eBPFSnitch
eBPFSnitch is a Linux Application Level Firewall based on eBPF and NFQUEUE. It is inspired by OpenSnitch, and Douane, but utilizing modern kernel abstractions, without a kernel module.
The eBPFSnitch daemon is implemented in C++ 20. The control interface is implemented in Python 3 utilizing Qt5.
Disclaimer
This is an experimental project. The security of this application has not been audited by a 3rd party, or even myself. There are likely mechanisms by which it could be bypassed. Currently the daemon control socket is unauthenticated, and an attacker could impersonate the user interface to self authorize.
Features
eBPFSnitch supports filtering all outgoing IPv4 based protocols (TCP / UDP / ICMP / etc). Filtering for IPv6, and incoming connections should be supported in the near future.
A core goal of this project is to integrate well with containerized applications. If an application is running in a container that container can be controlled independently of the base system or other containers.
Additionally targeting can occur against specific system users. Blanket permissions for every instance of Firefox for every user are not required.
Daemon Configuration
eBPFSnitch is configured via command line arguments. The available arguments
can be listed with --help:
eBPFSnitch Allowed options:
-h [ --help ] produce help message
-v [ --version ] print version
--remove-rules remove iptables rules
--group arg group name for control socket
--rules-path arg file to load / store firewall rulesControl socket authorization
The control interface and daemon communicate utilizing a Unix socket. By default
the socket can be accessed by any system user. It is recommended to associate
a specific group with the socket to limit access. For example --group='wheel'.
Firewall rule persistence
Firewall rules that are marked as persistent are stored on the filesystem in a
JSON encoding. By default the current working directory is used to store the
file rules.json. To specify a custom path use the --rules-path option.
System requirements
eBPFSnitch currently requires a recent kernel. The minimum supported version is Linux 5.8. This required version may be lowered in the future.
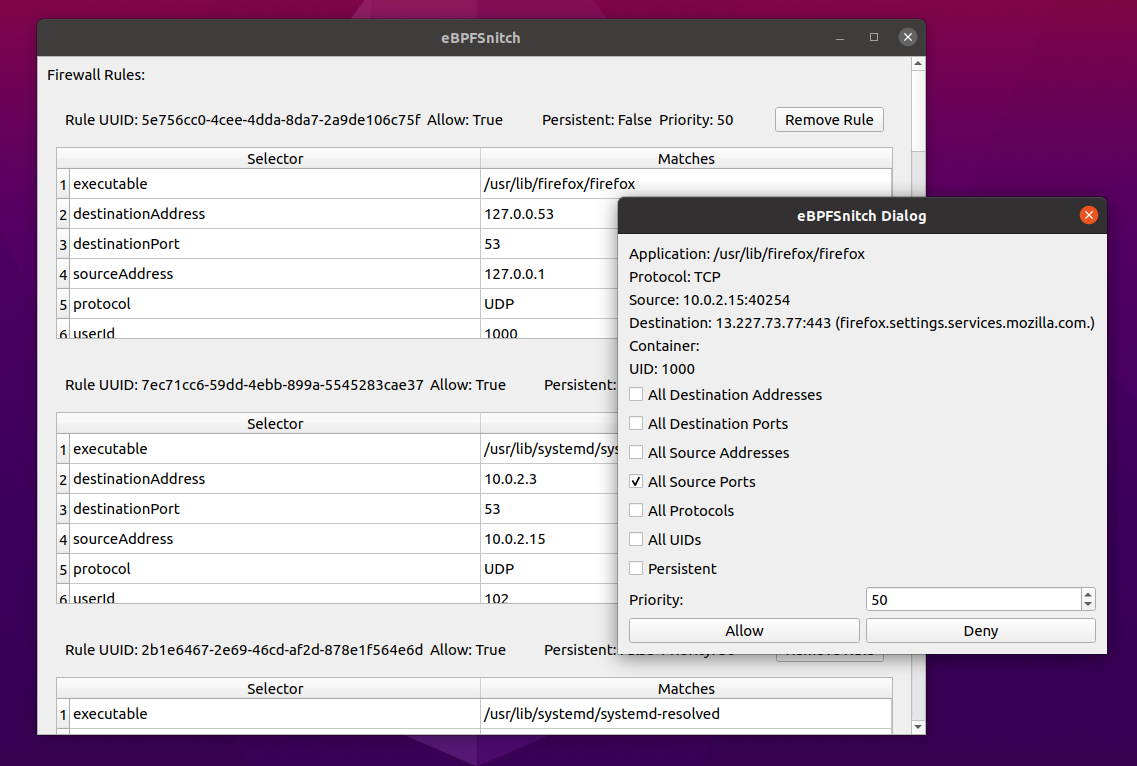
How firewall rules operate
Each rule is comprised of a set of clauses, and a verdict. Each clause matches a property of a packet to value. If every clause in a rule matches then the packet matches the rule, and the verdict for that rule is used (allow / deny).
Rules are sorted by a configured priority. Each rule is tried until a match is found, and a verdict can be determined. If no rule matches a packet the daemon will send a query to the interface which then displays a dialog asking to create a new rule to match that packet.
By default rules are not persisted to disk, and when the daemon restarts rules
will be lost. If through the dialog you check the persistent box, the new rule
will be saved to disk, and be active when the daemon is restarted.
Dependencies
C++: pthread, libbpf, netfilter_queue, spdlog, fmt, nfnetlink, boost, libmnl
Python: PyQT5
Compilation and quick start instructions
Installing dependencies on Arch
sudo pacman -S clang cmake bpf libnetfilter_queue spdlog boost libmnl \
nlohmann-json python3 python-pyqt5 Installing dependencies on Ubuntu 20.10 (minimum version)
sudo apt-get install cmake clang libboost-all-dev libspdlog-dev \
libnetfilter-queue-dev libmnl-dev linux-tools-common nlohmann-json3-dev \
libbpf-dev linux-tools-generic python3 python3-pyqt5Setting up the daemon
From the eBPFSnitch repository directory:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo ./ebpfsnitchStarting the GUI
From the eBPFSnitch repository directory:
cd ui
python3 main.py