toHaveProperty(
'character',
expect.not.arrayContaining(['a'])
);
expect(actual.extraInfo).toBeUndefined();
expect(actual).not.toHaveProperty('extraInfo');
expect(actual.extraInfo).not.toBeTruthy();
});output
the above test is a bit long let's refactor it
describe('should return string info of a valid string', () => {
const sut = getStringInfo;
// arrange
const expected = {
loweCase: 'hello',
upperCase: 'HELLO',
length: 5,
character: ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']
};
const actual = sut('hello');
describe('getStringInfo() for argument "hello"', () => {
it('should return the right lowercase string', () => {
expect(actual.loweCase).toBe(expected.loweCase);
expect(actual.loweCase).toHaveLength(expected.length);
expect(actual.loweCase).toContain<string>('h');
});
it('should return the right uppercase string', () => {
expect(actual.upperCase).toBe(expected.upperCase);
expect(actual.upperCase).toHaveLength(expected.length);
expect(actual.upperCase).toContain<string>('H');
});
it('should return the right length', () => {
expect(actual.length).toBe(expected.length);
});
it('should return the right character array', () => {
expect(actual.character).toEqual(expected.character);
expect(actual.character).toHaveLength(expected.length);
expect(actual.character).toContain<string>('h');
// when u don't know the order
expect(actual.character).toEqual(
expect.arrayContaining(['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'])
);
});
it('should return the right info', () => {
expect(actual.extraInfo).toBeUndefined();
expect(actual).not.toHaveProperty('extraInfo');
expect(actual.extraInfo).not.toBeTruthy();
});
});
});output
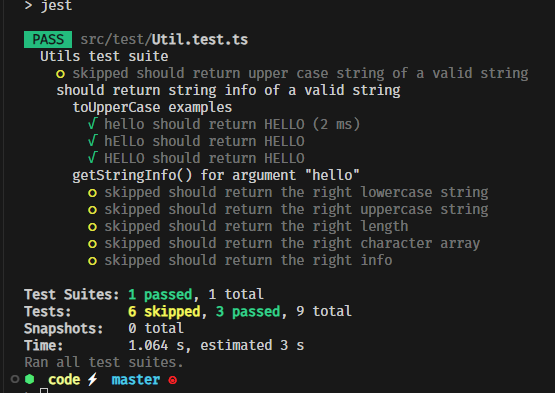
let's write a test for the following function
describe('toUpperCase examples', () => {
it.only.each([
{
input: 'hello',
expected: 'HELLO'
},
{
input: 'hElLo',
expected: 'HELLO'
},
{
input: 'HELLO',
expected: 'HELLO'
}
])('$input should return $expected', ({ input, expected }) => {
expect(toUpperCase(input)).toBe(expected);
});
});output
- by doing so we can test multiple cases with a single test
- reduce the number of tests
- improve readability
- improve maintainability
- improve test coverage
- and more
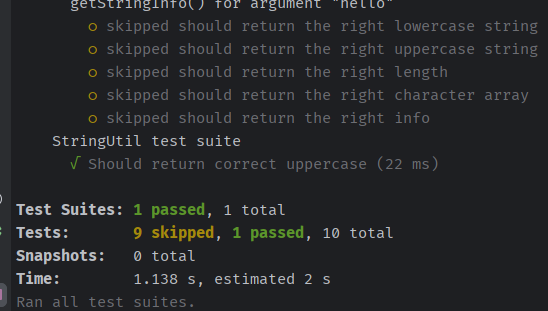
let's add a new class to test
export class StringUtil {
public toUpperCase(s:string){
return toUpperCase(s);
}
}let's write a test for it
describe.only("StringUtil test suite", () => {
let sut: StringUtil|null;
beforeEach(()=>{
console.log("beforeEach");
sut = new StringUtil();
});
afterEach(()=>{
console.log("afterEach");
sut = null;
});
it("Should return correct uppercase",()=>{
const expected = "HELLO";
// act
const actual = sut && sut.toUpperCase("hello");
// assert
expect(actual).toBe(expected);
})
});these hooks are called beforeEach and afterEach
and there context is relative to the place where they are defined.
let's thow an error in the toUpperCase function
export class StringUtil {
public toUpperCase(s:string){
if (!s){
throw new Error('Invalid input');
}
return toUpperCase(s);
}
}let's write a test for it
describe.only("StringUtil test suite", () => {
let sut: StringUtil|null;
beforeEach(()=>{
console.log("beforeEach");
sut = new StringUtil();
});
afterEach(()=>{
console.log("afterEach");
sut = null;
});
it("Should return correct uppercase",()=>{
const expected = "HELLO";
// act
const actual = sut && sut.toUpperCase("hello");
// assert
expect(actual).toBe(expected);
});
it("Should throw error for invalid input:1",()=>{
// arrange
const expected = "Invalid input";
// act
const actual = ()=>sut && sut.toUpperCase("");
// assert
expect(actual).toThrowError(expected);
});
it("Should throw error for invalid input function",()=>{
// arrange
function expectError() {
const actual = sut && sut.toUpperCase("");
}
// assert
expect(expectError).toThrow();
expect(expectError).toThrowError('Invalid input');
});
it("Should throw error for invalid input arrow function",()=>{
expect(()=>sut && sut.toUpperCase("")).toThrowError('Invalid input');
});
it("Should throw error for invalid input try catch block",(done)=>{
try {
sut && sut.toUpperCase("");
done("UpperCase method should throw error for invalid input");
}catch (e) {
expect(e).toBeInstanceOf(Error);
expect(e).toHaveProperty('message', 'Invalid input');
done();
}
});
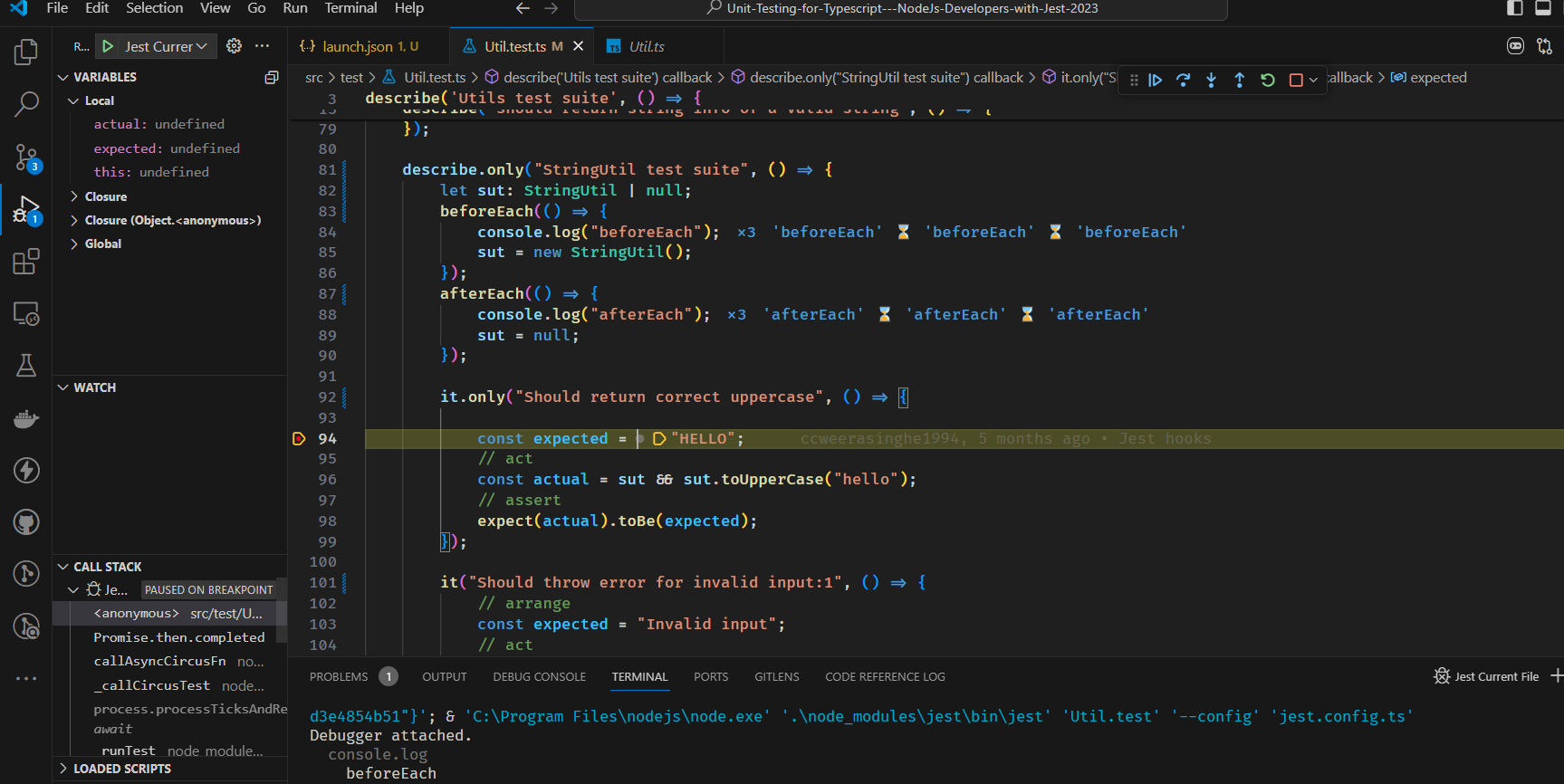
});xit - skip test xdescribe - skip suite
sit - skip test
we can add --watch to the test script in package.json
"scripts": {
"test": "jest --watch"
},doing so will run the tests in watch mode.
let's create a launch.json file.
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "node",
"request": "launch",
"name": "Jest Current File",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/node_modules/.bin/jest",
"args": [
"${fileBasenameNoExtension}",
"--config",
"jest.config.ts"
],
"console": "integratedTerminal",
"internalConsoleOptions": "neverOpen",
"disableOptimisticBPs": true,
"windows": {
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/node_modules/jest/bin/jest",
}
}
]
}then we can run debug.
import type { Config } from '@jest/types';
const Config: Config.InitialOptions = {
preset: 'ts-jest',
testEnvironment: 'node',
verbose: true,
collectCoverage: true,
collectCoverageFrom: [
'<rootDir>/src/app/**/*.ts',
],
};
export default Config;