The following project serves as a proof of concept for a retrieval-augmented chatbot. This PoC primarily utilizes langchain for pipelining and incorporates open-source models from Hugging Face.
The model that are used are the following one:
- Embedding model: Distilbert
- LLM model: Mistral 7B Instruct
The principle of retrieval augmentation is to enhance the model's output by providing contextual information. In this project, I concentrated on using PDFs for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). The methodology necessitates in-memory storage for storing document embeddings, which are segmented into several parts. I chose an arbitrary division of 500 characters per embedding. This aspect could be refined by analyzing the model's performance with various hyperparameters. ChromaDB was selected for its user-friendliness and its seamless integration capabilities.
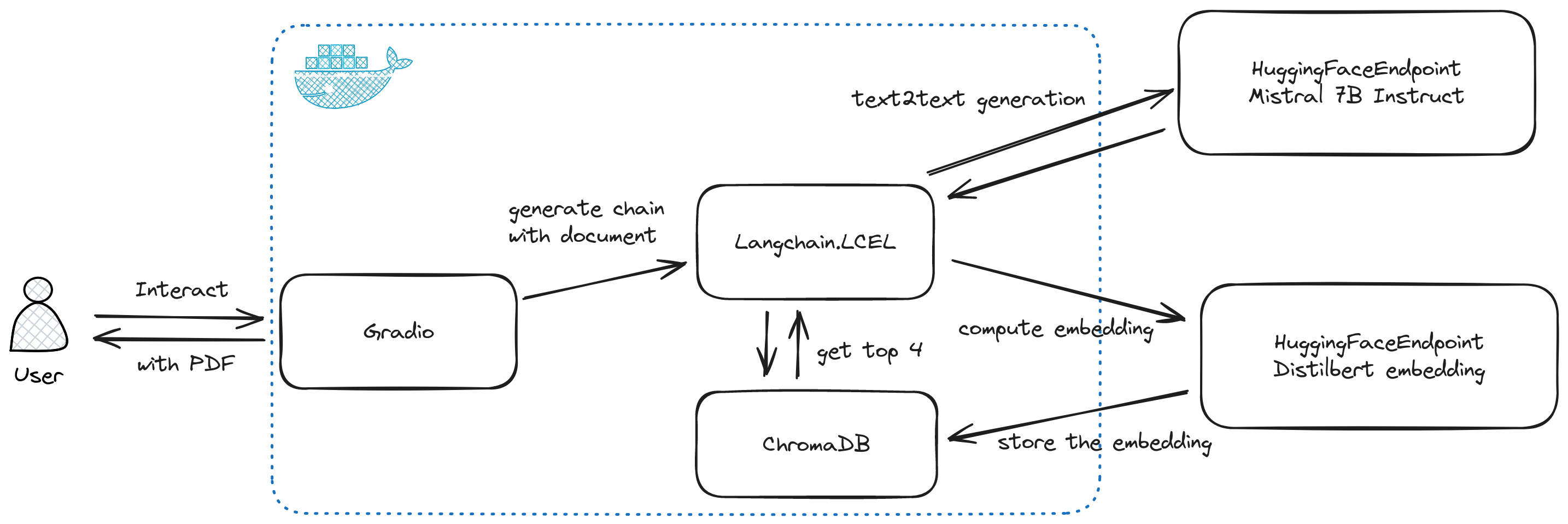
The project is deployable using docker compose, as it is packaged within a single Docker container. Initially, I considered using multiple Docker containers and Langserver, but I opted to keep it simple. This decision was due to the added complexity of transmitting files through the API and the need for additional storage accessible by multiple Docker containers. The following architecture provides an overview of the project.
The project can be easily run with docker Compose, but in order to function, a .env file must be present alongside the docker-compose.yml file with a key for Hugging Face. The format of the environment variable is as follows:"
HF_API_KEY=hf_<rest of the key>The following command will execute the docker-compose.yml
docker compose up -d
The UI will be available at the following address: http://localhost:7860/.
The file can be passed in additional input section.
Examples were provided in the data directory.
The LECL is a good way to test the dataset since it is a recent feature.
A good question to ask is:
- What is LECL ?
The second example is the paper Attention Is All You Need by Google.
Good questions to ask:
- What BLEU score does the model achieve?
- What is the composition of the encoder?
- On what data has the model been trained?
The project remains a proof of concept (PoC) that offers a straightforward implementation using Langchain, but it has several limitations and areas for improvement. The primary limitation is that embeddings are computed every time a request is made. Ideally, if the files remain unchanged, the embeddings do not need to be recomputed. However, this would require a different design pattern in the file handling logic. Currently, all embeddings are stored in ChromaDB.
A few potential improvements could be considered:
- Choosing a type of storage other than in-memory to enable persistence over time.
- Storing embeddings in a Q&A format could enhance the model's retrieval capabilities.
- Incorporating conversational history might be advantageous, as it allows for multiple questions to be asked about the same data. However, this would require managing conversation through the user interface.