This project explores advanced robotics, focusing on adaptive path planning in dynamic environments. The goal is to create a robot capable of real-time navigation and decision-making in settings with constantly changing obstacles and environmental factors. The challenge is developing an algorithmic solution for intelligent path adaptation under unpredictable conditions. This is crucial for applications like disaster response and industrial automation.
The project aims to develop a robust path-planning system for robots in dynamic environments using sophisticated models and algorithms that combine machine learning and spatial analysis.
- Integrates machine learning and spatial analysis to process sensory inputs and evaluate potential paths.
- Inputs: Real-time sensory data providing spatial information about the environment.
- Outputs: An evolving navigation path recalculated in response to sensory data.
- Implemented in Python using Gym, NumPy, and PyTorch.
DynamicObstaclesEnvandDynamicObstaclesEnvContclasses simulate dynamic environments.- Reinforcement learning models (DQN, PPO, A2C, and TD3) are trained with various hyperparameters.
- Uses a custom-built environment,
DynamicObstaclesEnv, with a grid setup. - Agent's Objective: Reach the goal while avoiding dynamically moving obstacles.
- Sensory Inputs: Grid representation indicating position, goal location, and obstacles.
- Q-Learning (Baseline): Establishes initial benchmarks; effective in discrete action spaces.
- Advantage Actor-Critic (A2C) (Advanced): Combines policy gradient and value-based methods; suitable for discrete and continuous action spaces.
- Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (TD3): Improves learning stability in continuous action spaces.
- Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO): Balances simplicity, performance, and stability.
- Learning Rate: Affects convergence speed and learning stability.
- Clip Range: Manages policy network updates in PPO.
- Batch Size: Influences stability and sample efficiency.
- DQN: -173.83 average reward, 0.07 success rate.
- PPO: 35.67 average reward, 0.72 success rate.
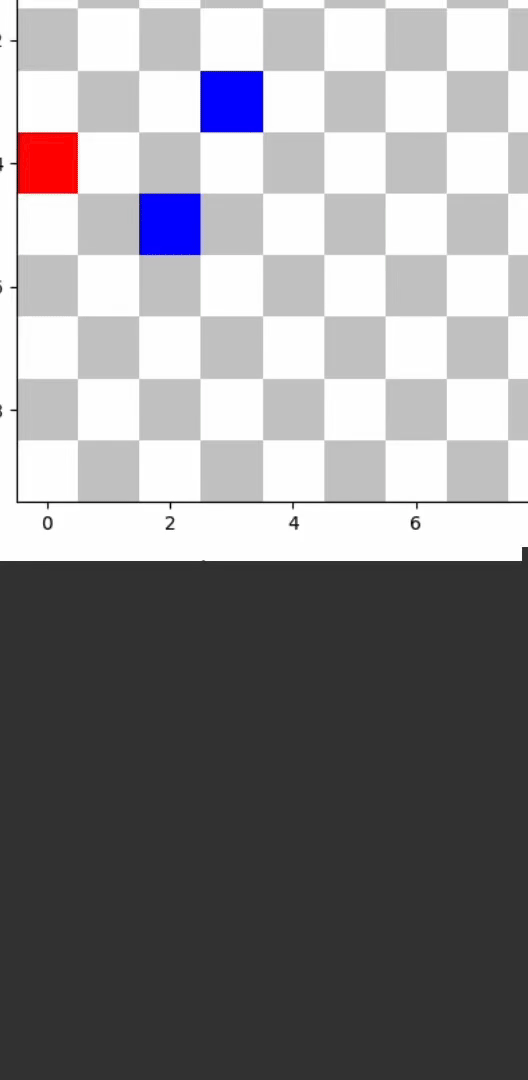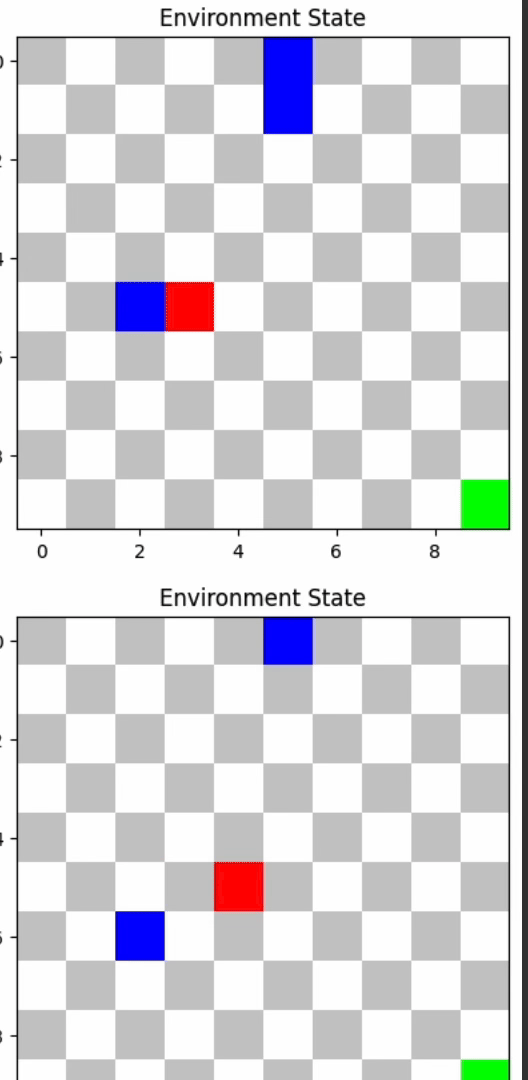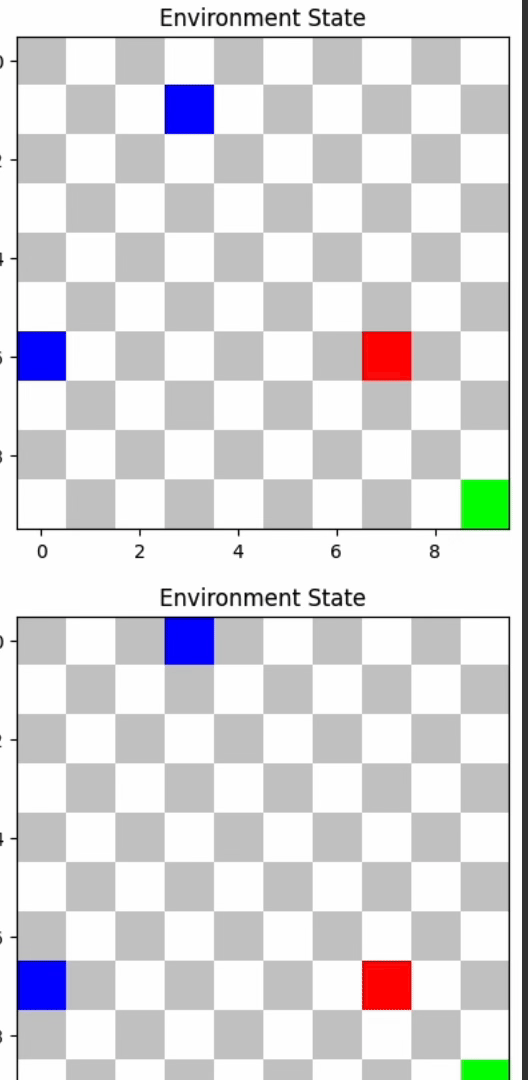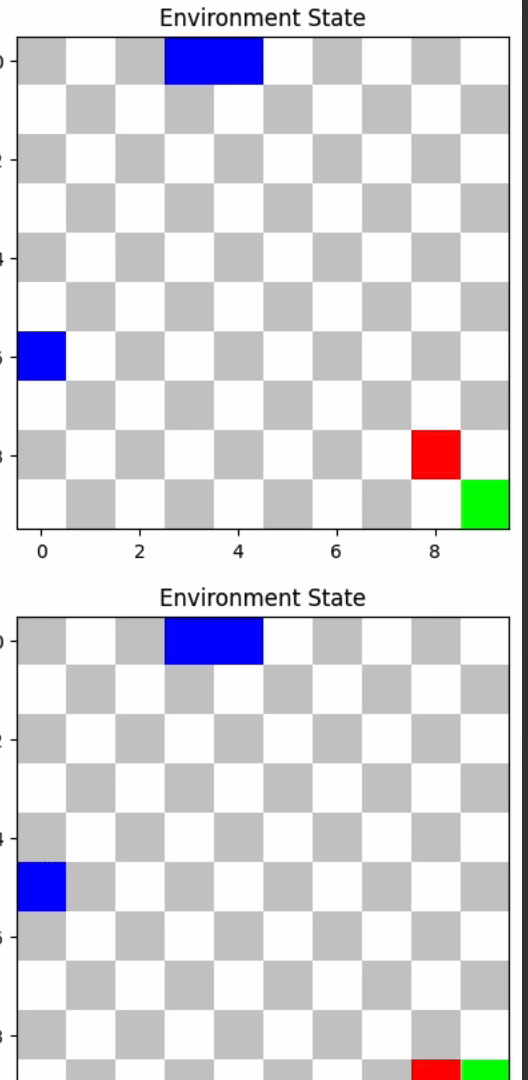
- A2C: 62.48 average reward, 0.
 86 success rate.
86 success rate. - TD3: 77.32 average reward, 0.91 success rate.
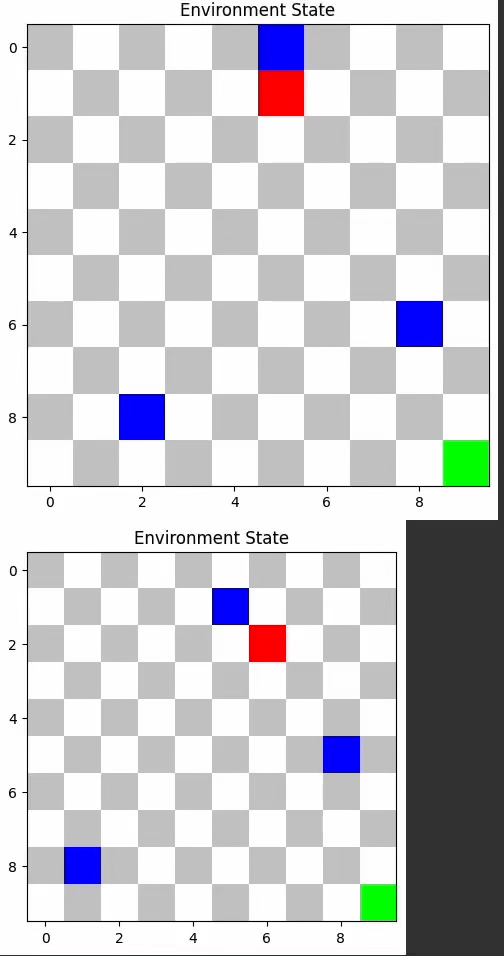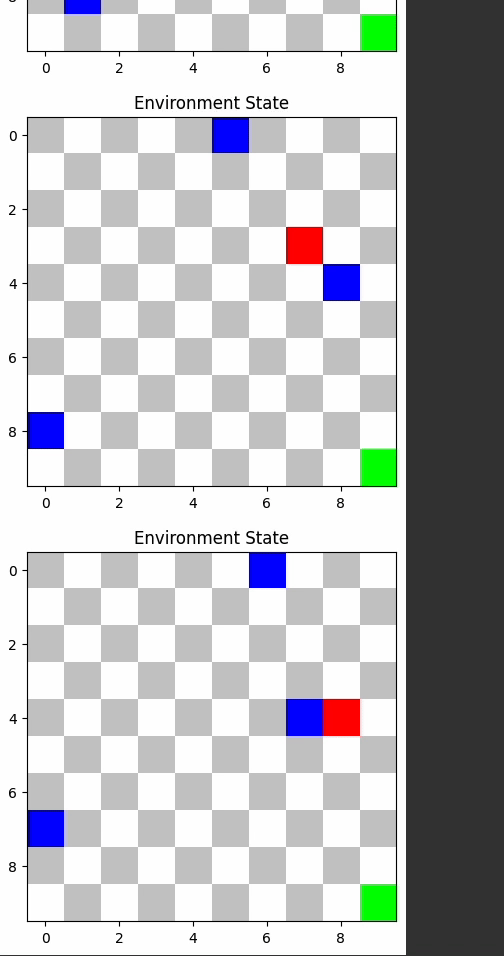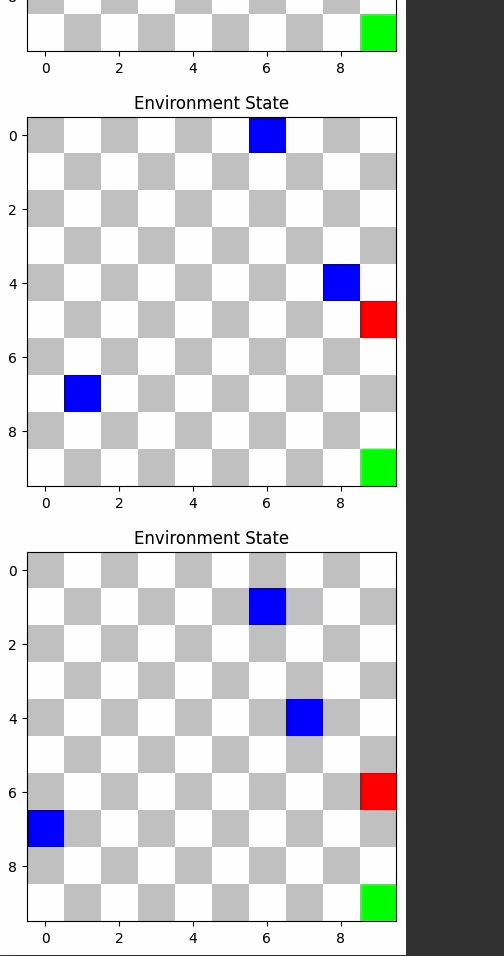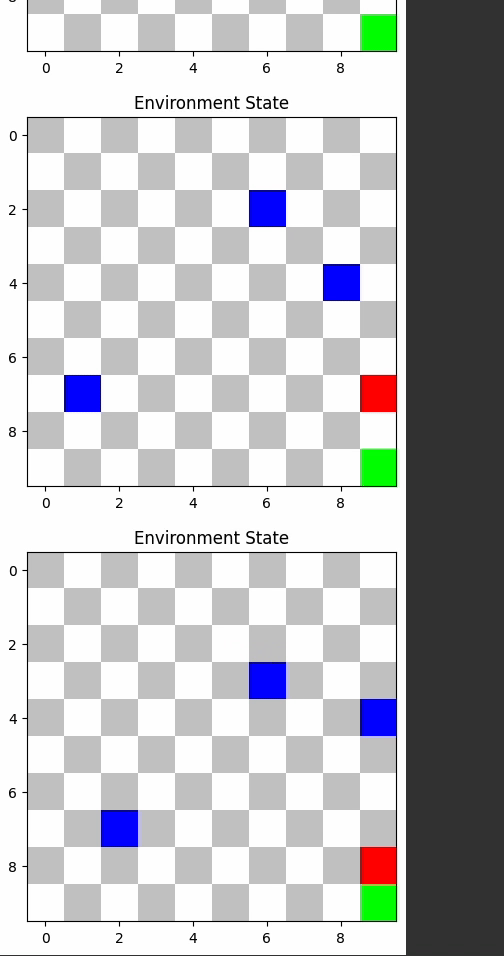
TD3 and A2C outperformed others, demonstrating their efficacy in dynamic environments.
TD3's advanced architecture, including twin Q-networks and policy smoothing, helped it excel. A2C's dual approach in policy and value estimation was also effective. PPO provided stable learning updates, while DQN struggled in complex scenarios.
Future work includes testing in more complex environments, integrating diverse sensory inputs, and enhancing algorithm adaptability.
Advanced reinforcement learning algorithms, particularly TD3, are more capable in dynamic path planning than basic models like DQN.
- Sutton, R. S., & Barto, A. G. (2018). Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction.
- Lillicrap, T. P., et al. (2016). Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning.