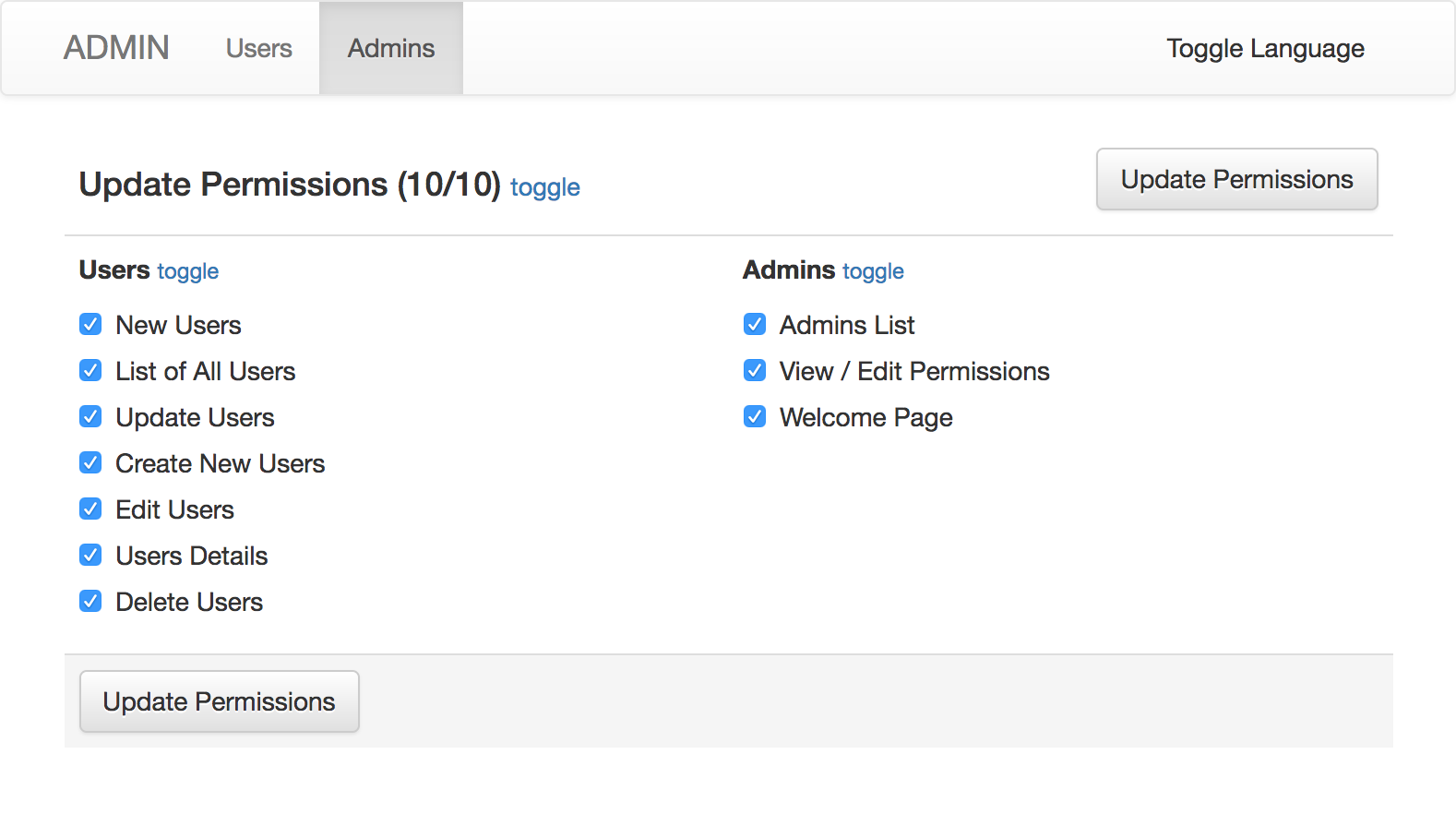
Control user / admin permissions with cancancan.
Easily integrate cancancan into your application with permission control of every controller action.
Add this line to your application's Gemfile:
gem 'act_as_permission_controllable'And then execute:
$ bundleOr install it yourself as:
$ gem install act_as_permission_controllableAdd a permissions JSONB field to your model:
rails g migration AddPermissionsToAdmins permissions:jsonbAdd default: {}, nil: false:
class AddPermissionsToAdmins < ActiveRecord::Migration[5.1]
def change
add_column :admins, :permissions, :jsonb, default: {}, nil: false
end
endAdd act_as_permission_controllable to your model:
class Admin < ApplicationRecord
act_as_permission_controllable # methods added: ban, permit, assign_permissions, can?
endCreate app/models/ability.rb:
class Ability
include ActAsPermissionControllable::Ability
endAdd grant_permission to your base controller.
Controllers inherited from it will need authorization.
You can rescue from CanCan::AccessDenied error to show permission error message.
You also need to define current_ability for cancancan to work.
class Admin::BaseController < ApplicationController
# ... other code ...
grant_permission
rescue_from CanCan::AccessDenied do |exception|
respond_to do |format|
format.json {
render json: { message: exception.message }, status: 403
}
format.html {
render 'act_as_permission_controllable/forbidden', layout: 'admin', status: 403, locals: { exception: exception }
}
end
end
private
def current_ability
@current_ability ||= Ability.new(current_admin)
end
# ... other code ...
endIf you don't want a controller to check user permission, use skip_grant_permission.
class Admin::HomeController < Admin::BaseController
skip_grant_permission
endIf your controller has different index page:
class Admin::AdminsController < Admin::BaseController
grant_permission index: :welcome
def welcome
end
endTo edit permissions on the web page, add actions to your routes:
resources :admins do
member do
match :permissions, via: [ :get, :post ]
end
endAnd in your controller:
class Admin::AdminsController < Admin::BaseController
# ... other code ...
def permissions
if request.post?
@admin.assign_permissions(params.fetch(:actions, []))
if @admin.save
flash[:notice] = 'OK!'
else
flash[:error] = 'ERROR!'
end
redirect_to params[:referer].presence || permissions_admin_admin_path(@admin)
return
end
render 'act_as_permission_controllable/permissions'
end
# ... other code ...
endYou can use controllable_nav_items to list permitted pages for current user:
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<% controllable_nav_items do |item| %>
<%= content_tag :li, class: (name = item.controller_name) == controller.controller_name ? 'active' : nil do %>
<%= link_to item.i18n_name, (url_for(controller: name, action: item.index) rescue nil) %>
<% end %>
<% end %>
</ul>You can customize the names of each controller action and the order of each controller:
# config/locales/aapc.en.yml
en:
act_as_permission_controllable:
order:
- Admin::OrdersController
- Admin::SettingsController
- Admin::AdminsController
controllers:
Admin::AdminsController: 'Admins'
Admin::OrdersController: 'Orders'
Admin::SettingsController: 'Settings'
actions:
Admin::AdminsController:
permissions: 'View and Set Permissions'
Admin::OrdersController:
export: 'Export Orders'# permit multiple actions of a controller
Admin.find(1).permit(:user, :create, :update, :destroy).save
# permit all actions in user controller
Admin.find(1).permit(:user, :all).save
# ban all except some permissions
Admin.find(1).ban(:all).permit(:settings, :update).save
# permit all except some permissions
Admin.find(1).permit(:all).ban(:admin, :permissions).save
# you can use controller class name as subject
Admin.find(1).ban(:all).permit('Admin::SettingsController', :update).saveif current_admin.can?(:destroy, :user)
# admin can destroy user
endYou can run the app in test/dummy directory and visit http://admin.localhost.com:3000.
You can open issues or pull requests on GitHub.
The gem is available as open source under the terms of the MIT License.