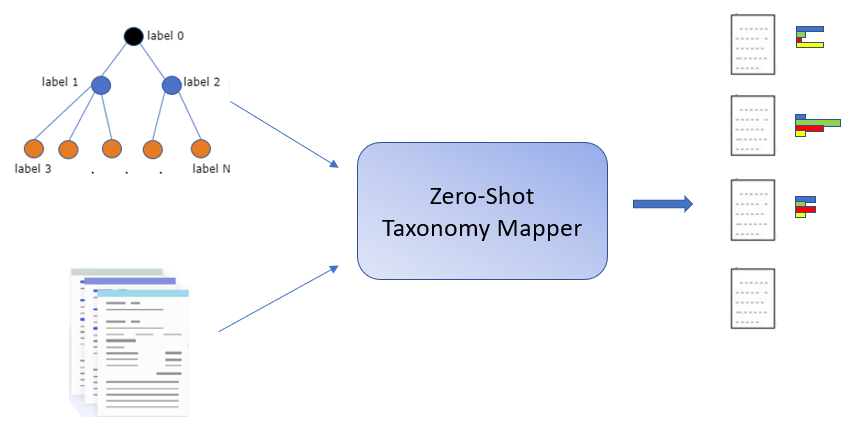
Classification of text according to a custom (hierarchical) taxonomy of categories. Does not need any labelled data or any fine-tuning of the model.
- Python version 3.8.8
- App version: 1.3.0-beta
- Install modules:
pip install -r requirements.txt
To map a set of texts according to a custom taxonomy call
from classifier import ZeroShootTaxonomyMapper
top_scores, usp_scores = ZeroShootTaxonomyMapper.run(
taxonomy,
texts,
compute_alpha_thresholds,
'path/to/stored/alpha_thresholds')
results = list(zip(texts, usp_scores, top_scores))- Set
compute_alpha_thresholdstoTrueduring the initial run. This allows the model to gather and compute statistics on the taxonomy labels. For all subsequent runs with the same taxonomy, set this parameter toFalse, as the statistics will already have been computed. 'path/to/stored/alpha_thresholds'refers to the file path where the computed label statistics are saved. During later runs, the model will load the statistics from this location, eliminating the need for recomputation.
For each input text, results contains:
- text
- custom
taxonomytree with posterior USP scores for each label - top label for each layer of the taxonomy
The custom taxonomy should be formatted in the follwoing structure:
{
"category 0": {
"subcategory 00": {...},
"subcategory 01": {...},
...:{...}
},
"category 1": {
"subcategory 10": {...},
"subcategory 11": {...},
...: {...}
},
...: {...}
}The input texts can be a simple list of strings:
[
"text 0",
"text 1",
...
]Classification of documents according to a custom internal hierarchical taxonomy is a common problem for many organizations that deal with textual data. Approaches aimed to address this challenge are, for the vast majority, supervised methods, which have the advantage of producing good results on specific datasets, but the major drawbacks of requiring an entire corpus of annotated documents, and the resulting models are not directly applicable to a different taxonomy. In this paper, we aim to contribute to this important issue, by proposing a method to classify text according to a hierarchical taxonomy entirely without the need of labelled data. The idea is to first leverage the semantic information encoded into pre-trained Deep Language Models to zero-shot a prior confidence score for each label of the taxonomy, and secondly take advantage of the hierarchical structure to reinforce this prior belief. Experiments are conducted on three hierarchically annotated datasets: WebOfScience, DBpedia Extracts and Amazon Product Reviews, which are very diverse in the type of language adopted and have taxonomy depth of two and three levels. On those datasets, we first compare different zero-shot methods, and then we show that our approach improves the results everywhere.
Our method combine several elements to be able to both understand how the document is semantically related to each label of the taxonomy, and to leverage the hierarchical structure of the latter in order to reinforce labels relevance score. These elements can be summarized into three main steps:
- Perform Zero-shot Semantic Text Classification (Z-STC), a simple method that produces zero-shot state-of-the-art prior scores for each label of the taxonomy purely based on semantics. These scores represents the likelihood of a label to be relevant for the document in object. In this step, the hierarchical structure of the taxonomy is disregarded and the task is essentially standard zero-shot text classification. We compare multiple DLMs to find the one best suited for Z-STC, and we also compare with existing zero-shot text classification methods.
- Determine a Relevance Threshold
$\alpha$ for each label. This threshold is automatically selected by the statistical distribution of prior Z-STC scores of each label over a set of irrelevant documents and it represent the minimum relevance score of a label for it be considered relevant to a document with high confidence. - Apply the Upwards Score Propagation (USP) method that propagates confidence scores from the lowest level of the taxonomy up, leveraging prior Z-STC scores, Relevance Thresholds
$\alpha$ and the hierarchical structure of the taxonomy.
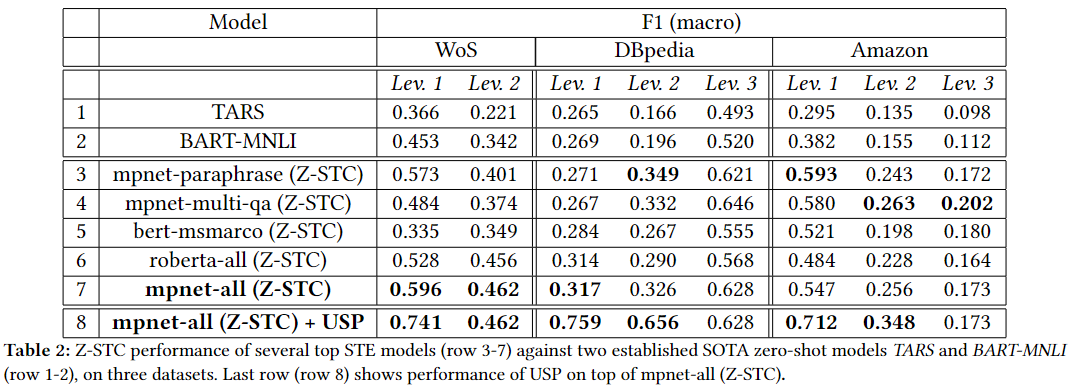
To validate our approach we first verify that the Z-STC step is solid, by considering multiple Semantic Text Embedding models on the task of raw (not hierarchical) Zero-Shot Text Classification and by comparing our Z-STC approach with other two state of the art Zero-Shot approaches. After that, we 1) choose the best performing model for Z-STC, 2) run the Relevance Threshold algorithm to statistically determine which value of similarity indicates high relevance of each label to documents and, 3) apply the Upwards Score Propagation mechanism to bring everything together and include the taxonomy structure information into the classification task. We compare the results obtained like this with the ones obtained by simply performing raw Z-STC using the 'flatten' taxonomy, i.e., without USP mechanism, and we show that the results are greatly improved on all the layers affected of all the datasets considered.
We pick five top STE performing models for comparison, to cover, at least in part, the variability of STE tasks and Deep Language Model training paradigms:
- paraphrase-mpnet-base-v2: MPNet is a model pre-trained using a Masked and Permuted Language Modelling. This particular MPNet model has been fine-tuned for Semantic Text Embedding (STE) to be able to detect if a sentence is paraphrasing another.
- multi-qa-mpnet-base-cos-v1: MPNet based model specialised on Semantic Search and Question Answering. It has been tuned on multiple datasets.
- msmarco-bert-base-dot-v5 BERT based model, also specialised on Question Answering and trained on the MSMARCO dataset.
- all-mpnet-base-v2: all-round MPNet based model, fine-tuned for many use-cases over a large and diverse STE dataset of over 1 billion examples.
- all-roberta-large-v1: BERT-based model, is trained with the same general STE intent as the previous all-mpnet-base-v2 model, and on the same dataset.
The two main results are:
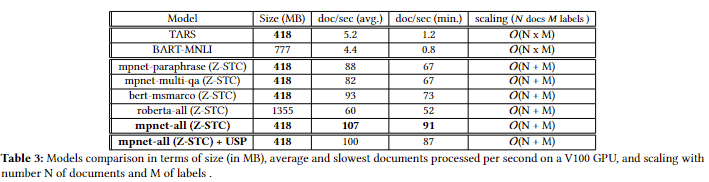
- Showing that our simple Z-STC method for flat (i.e. not hierarchical) text classification is superior when it comes to performance and time complexity with respect to other state-of-the-art approaches to zero shot text classification.
- Showing that our novel Upwards Score Propagation mechanism, that computes Relevance Thresholds and propagate relevance scores upwards to the structure of the Taxonomy, greately improves results everywhere compared to perform starightforward zero-shot text classification on flatten Taxonomy.
-
Download benchmark Datasets:
-
Web Of Science and save it as
'/datasets/WebOfScience' -
DBPedia Extract and save it as
'/datasets/DBPedia_Extract' -
Amazon Reviews and save it as
'/datasets/Amazon_Reviews'
-
Web Of Science and save it as
-
Run benchmark scripts:
- Zeros-Shot Text Classification (Z-STC):
classification of text according to all the categories, disregarding the structure of the Taxonomy and, therefore, regarding each category as independent from the others.python ZSTC_benchmarking.py --gpu_no --topn --dataset --savefile
- Upwards Score Propagation mechanism (USP):
compute Posterior Relevance scores for each category in the Taxonomy by leveraging: prior Z-STC scores, Relevance Thresholds and the structure of the Taxonomy.python USP_benchmarking.py --gpu_no --topn --dataset --savefile
- Entropy based Sentence Selection (ESS):
mechanism to focus the attention of the encoding model on the important sentences of the document. Importance here is represented by the value of the entropy of the sentence with respect to the categories of the Taxonomy.
python ESS_benchmarking.py --gpu_no --level --topn --dataset
- Compute Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) for Ground Distribution modelling:
Relevanche Threshold
$\alpha_l$ of each label l, is a central parameter of the Upwards Score Propagation (UPS) mechanism, and it is found by computing the distribution of Z-STC scores of l over a set of irrelevant Wikipedia articles. The Ground Distribution obtained is then parametrized by some known distribution, which is chosen out of a pool of known distributions by applying the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) for model selection:python ground_PDF_modelling.py
- Zeros-Shot Text Classification (Z-STC):