Boilerplate Android Project with MVVM & Jet Compose
This project is a Android app of Boilerplate that building by Kotlin.
- Always think about the million users are using this app, so it must be the World Class app
- Coding is not just feature done, it's the reflection of success
- To get the best quality, must have the best solution
- Always think about & follow up SOLID principal for every solutions
- Naming is VERY VERY IMPORTANT, it's not coding, it's solution
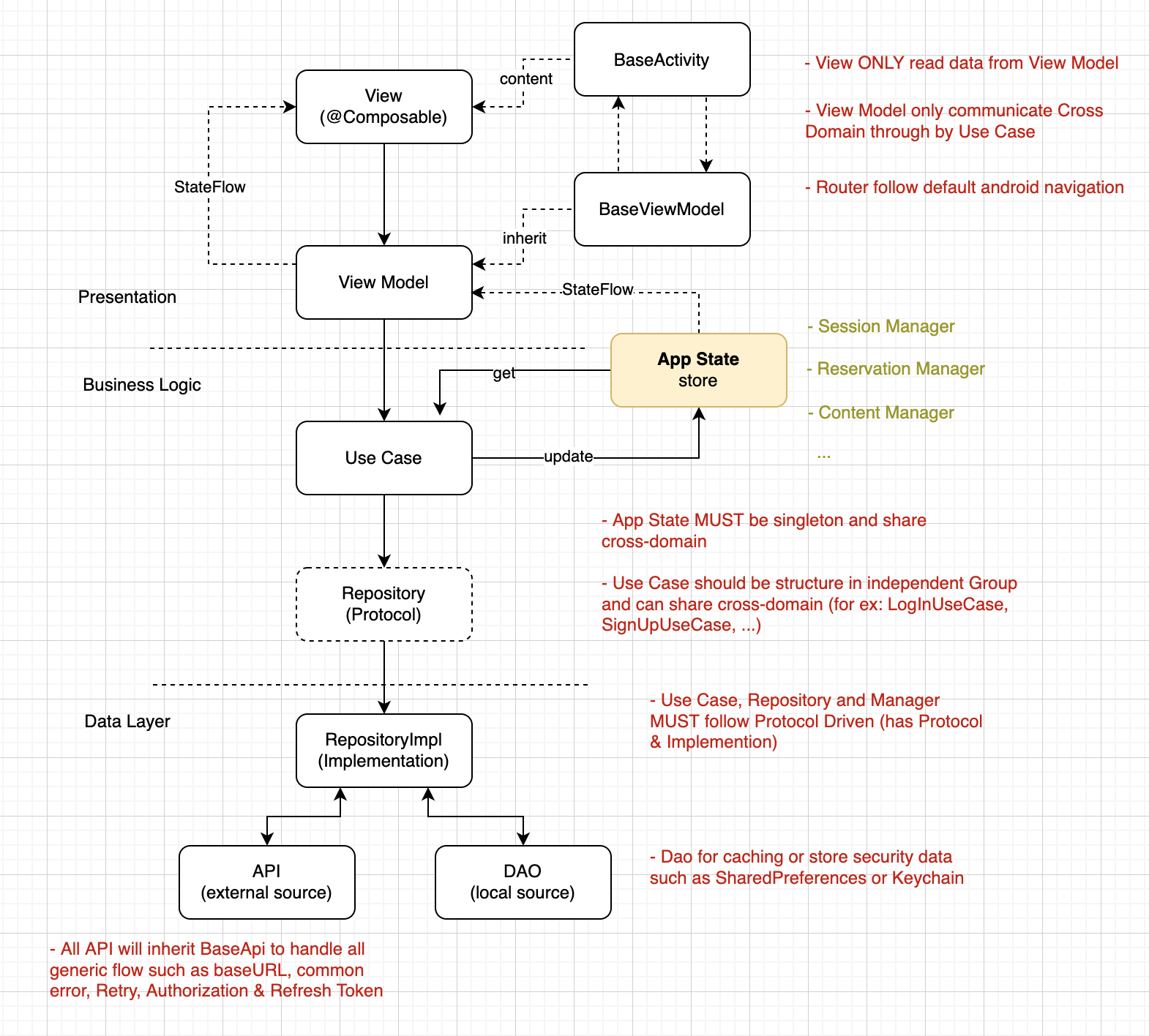
Apply Clean Architecture + MVVM
|----------------- Layers ------------------|
| Presentations | Business Logic | Data Layer |
|:-------------------------------------------:|
|-------------------------- Actual ---------------------------|
| Presentations | Business Logic | Data |
|:-------------------------------------------------------------:|
| View <--> ViewModel <--> UseCase <--> Repository <--> API/Dao |
|:-------------------------------------------------------------:|
|:---- Extension Entity ----|---- Basic Entity --------:|
|:-------------------------------------------------------------:|
- This is the major view layer of Android app and is categorized by module (feature or epic).
- View is built by Kotlin
- View is rendered based on the data from ViewModel
- View that are used across module will be placed in CommonUI folder and MUST NOT build based on ViewModel.
Examples of a standard view that build based on view-model:
@Composable
fun ContactDetailScreen(
viewModel: ContactDetailViewModel
) {
val contact = viewModel.getContact()
if (contact is Contact) {
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(horizontal = 32.dp),
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally
) {
Text(text = contact.fullName())
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(32.dp))
Avatar(imageUrl = contact.avatar, sizeInDp = 92F)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(32.dp))
PrimaryButton(
onClickListener = {
}
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.height(32.dp))
}
} else {
Box(
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center,
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize() ){
Text("Not found contact with id = ${viewModel.contactId()}")
}
}
}- It aims to handle business logic for a specific view such as validation, retrieve data, ...
- ViewModel uses use-case to retrieve data or handle domain business logic
- ViewModel observes AppState data to get application state
and provide ViewModel into View in Activity:
override fun viewModelBuilder(): ViewModelProvider.Factory {
return viewModelFactory {
ContactDetailViewModel(
contactId = contactId,
contactManager = AppState.instance.contactManager()
)
}
}- It's the main layer to handle all data business
- It's a stateless layer, so it will be constructed on demand
- A use-case usually handle one use-case of a specific epic
- A use-case can communicate with other use-cases
- All use-case MUST be defined with an interface (abstract class), use-case communicate with view-model through by the interface
- Constructor in UseCases class (DI class)
class UseCase {
companion object {
fun loadContactListUseCase() : LoadListUseCase<Contact> {
return LoadContactListUseCaseImpl(
contactManager = AppState.instance.contactManager(),
contactRepository = Repository.instance.contactRepository()
)
}
}
}- It's singleton that stores all application state
- Each kind of state-manager is accessed through by protocol
class AppState {
companion object {
val instance = AppState()
}
private lateinit var contactManagerInstance: ContactManager
fun contactManager(): ContactManager {
if (::contactManagerInstance.isInitialized) {
return contactManagerInstance
}
contactManagerInstance = ContactManagerImpl()
return contactManagerInstance
}
}- It's imported from local library project name Repository
- The main data source of app that is used by service layer
- It's a stateless layer, so it will be constructed on demand
- It contains a little bit business rules to branch data source that should be used, from client or dao
- It also handle the caching logic rules, from memory or local storage
- All repositories MUST be defined with an interface (abstract class), service communicate with repository through by the interface
- Constructor in Repository class (DI class)
class Repository {
companion object {
val instance = Repository()
}
// repository
fun contactRepository(): ContactRepository {
return ContactRepositoryImpl(
contactApi = contactApi()
)
}
// api
fun contactApi(): ContactApi {
return ContactApiImpl()
}
}- It's data source layer, client means data is from RestFul API and Dao means data is from local storage
- BaseAPI is advanced class to handle all generic calling API, retry when access token is expired and need to refresh, also for general API error handling
- BaseDao is advanced class to handle the generic storage, save/get list or item, or even for a string or an integer
- All APIs & Dao MUST be defined with an interface (abstract class), repository communicate with api/dao through by the interface
- It covers all entities in app
- Have 2 kind of models, basic entity and extension entity.
- Basic entity is belong to repository, it defines all entity's properties and support basic parsing with JSON
- Extension entity is belong to UI layer, it defines all utility methods of an entity
- There are 3 kinds of class to support construct instance for DI, AppState, UseCases and Repository
- AppState provide the instance of State-Manager
- UseCases is a singleton class that provide the instance of use-case.
- Repository is a singleton class that provide the instance of repository, api & dao
Here is list all of key folders or files in code structure:
.
|-- boilerplate-mvvm-jet-compose
| |-- app
| | |-- use_case *all use case that need in project*
| | |-- app_state *all app state that need in project*
| | |-- theme *includes Design Tokens to manage all Styles such as font, size, color, spacing
| | |-- ui *define all ui modules & theme*
| | | |-- modules *define all UI Views & ViewModel that categorized by module*
| | | |-- theme *define all theme styles*
|-- repository
| |-- main
| | |-- Api *define all api classes*
| | |-- Dao *define all dao classes*
| | |-- Enum *define all enum*
| | |-- Model *define all basic entities*
| | |-- Repository *define all repository classes*
| | |-- Repository.kt *Repository class, singleton class that support DI for data layer*
| |-- test *unit testing for repository (Repository, Dao, API, ...), require testing for repository only*
Navigate by default android navigation by Intent & Activity
val intent = Intent(context, ContactDetailActivity::class.java)
intent.putExtra("contactId", it.id)
context.startActivity(intent)- All ViewModels MUST have unit testing for all Events and StreamSubscriptions, except static constructor.
- All UseCases MUST have unit testing for all public methods.
- All Repositories MUST have unit testing for all public methods.
- Support logging for 6 standard levels of logs, here is lists (order by the priority of log)
- fatal: for any issues that kill the app or business
- error: for any exception that the app catch
- warning: for any potential error, invalid data or unexpected value that cause lead to error
- info: for log actions or events from end-user
- debug: for debug purpose and will not see in production, only see in development or testing mode
- trace: for tracking in order to identify bugs, do not keep it when bug is resolved
- The logging level for each environment will be set in .env files
- The Log class is a singleton and be able to get from singleton instance of Common class