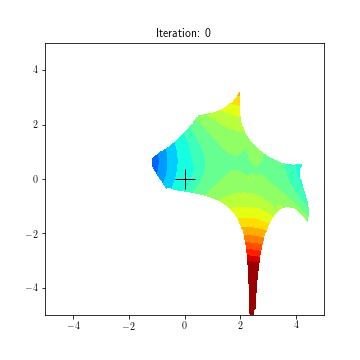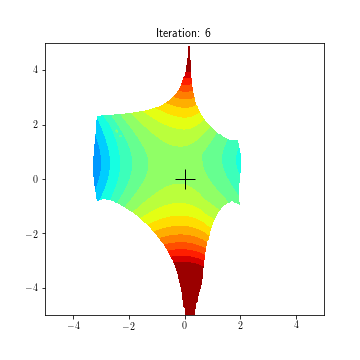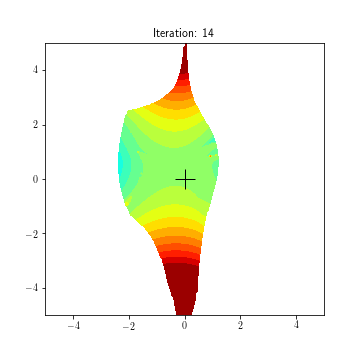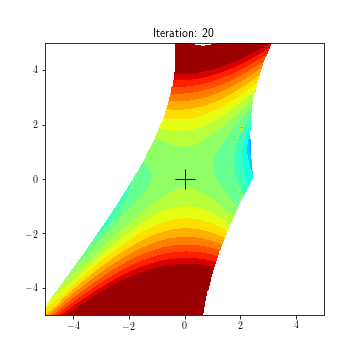
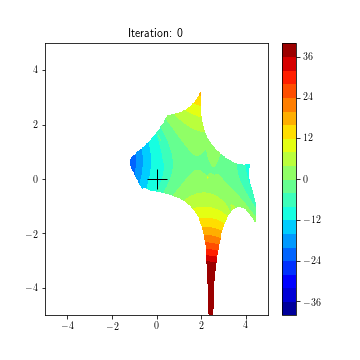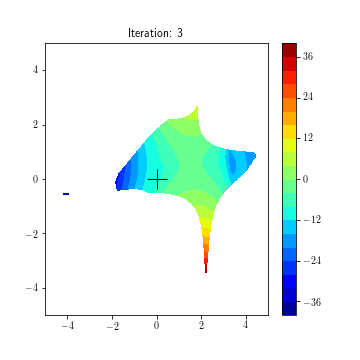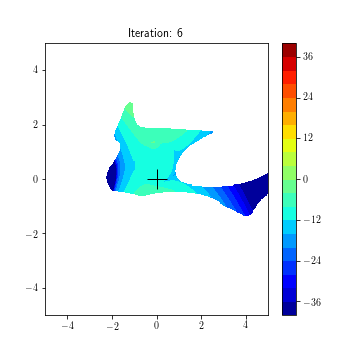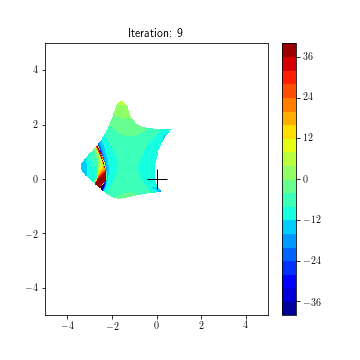
Gradient learning in linear quadratic games.
State dynamics (A, B1, B2):
x(t+1) = A*x(t) + B1*u1(t) + B2*u2(t)
where * is matrix multiplication.
Feedback policies:
u1(t)=K1*x(t)
u2(t)=K2*x(t)
Agent costs (Q1, R11, R12) and (Q2, R21, R22) define a game (f1, f2):
f1(x,u) = sum_t ||x(t)||^2_Q1 + ||u1(t)||^2_R11 + ||u2(t)||^2_R12
f2(x,u) = sum_t ||x(t)||^2_Q2 + ||u1(t)||^2_R21 + ||u2(t)||^2_R22
where ||z||^2_A=z^T*A*z is the quadratic form.
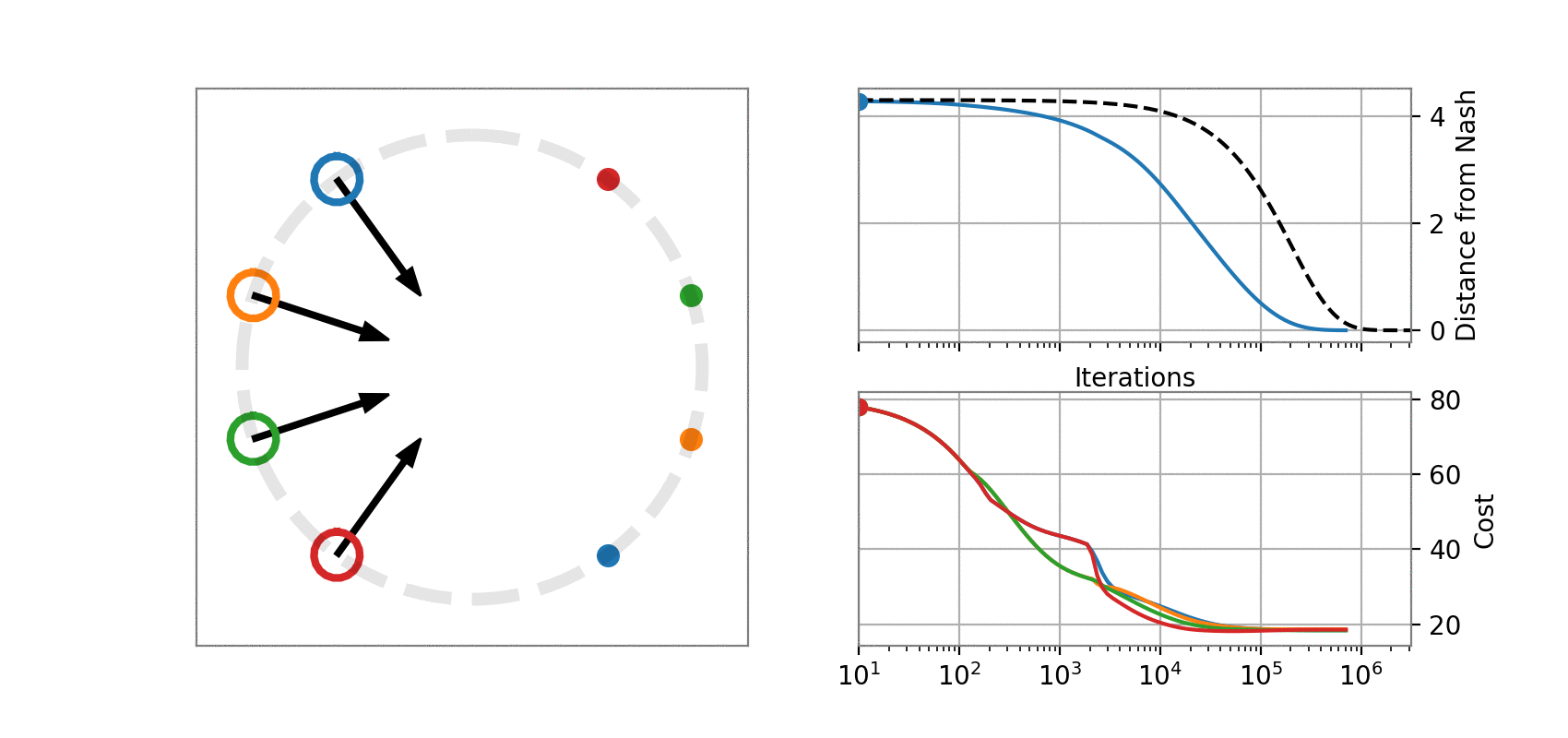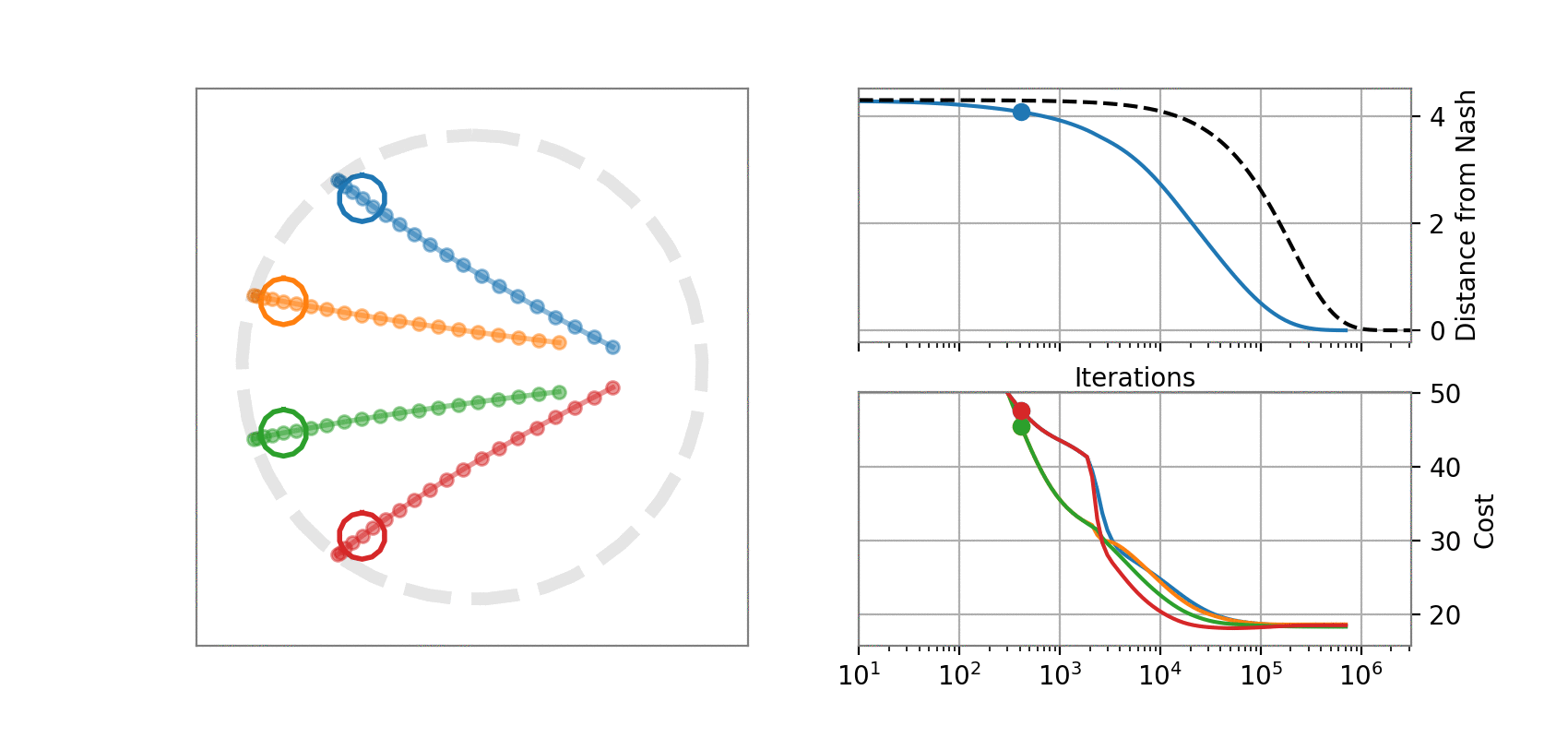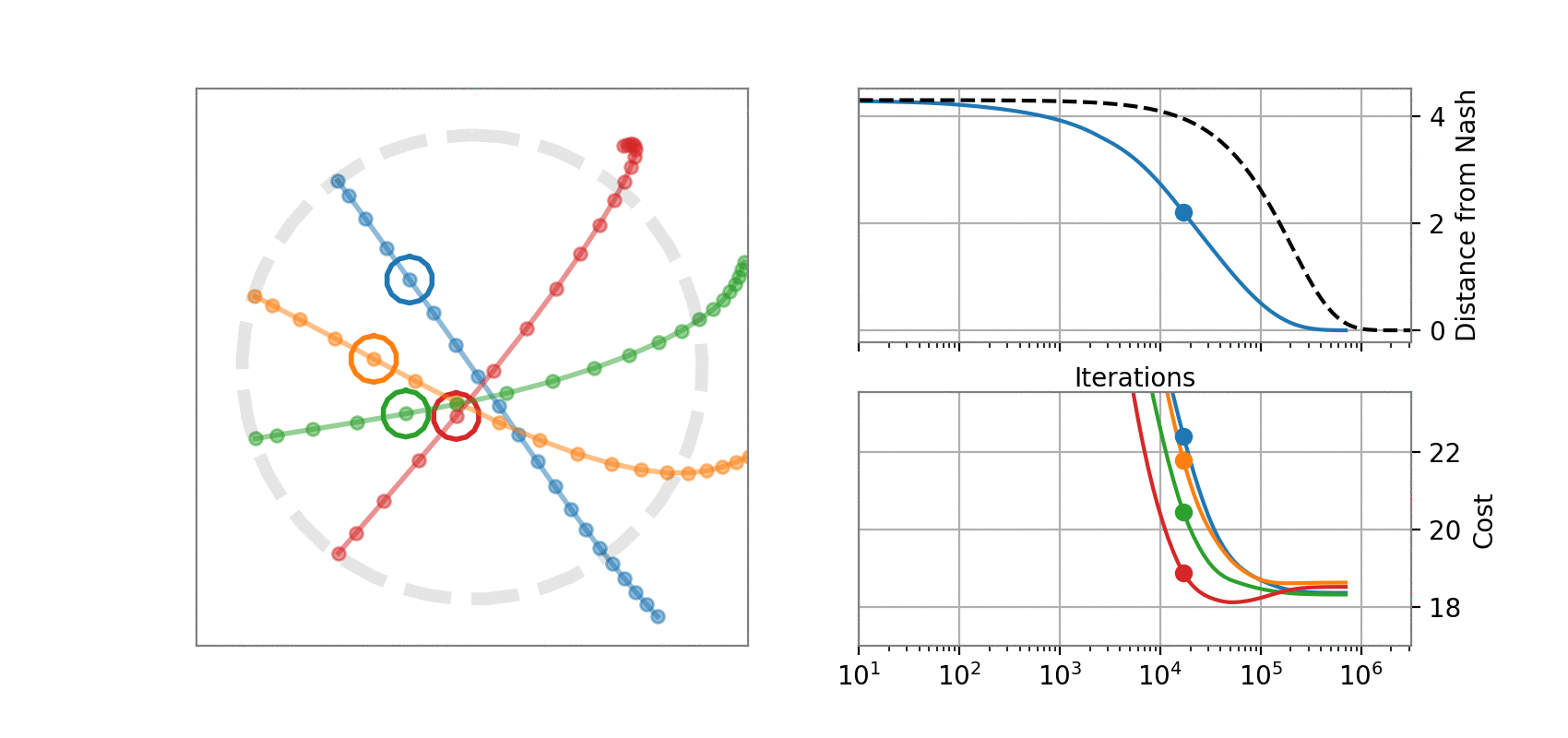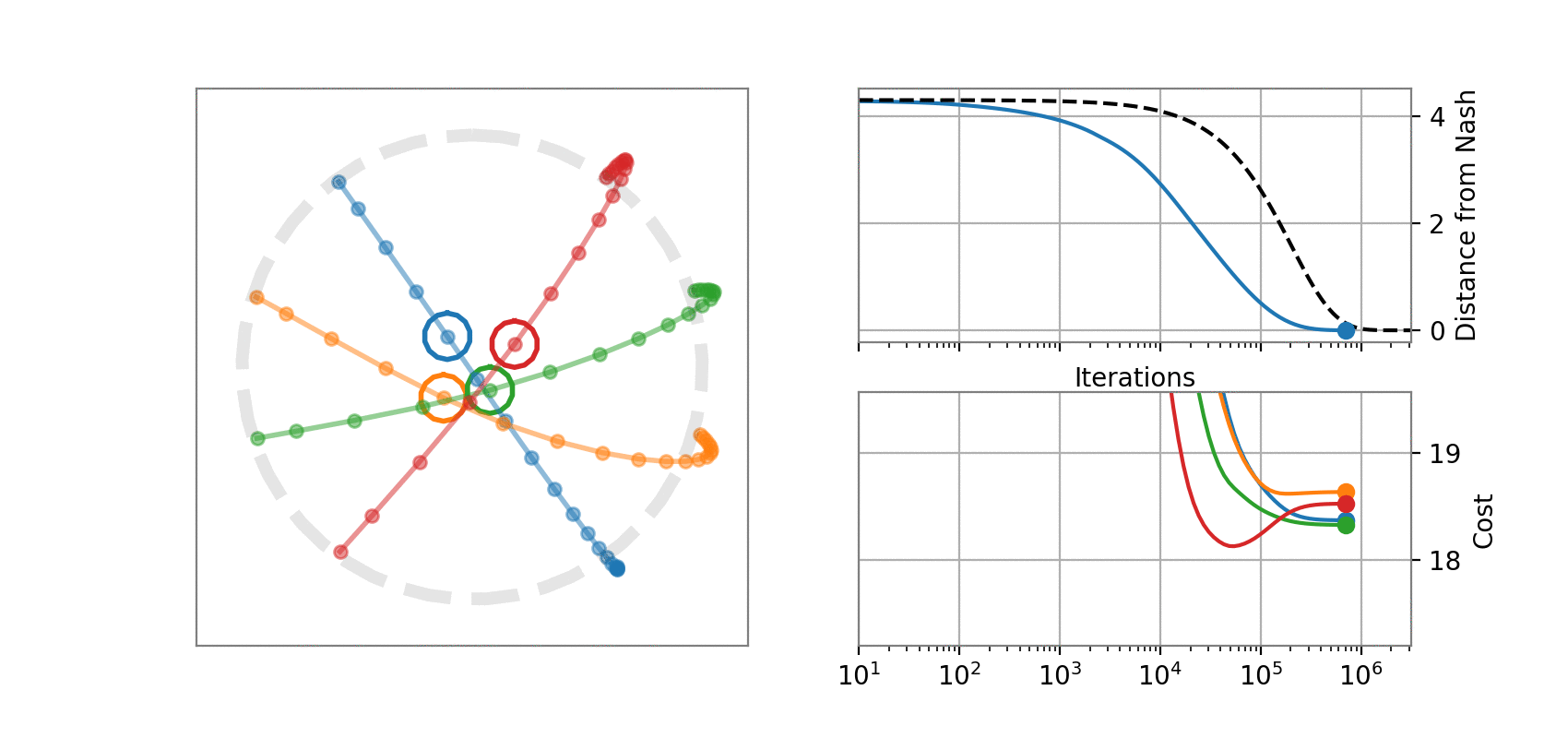
Updating feedback policies K1, K2 over time for game (f1, f2)
K1(k+1) = K1(k) - lr1*(df1/dK1)(K1(t), K2(t))
K2(k+1) = K2(k) - lr2*(df2/dK2)(K1(t), K2(t))
Updating feedback policies K1, K2 over time for game (f, -f)
K1(k+1) = K1(k) - lr1*(df/dK1)(K1(t), K2(t))
K2(k+1) = K2(k) + lr2*(df/dK2)(K1(t), K2(t))
Updating feedback policies K1, K2 over time for Stackelberg game (f1, f2)
K1(k+1) = K1(k) - lr1*(df1/dK1)(K1(t), argmin_K2 f2(K1(t), K2))
K2(k+1) = K2(k) - lr2*(df2/dK2)(K1(t), K2(t))