tfjs-vis
tfjs-vis is a small library for in browser visualization intended for use with TensorFlow.js.
It's main features are:
- A set of visualizations useful for visualizing model behaviour
- A set of high level functions for visualizing objects specific to TensorFlow.js
- A way to organize visualizations of model behaviour that won't interfere with your web application
The library also aims to be flexible and make it easy for you to incorporate custom visualizations using tools of your choosing, such as d3, Chart.js or plotly.js.
Demos
Installation
You can install this using npm with
npm install @tensorflow/tfjs-vis
or using yarn with
yarn add @tensorflow/tfjs-vis
You can also load it via script tag using the following tag, however you need to have TensorFlow.js also loaded on the page to work. Including both is shown below.
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow/tfjs"> </script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@tensorflow/tfjs-vis"></script>
Building from source
To build the library, you need to have node.js installed. We use yarn
instead of npm but you can use either.
First install dependencies with
yarn
or
npm install
Then do a build with
yarn build
or
npm run build
This should produce a tfjs-vis.umd.min.js file in the dist folder that you can
use.
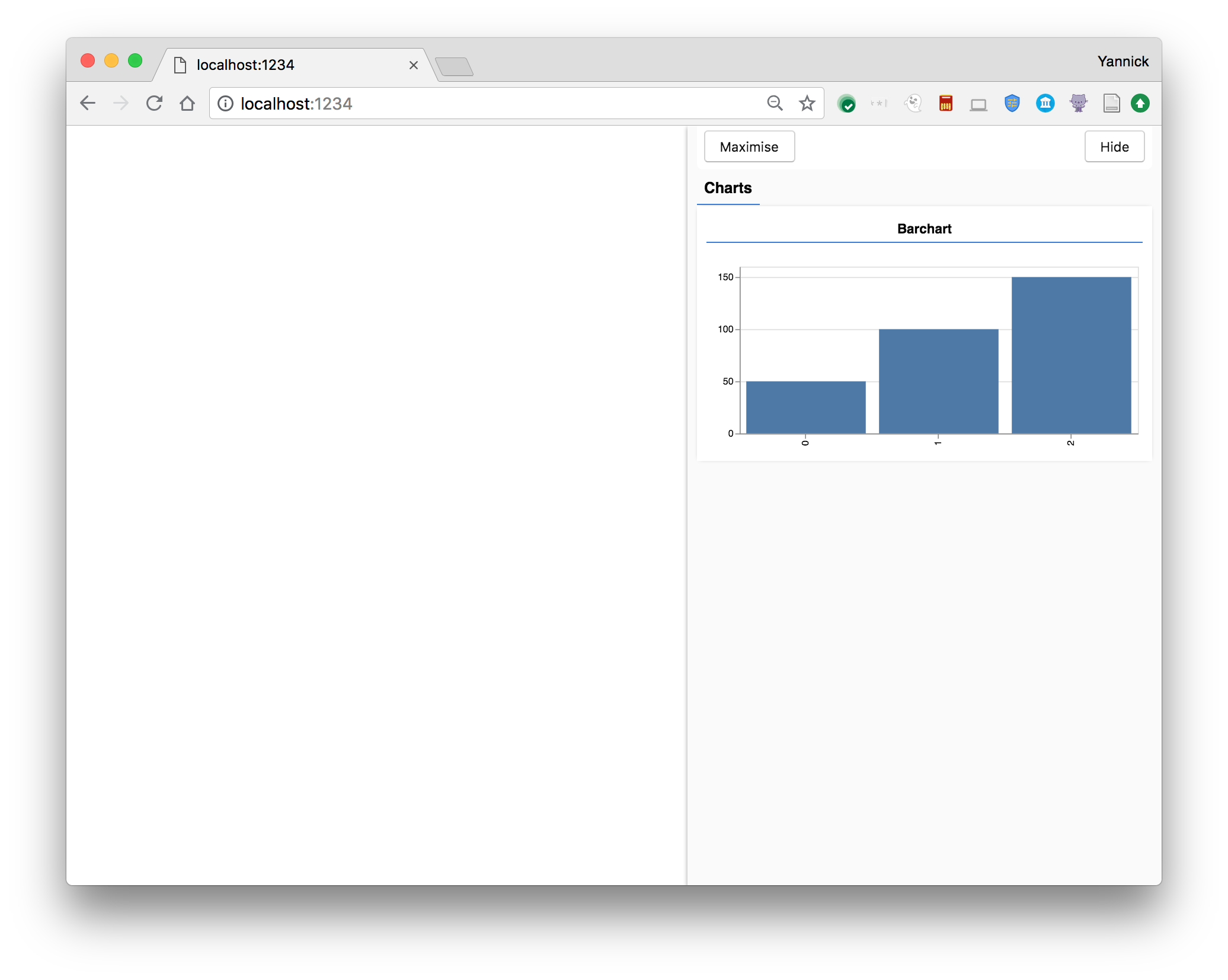
Sample Usage
const data = [
{ index: 0, value: 50 },
{ index: 1, value: 100 },
{ index: 2, value: 150 },
];
// Get a surface
const surface = tfvis.visor().surface({ name: 'Barchart', tab: 'Charts' });
// Render a barchart on that surface
tfvis.render.barchart(data, surface, {});This should show something like the following
API
Visors, Surfaces and Tabs
visor() => Visor
Returns a singleton object with the public API of the visor. This will create the necessary DOM elements for the visor on initialization.
Initially calling visor() will create a panel that is displayed on the right. It hovers over your pages content and shouldn't disturb the flow of your page's DOM Elements. It has some display controls and by default also supports the following keyboard shortcuts:
- ` (backtick): Shows or hides the visor
- ~ (tilde, shift+backtick): Toggles betweeen full width and smaller width view of the visor.
The returned object has the following properties, documented here with the
prefix visor() and annotated with type information. You can call visor() as much as you want or store a reference to the returned object.
visor().el: HTMLElement
The containing HTMLElement for the whole visor.
visor().surface(options: SurfaceInfo) => Surface;
Returns a Surface, creating one if necessary. This is the primary container
of visualizations. Surfaces are organized onto Tabs.
options has the following structure.
{
//The name / label of this surface
name: string,
// The name of the tab this surface should appear on (optional)
tab?: string,
// Display Styles for the surface (optional)
styles?: StyleOptions,
}StyleOptions has the following structure. All properties are optional
and generally represent css styles that will be added to the Surface. As these are css properties, they can be in any valid css unit e.g. % or px.
{
width?: string;
height?: string;
maxWidth?: string;
maxHeight?: string;
}visor().isOpen() => boolean;
Returns true if the visor is currently open/visible.
visor().isFullscreen() => boolean;
Returns true if the visor is in fullscreen mode. Note that the visor may be in a closed state even if it is in fullscreen mode.
visor().open() => void;
Opens the visor.
visor().close() => void;
Closes the visor.
visor().toggle() => void;
Toggles the visor open and closed.
visor().toggleFullScreen() => void;
Toggles the fullscreen mode of the visor.
visor().setActiveTab(tabName: string) => void;
Set the currently active tab. tabName must be the name of an existing tab.
visor().unbindKeys() => void;
Removes the default keyboard handlers that control visor visibility.
visor().bindKeys() => void;
Restores the default keyboard handlers that control visor visiblity.
Surface
A surface is the object returned by a call to visor().surface(...). It returns an object with no methods and the following properties:
{
//The containing HTML element for this surface
container: HTMLElement;
// A textual label for the surface.
label: HTMLElement;
// A container for plots and other renderings
drawArea: HTMLElement;
}Generally speaking you would only access .drawArea to add plots and other renders.
Show Functions
This library exposes a show namespace that provides a number of higher level functions useful for rendering tfjs concepts. They lean towards being opinionated
rather than flexible but are generally combinations of Renderers (see below), so one can easily roll their own.
Model Training Visualization
show.history(container: Surface, history: HistoryLike, metrics: string[], opts?: {}) => Promise
Renders a tf.Model training 'History' or callback 'Logs'. These are useful for plotting training metrics after or during
training respectively.
- @param container A
Surfaceor{name: string, tab?: string}object specifying which surface to render to. - @param history A history-like object. Either a tfjs-layers
Historyobject or an array of tfjs-layersLogsobjects.Logsare produced by the callbacks on model.fit and aHistoryobject is returned from model.fit. - @param metrics An array of strings reprenting training metrics of a tf.model
- @param opts Optional parameters for the line charts. See the opts parameter for render.linechart for details. Notably for 'accuracy' related plots the domain of the yAxis will always by 0-1, i.e.
zoomToFitandyAxisDomainoptions are ignored. - @param opts.zoomToFitAccuracy a boolean controlling whether to set
zoomToFitto true on accuracy plots as well. Generally speakingzoomToFitis disabled for accuracy plots as that is desireable most of the time. However there may be cases, such as when doing transfer learning, where more resolution is desired. SetzoomToFitAccuracyto true to turn on zoomToFit for accuracy plots.
show.fitCallbacks(container: Surface metrics: string[], opts?: {}) => {[key: string]: (iteration: number, log: Logs) => Promise}
Returns a collection of callbacks to pass to model.fit.
Callbacks are returned for the following events, onBatchEnd & onEpochEnd.
These callbacks will plot line charts for the metrics specified at the end of every batch and every opoch.
See model.fit for more info on how to pass in callback functions to the training process.
- @param container A
Surfaceor{name: string, tab?: string}object specifying which surface to render to. - @param metrics An array of strings representing training metrics of a tf.model
- @param opts Optional parameters for the line charts. See the opts parameter for render.linechart for details. Notably for 'accuracy' related plots the domain of the yAxis will always by 0-1, i.e. zoomToFit and yAxisDomain options are ignored.
- @param opts.zoomToFitAccuracy a boolean controlling whether to set
zoomToFitto true on accuracy plots as well. Generally speakingzoomToFitis disabled for accuracy plots as that is desireable most of the time. However there may be cases, such as when doing transfer learning, where more resolution is desired. SetzoomToFitAccuracyto true to turn on zoomToFit for accuracy plots. - @param opts.callbacks Array of strings with callback names. Valid options are 'onEpochEnd' and 'onBatchEnd'. Defaults to ['onEpochEnd', 'onBatchEnd'].
show.perClassAccuracy(container: Drawable, classAccuracy: {accuracy: number[], count: number[]}, classLabels?: string[]) => Promise
Renders a per class accuracy table for classification task evaluation
- @param container A
{name: string, tab?: string}object specifying which surface to render to. - @param classAccuracy An
Array<{accuracy: number, count: number}>array with the accuracy data. See metrics.perClassAccuracy for details on how to generate this object. - @param classLabels An array of string labels for the classes in
classAccuracy. Optional.
show.confusionMatrix(container: Drawable, confusionMatrix: number[][], classLabels?: string[]) => Promise
Renders a confusion matrix for classification task evaluation
- @param container A
{name: string, tab?: string}object specifying which surface to render to. - @param confusionMatrix A nested array of numbers with the confusion matrix values. See metrics.confusionMatrix for details on how to generate this.
- @param classLabels An array of string labels for the classes in
classAccuracy. Optional.
show.valuesDistribution(container: Drawable, tensor: Tensor) => Promise
Renders a histogram showing the distribution of all values in a tensor.
- @param container A
{name: string, tab?: string}object specifying which surface to render to. - @param tensor a
Tensor
show.modelSummary(container: Drawable, model: tf.Model) => Promise
Renders a summary of a tf.Model. Displays a table with layer information.
- @param container A
{name: string, tab?: string}object specifying which surface to render to. - @param model a
tf.Model
show.layer(container: Drawable, layer: Layer) => Promise
Renders summary information about a layer and a histogram of parameter values in that layer.
- @param container A
{name: string, tab?: string}object specifying which surface to render to. - @param layer a
tf.layers.Layer
Renderers
The library exposes a render namespace that provides a number of functions that plot particular visualizations.
render.barchart(data: [], container: Surface|HTMLElement, opts: {}) => Promise
Renders a barchart.
- @param data Data in the following format:
[ {index: number, value: number} ... ]
- @param container A
SurfaceorHTMLElementin which to draw the barchart. Note thatthis chart expects to have complete control over the contents of the container and can clear its contents at will. - @param opts optional parameters
- @param opts.width width of chart in px
- @param opts.height height of chart in px
- @param opts.xLabel label for x-axis, set to null to hide the
- @param opts.yLabel label for y-axis, set to null to hide the
- @param opts.fontSize fontSize in pixels for text in the chart
- @returns Promise - indicates completion of rendering
render.table(data: {headers: [], values: [][]}, container: Surface|HTMLElement) => void
Renders a table.
-
@param data Data in the following format
{ headers: string[], values: any[][] }- data.headers are the column names
- data.values is an array of arrays (one for each row). The inner array length usually matches the length of data.headers else there will be some empty cells. Usually the values are strings or numbers, these are inserted as html content so html strings are also supported.
-
@param container An
HTMLElementorSurfacein which to draw the table. Note that the chart expects to have complete control over the contents of the container and can clear its contents at will. -
@param opts.fontSize fontSize in pixels for text in the chart
render.histogram(data: [], container: Surface|HTMLElement, opts: {}) => Promise
Renders a Histogram.
-
@param data Data in the following format:
[ {value: number}, ... ]or[number]orTypedArray
-
@param container An
HTMLElementorSurfacein which to draw the chart -
@param opts optional parameters
-
@param opts.width width of chart in px
-
@param opts.height height of chart in px
-
@param opts.fontSize fontSize in pixels for text in the chart
-
@param opts.maxBins maximimum number of bins to use in histogram
-
@param opts.stats summary statistics to show. These will be computed internally if no stats are passed. Pass
falseto not compute any stats. Callers are allowed to pass in their own stats as in some cases they may be able to compute them more efficiently. Stats should have the following format:{ numVals?: number, min?: number, max?: number, numZeros?: number, numNans?: number }
render.linechart(data: [], container: Surface|HTMLElement, opts: {}) => Promise
Renders a Line Chart.
- @param data Data in the following format
{ // A nested array of objects each with an x and y property, // one per series. // If you only have one series to render you can just pass an array // of objects with x, y properties values: {x: number, y: number}[][] // An array of strings with the names of each series passed above. // Optional series: string[] }
- @param container An HTMLElement in which to draw the chart
- @param opts optional parameters
- @param opts.width width of chart in px
- @param opts.height height of chart in px
- @param opts.xLabel label for x axis
- @param opts.yLabel label for y axis
- @param opts.fontSize fontSize in pixels for text in the chart
- @param opts.zoomToFit a boolean indicating whether to allow non-zero baselines setting this to true allows the line chart to take up more room in the plot.
- @param opts.yAxisDomain array of two numbers indicating the domain of the y axis
render.scatterplot(data: [], container: Surface|HTMLElement, opts: {}) => Promise
Renders a Scatter Plot.
- @param data Data in the following format
{ // A nested array of objects each with an x and y property, // one per series. // If you only have one series to render you can just pass an array // of objects with x, y properties values: {x: number, y: number}[][] // An array of strings with the names of each series passed above. // Optional series: string[] }
- @param container An HTMLElement in which to draw the chart
- @param opts optional parameters
- @param opts.width width of chart in px
- @param opts.height height of chart in px
- @param opts.xLabel label for x axis
- @param opts.yLabel label for y axis
- @param opts.fontSize fontSize in pixels for text in the chart
- @param opts.zoomToFit a boolean indicating whether to allow excluding zero from the domain of the charts axes setting this to true allows the points to take up more room in the plot.
- @param opts.xAxisDomain array of two numbers indicating the domain of the x axis this is overriden by zoomToFit
- @param opts.yAxisDomain array of two numbers indicating the domain of the y axis this is overriden by zoomToFit
render.confusionMatrix(data: {}, container: Surface|HTMLElement, opts: {}) => Promise
Renders a confusion matrix
- @param data Data consists of an object with a 'values' property
and a 'labels' property.
e.g.
{ values: number[][], // a matrix of numbers representing counts for each (label, prediction) pair labels?: string[] // Human readable labels for each class in the matrix. Optional }
{ values: [[80, 23], [56, 94]], labels: ['dog', 'cat'], }
- @param container An
HTMLElementorSurfacein which to draw the chart - @param opts optional parameters
- @param opts.shadeDiagonal boolean that controls whether or not to color cells
- on the diagonal. Defaults to false
- @param opts.width width of chart in px
- @param opts.height height of chart in px
- @param opts.fontSize fontSize in pixels for text in the chart
Metrics
The metrics namespace contains a few utility functions for computing quality metrics
like accuracy or creating confusion matrices.
metrics.confusionMatrix(labels: Tensor1D, predictions: Tensor1D, numClasses?: number, weights?: Tensor1D) => Promise<number[][]>
Computes a confusion matrix from predictions and labels. Each value in labels and predictions should correspond to some output class. It is assumed that these values go from 0 to numClasses - 1.
The result will be a 2D array of size numClasses * numClasses
- @param labels 1D tensor of true values
- @param predictions 1D tensor of predicted values
- @param numClasses Number of distinct classes. Optional. If not passed in numClasses will equal the highest number in either labels or predictions plus 1
- @param weights 1d tensor that is the same size as predictions. If weights is passed in then each prediction contributes its corresponding weight to the total value of the confusion matrix cell.
metrics.perClassAccuracy(labels: Tensor1D, predictions: Tensor1D, numClasses?: number, weights?: Tensor1D) => Promise<{accuracy: number[], count: number[]}>
Computes per class accuracy between prediction and labels. Each value in labels and predictions should correspond to some output class. It is assumed that these values go from 0 to numClasses - 1.
Returns an array of objects that each have an an accuracy and a count property for each class.
- @param labels 1D tensor of true values
- @param predictions 1D tensor of predicted values
- @param numClasses Number of distinct classes. Optional. If not passed in numClasses will equal the highest number in either labels or predictions plus 1
metrics.accuracy(labels: Tensor, predictions: Tensor) => Promise
Computes how often predictions matches labels.
- @param labels tensor of true values
- @param predictions tensor of predicted values