Welcome to the linux.conf.au Open Hardware Project. You can see information about this and other MiniConfs at http://www.openhardwareconf.org/wiki/Main_Page
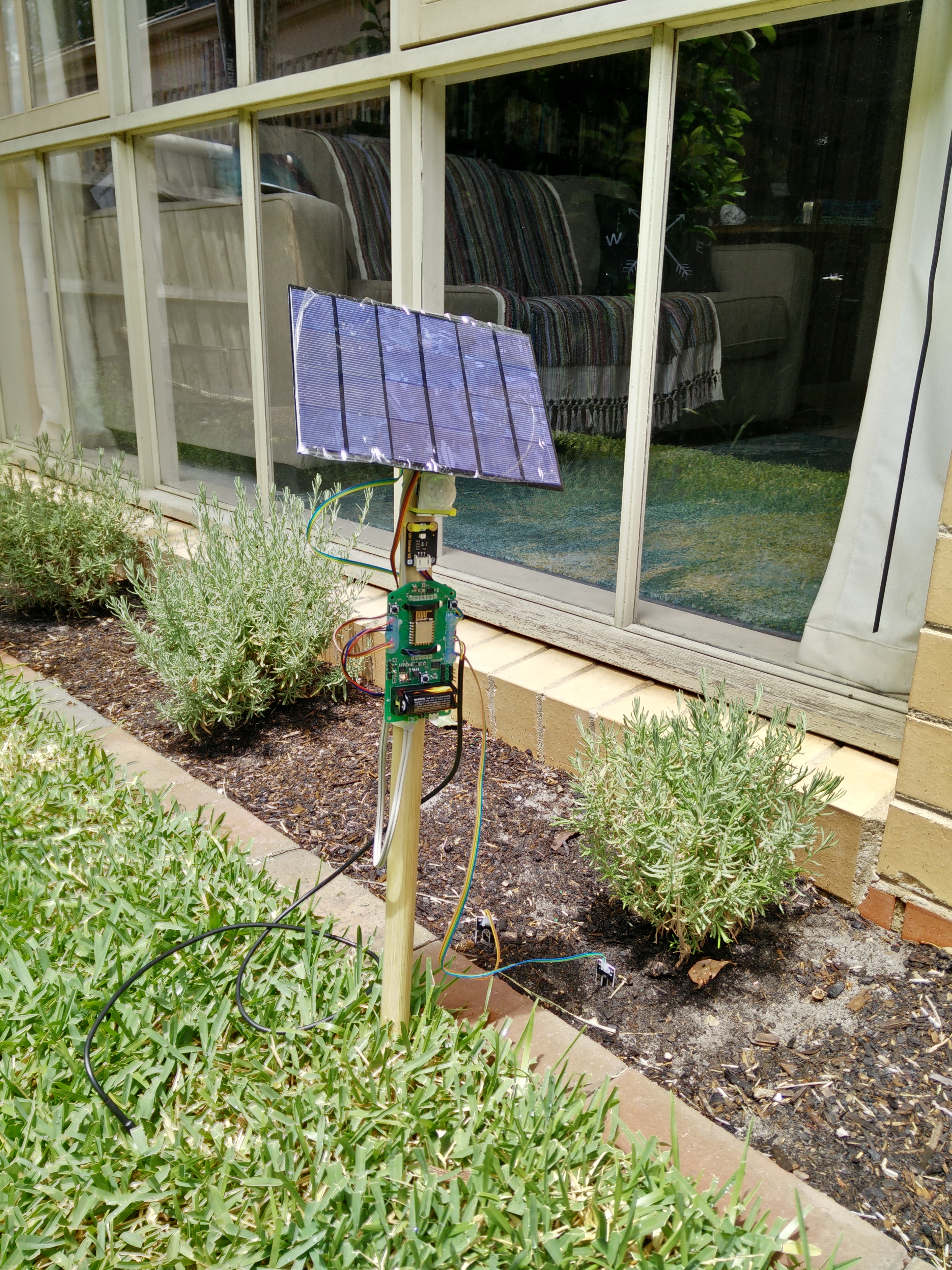
The ESPlant kit is designed to provide an open source platform to transmit environmental data to a central source using the power of wifi.
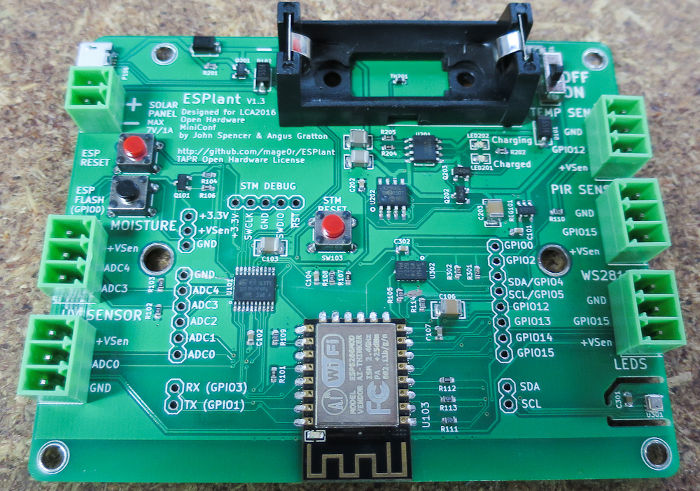
Assembled PCB:
Prototype board in action (before significant changes):
Check out a video of pick-n-placing components of the boards you'll be getting at LCA 2016. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=282qku2C4xo
- ESP8266 WiFi enabled microcontroller. You can program it via the Arduino IDE, or alternatively Espressif SDK or esp-open-rtos.
- Secondary microcontroller (STM32F042) acts as USB/Serial interface and i2c Analog to Digital Converter
- Battery holder for 16340 sized 3.7V lithium cell
- Lithium battery charger interface (solar input friendly)
- Board automatically switches power source between solar input, battery, and USB power as applicable.
- BME280 Temperature/Humidity/Barometric Pressure sensor
- ADXL345 accelerometer
- 2x soil moisture sensors (via ADC pins)
- DS18B20 connected to GPIO 12.
- PIR (infrared motion) sensor connected to GPIO 15.
- WS2812B LED strip connected to GPIO 13 (mislabelled as 15 on V1.3 PCB!)
The 3.3V "VSens" power rail is switchable on/off by the microcontroller. It defaults to unpowered (off). The GPIO to use is 14, and it is active low (ie driving the output low turns VSens on, driving it high turns it off).
To add ESP8266 support to the Arduino IDE (1.6.5 or newer), follow these instructions from the ESP8266 Arduino project.
To use the ESPlant with Arduino:
- No drivers required on Linux, OS X, or Windows 10.
- No manual reset or button pressing dance required to program.
- In ESP8266 Arduino IDE, under Tools menu, set Board to "NodeMCU V1.0" (fully compatible).
- Can set upload speed to 230400. 460800 works in most cases (you might get occasionl failures at 460800)
We recommend the following additional libraries for dealing with peripherals attached to ESPlant. All of these can be installed from inside the Arduino IDE under Sketch -> Include Library -> Manage Libraries
- Adafruit_BME280_Library - BME280 library by @adafruit.
- Adafruit_ADXL345 - ADXL345 library by @adafruit.
- Adafruit_NeoPixel - NeoPixel library by Adafruit.
... these libraries also rely on a common abstraction library that should also be installed
- Adafruit_Unified_Sensor_Driver - Adafruit Unified Sensor Driver
... for supporting WiFi and the MQTT client, there are additional libraries required. These are listed in the MQTTLogger README.
This project was designed by the 2016 linux.conf.au Open Hardware Team!
Made at hackmelbourne.org!
To the HackMelbourne (CCHS, http://hackmelbourne.org) community of Melbourne, Australia.
To all other open-source developers whose countless hours supported every other aspect of this design.
The specific terms of distribution of this project are governed by the license referenced below. Please contact the copyright owner if you wish to modify the board for distribution. Please utilize this design for personal or research projects. Please acknowledge all contributors.
Licensed under the TAPR Open Hardware License (www.tapr.org/OHL). The "license" sub-folder also contains a copy of this license in plain text format.
Copyright John Spencer, Angus Gratton, Andy Gelme, Jon Oxer 2015