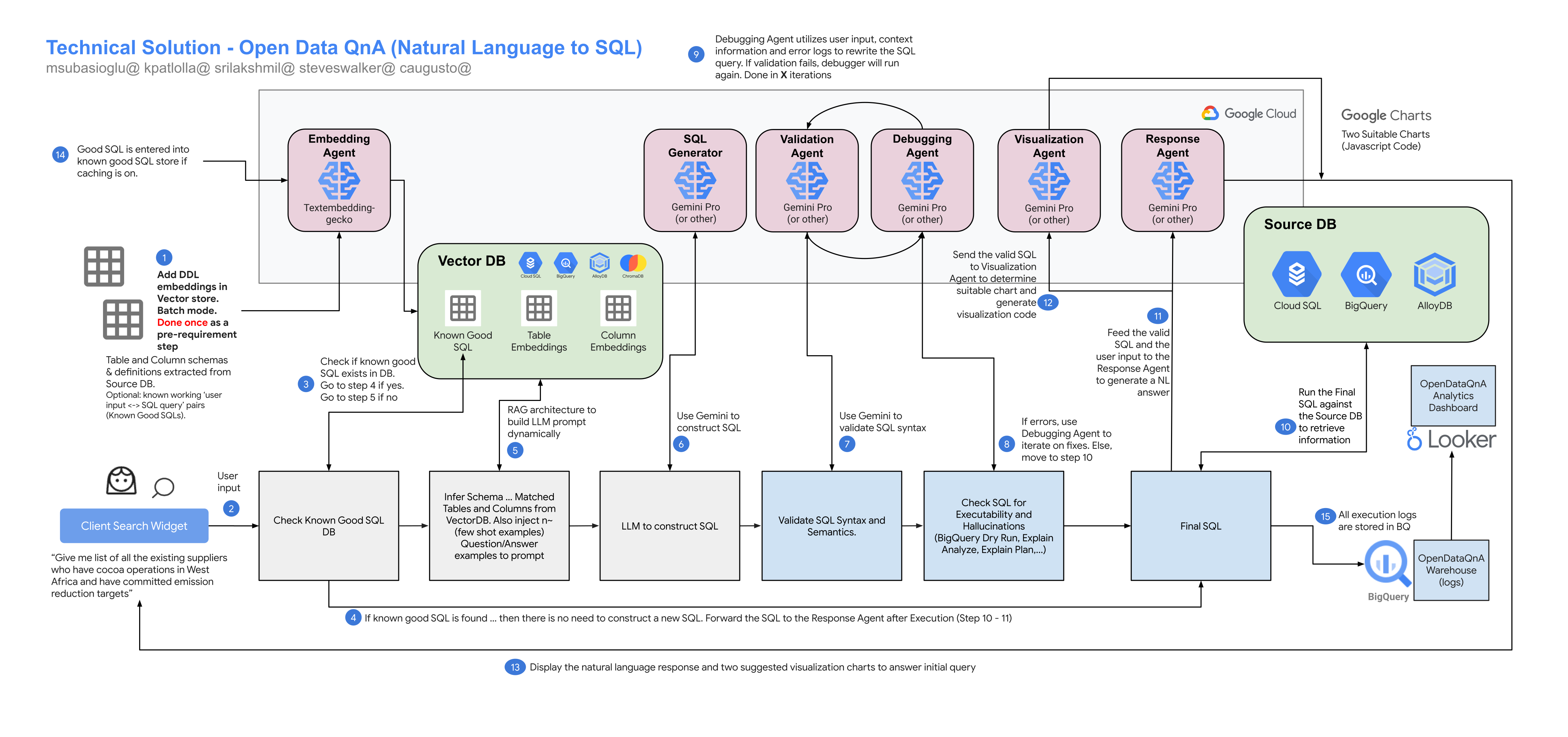
The Open Data QnA python library enables you to chat with your databases by leveraging LLM Agents on Google Cloud.
Open Data QnA enables a conversational approach to interacting with your data. Ask questions about your PostgreSQL or BigQuery databases in natural language and receive informative responses, without needing to write SQL. Open Data QnA leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to bridge the gap between human language and database queries, streamlining data analysis and decision-making.
Key Features:
- Conversational Querying: Ask questions naturally, without requiring SQL knowledge.
- SQL Generation: Automatically generates SQL queries based on your questions.
- Query Refinement: Validates and debugs queries to ensure accuracy.
- Natural Language Responses: DRun queries and present results in clear, easy-to-understand language.
- Visualizations (Optional): Explore data visually with generated charts.
- Extensible: Customize and integrate with your existing workflows(API, UI, Notebooks).
It is built on a modular design and currently supports the following components:
- Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL
- Google BigQuery
- PGVector on Google Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL
- BigQuery Vector Store
- ChromaDB (WIP)
- BuildSQLAgent: An agent specialized in generating SQL queries for BigQuery or PostgreSQL databases. It analyzes user questions, available table schemas, and column descriptions to construct syntactically and semantically correct SQL queries, adapting its process based on the target database type.
- ValidateSQLAgent: An agent that validates the syntax and semantic correctness of SQL queries. It uses a language model to analyze queries against a database schema and returns a JSON response indicating validity and potential errors.
- DebugSQLAgent: An agent designed to debug and refine SQL queries for BigQuery or PostgreSQL databases. It interacts with a chat-based language model to iteratively troubleshoot queries, using error messages to generate alternative, correct queries.
- DescriptionAgent: An agent specialized in generating descriptions for database tables and columns. It leverages a large language model to create concise and informative descriptions that aid in understanding data structures and facilitate SQL query generation.
- EmbedderAgent: An agent specialized in generating text embeddings using Large Language Models (LLMs). It supports direct interaction with Vertex AI's TextEmbeddingModel or uses LangChain's VertexAIEmbeddings for a simplified interface.
- ResponseAgent: An agent that generates natural language responses to user questions based on SQL query results. It acts as a data assistant, interpreting SQL results and transforming them into user-friendly answers using a language model.
- VisualizeAgent: An agent that generates JavaScript code for Google Charts based on user questions and SQL results. It suggests suitable chart types and constructs the JavaScript code to create visualizations of the data.
Note: the library was formerly named Talk2Data. You may still find artifacts with the old naming in this repository.
A detailed description of the Architecture can be found here in the docs.
Details on the Repository Structure can be found here in the docs.
This library assumes that the source database is already set up in your GCP project. If a data source has not been set up, use the notebooks below to copy a public dataset from BigQuery to Cloud SQL PostgreSQL or from BigQuery into your GCP project.
- PostgreSQL on Google Cloud SQL (Copy Sample Data: 0_CopyDataToCloudSqlPG.ipynb)
- BigQuery (Copy Sample Data: 0_CopyDataToBigQuery.ipynb)
Quickstart with Open Data QnA: Standalone BigQuery Notebook
This notebook offers a streamlined way to experience the core functionality of Open Data QnA using BigQuery as both the data source and vector store. While it doesn't encompass the full flexibility of the repository setup, it's a perfect starting point to quickly test and explore the conversational querying capabilities of Open Data QnA with your own BigQuery datasets.
ℹ️ You can setup this solution with two approaches. Choose one based on your requirements:
- A) Using Jupyter Notebooks (For better view at what is happening at each stage of the solution)
- B) Using CLI (For ease of use and running with simple python commands, without the need to understand every step of the solution)
git clone git@github.com:GoogleCloudPlatform/Open_Data_QnA.git
cd Open_Data_QnA
1. Run the 1_Setup_OpenDataQnA (Run Once for Initial Setup)
This notebook guides you through the setup and execution of the Open Data QnA application. It provides comprehensive instructions for configuring your environment, preparing the vector store.
2. Run the 2_Run_OpenDataQnA
This notebook guides you by reading the configuration you setup with 1_Setup_OpenDataQnA and running the pipeline to answer questions about your data.
In case you want to separately load Known Good SQLs please run this notebook once the config variables are setup in config.ini file. This can be run multiple times just to load the known good sql queries and create embeddings for it.
1. Add Configuration values for the solution in config.ini
For setup we require details for vector store, source database etc. Edit the config.ini file and add values for the parameters based of below information.
ℹ️ Follow the guidelines from the config guide document to populate your config.ini file.
pip install poetry --quiet
poetry lock
poetry install --quiet
poetry env info
poetry shell
Authenticate your credentials
gcloud auth login
gcloud auth application-default login
gcloud services enable \
serviceusage.googleapis.com \
cloudresourcemanager.googleapis.com --project <<Enter Project Id>>
gcloud auth application-default set-quota-project <<Enter Project Id for using resources>>
Enable APIs for the solution setup
gcloud services enable \
cloudapis.googleapis.com \
iam.googleapis.com \
run.googleapis.com \
sqladmin.googleapis.com \
aiplatform.googleapis.com \
bigquery.googleapis.com \
storage.googleapis.com \ --project <<Enter Project Id>>
3. Run env_setup.py to create vector store based on the configuration you did in Step 1
python env_setup.py
4. Run opendataqna.py to run the pipeline you just setup
The Open Data QnA SQL Generation tool can be conveniently used from your terminal or command prompt using a simple CLI interface. Here's how:
python opendataqna.py --user_question "What are the top 5 cities with highest recalls?" --user_database "fda_food"
Where
user_question : Enter your question in string
user_database : Enter the BQ_DATASET_NAME for BigQuery sources or PG_SCHEMA for PostgreSQL sources (refer your config.ini file)
Optional Parameters
You can customize the pipeline's behavior using optional parameters. Here are some common examples:
# Enable the SQL debugger:
python opendataqna.py --user_question "..." --user_database "..." --run_debugger
# Execute the final generated SQL:
python opendataqna.py --user_question "..." --user_database "..." --execute_final_sql
# Change the number of debugging rounds:
python opendataqna.py --user_question "..." --user_database "..." --debugging_rounds 5
# Adjust similarity thresholds:
python opendataqna.py --user_question "..." --user_database "..." --table_similarity_threshold 0.25 --column_similarity_threshold 0.4
You can find a full list of available options and their descriptions by running:
python opendataqna.py --help
If you successfully set up the solution accelerator and want to start optimizing to your needs, you can follow the tips in the Best Practice doc.
Additionally, if you stumble across any problems, take a look into the FAQ.
If neither of these resources helps, feel free to reach out to us directly by raising an Issue.
If you are looking to deploy backend apis for the solution, refer to the README.md under /backend-apis.
If you are looking to deploy the frontend for the solution, refer to the README.md under /frontend.
To clean up the resources provisioned in this solution, use commands below to remove them using gcloud/bq:
For cloudsql-pgvector as vector store : Delete SQL Instance
gcloud sql instances delete <CloudSQL Instance Name> -q
Delete BigQuery Dataset Created for Logs and Vector Store : Remove BQ Dataset
bq rm -r -f -d <BigQuery Dataset Name for OpenDataQnA>
(For Backend APIs)Remove the Cloud Run service : Delete Service
gcloud run services delete <Cloud Run Service Name>
For frontend, based on firebase: Remove the firebase app
BigQuery quotas including hardware, software, and network components.
Open Data QnA is distributed with the Apache-2.0 license.
It also contains code derived from the following third-party packages:
If you have any questions or if you found any problems with this repository, please report through Hub issues.