npx create-expo-app AwesomeProject
cd AwesomeProject
npx expo start- In order to preview the app you need to install the Expo Go app on your phone.
- Then scan the qr code generated in the cli with your camera in order to view the app.
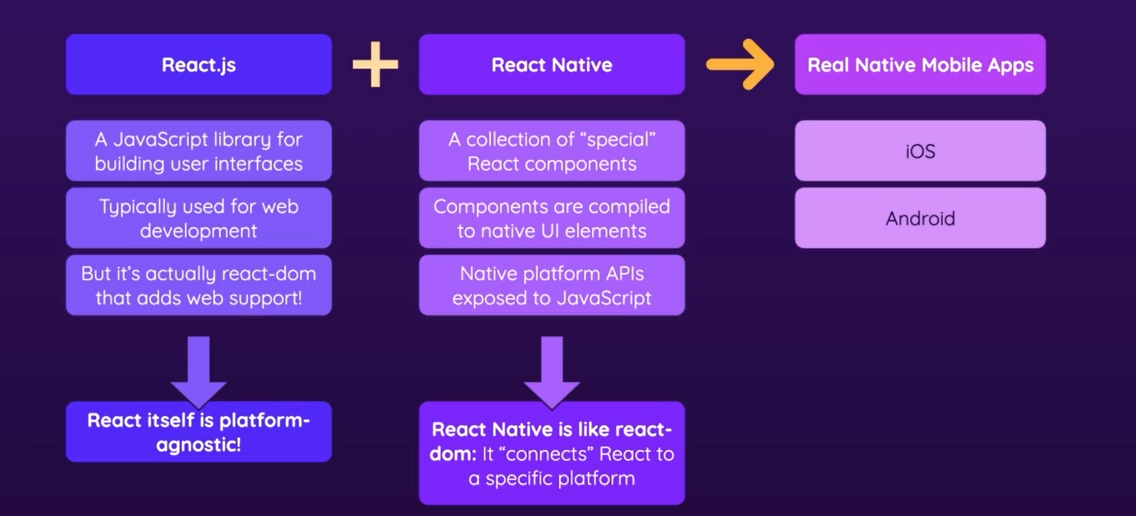
- In normal React we have the DOM in the browser which supports html elements like a
<div/>... The native components for android and IOS do not support html elements...
-
There also are not any css files... you can style components with inline styles or stylesheet objets.
-
This is written in Javascript and mimics css syntax but only suports a subset of the properties and features of css.
-
In normal react for html, text between elements is ok... i.e.
<div>This is some text </div>, however, this will not work in React Native... text must go inside of a<Text>Hello World!!!!</Text>element. -
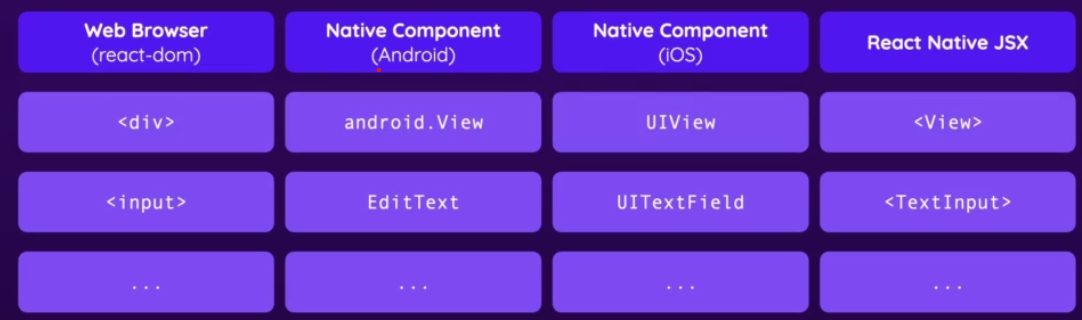
The
<View>component is a container component... similar to a div.
The most fundamental component for building a UI,AViewAis a container that supports layout withAflexbox,Astyle,Asome touch handling, andAaccessibilityAcontrols.AViewAmaps directly to the native view equivalent on whatever platform React Native is running on, whether that is aAUIView,A<div>,Aandroid.view, etc.
ViewAis designed to be nested inside other views and can have 0 to many children of any type.
- When using html elements in react you don't need to import anything... in react native you need to import all of the components...i.e.
import { StyleSheet, Text, View, Button } from "react-native";
export default function App() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<View>
<Text>Another piece of text</Text>
</View>
<Text>Hello World!!!!</Text>
<Button></Button>
</View>
);
}- In react native you don't put the text for a button between button tags... instead you write it like this:
<Button title="Press me!!" />- To style prop is not supported on all React Native elements but it is supported on the view element.
Inline Styling
import { StyleSheet, Text, View, Button } from "react-native";
export default function App() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<View>
<Text>Another piece of text</Text>
</View>
<Text>Hello World!!!!</Text>
<Text style={{ margin: 100 }}>Part 2</Text>
<Button title="Press me!!" />
</View>
);
}- This is how style objects are created:
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
backgroundColor: "#fff",
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center",
},
text: {
margin: 16,
borderWidth: 2,
borderColor: "blue",
padding: 16,
},
});- You can just create an object without using the StyleSheet.create function but then this deprives you of error catching and auto complete functionalities.
Flexbox
- A set of styling properties that define how elements are positioned inside of containers.
Flexbox works the same way in React Native as it does in CSS on the web, with a few exceptions. The defaults are different, with flexDirection defaulting to column instead of row, alignContent defaulting to flex-start instead of stretch, flexShrink defaulting to 0 instead of 1, the flex parameter only supporting a single number.
-
Unlike in normal react web development, in React Native every view defaults to flex box positioning.
-
For
rowthe main axis is from left to right, forrow-reversethe main axis is right to left forcolumnit is top to bottom and forcolumn-reverseit is bottom to top. -
We can use
justifyContentto organize elements along the main axis andalignItemsto organize elements along the cross axis.
import { useState } from "react";
import { StyleSheet, Text, View, Button, TextInput } from "react-native";
export default function App() {
const [enteredGoalText, setEnteredGoalText] = useState("");
const [courseGoals, setCourseGoals] = useState([]);
function goalInputHandler(enteredText) {
setEnteredGoalText(enteredText);
}
function addGoalHandler() {
setCourseGoals((currentCourseGoals) => [...courseGoals, enteredGoalText]);
}
return (
<View style={styles.appContainer}>
<View style={styles.inputContainer}>
<TextInput style={styles.textInput} placeholder="Your course goal" onChangeText={goalInputHandler} />
<Button title="Add Goal" onPress={addGoalHandler} />
</View>
<View style={styles.goalsContainer}>
{courseGoals.map((goal) => {
return (
<View style={styles.goalItem} key={goal}>
<Text>{goal}</Text>
</View>
);
})}
</View>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
appContainer: {
flex: 1,
paddingTop: 50,
paddingHorizontal: 16
},
inputContainer: {
flex: 1,
flexDirection: "row",
justifyContent: "space-between",
alignItems: "center",
marginBottom: 24,
borderBottomWidth: 1,
borderBottomColor: "#cccccc"
},
textInput: {
borderWidth: 1,
borderColor: "#cccccc",
width: "70%",
marginRight: 8,
padding: 8
},
goalsContainer: {
flex: 5
},
goalItem: {
margin: 8,
padding: 8,
borderRadius: 6,
backgroundColor: "#5e0acc",
color: "white"
}
});-
In the example above the goal item
<Text>component had to be wrapped in a<View>component because IOS does not support border radius on the native UI component that<Text>compiles to. -
Styling in React Native is not cascading like CSS, in other words, child elelements do not inherit the styling of their parents.