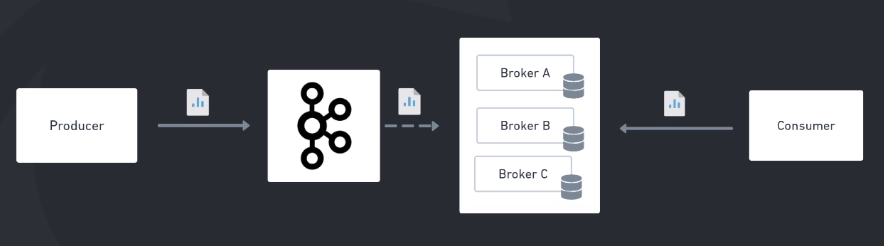
Files I produced during the Apache Kafka classes of my Microservices Full Cycle 3.0 course.
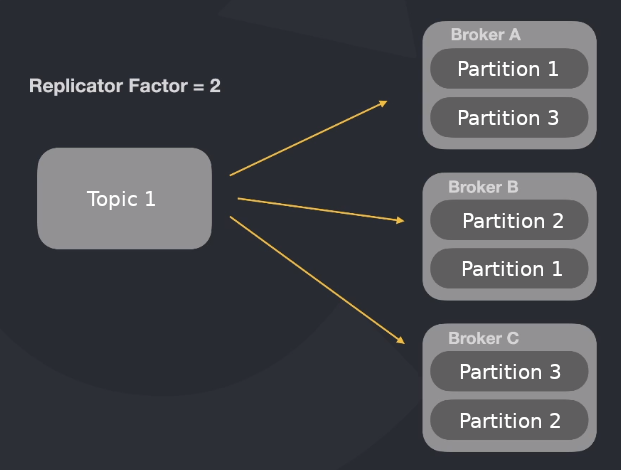
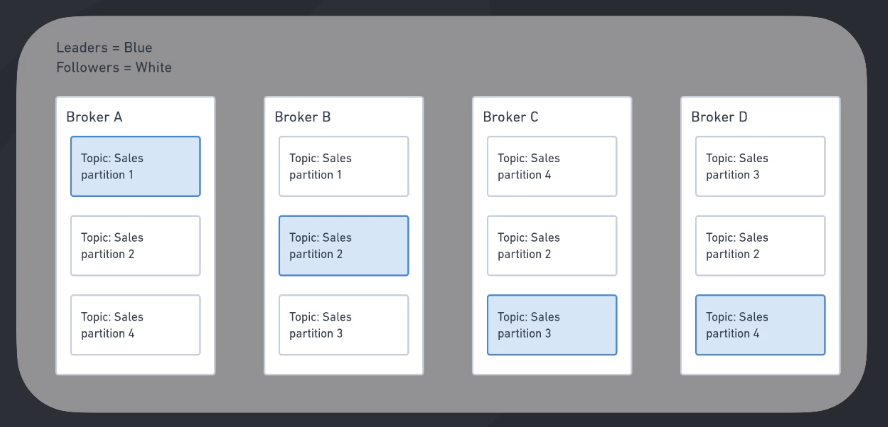
Usually you will want to have the topic partitions inside different brokers. So you can imagine that the partitions 1, 2 and 3 are in different machines. If one machine dies, you have 2/3 of the messages of this topic in other brokers.
You can also choose to duplicate the partitions and distribute them along all brokers using Replication Factor = 2. In this way, if one broker dies, you will have the same partition in another one.
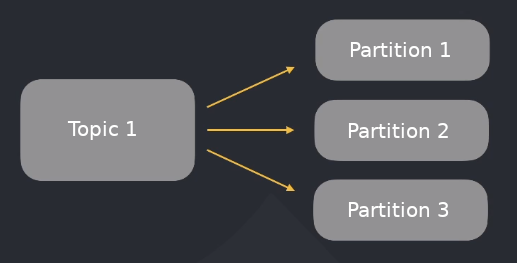
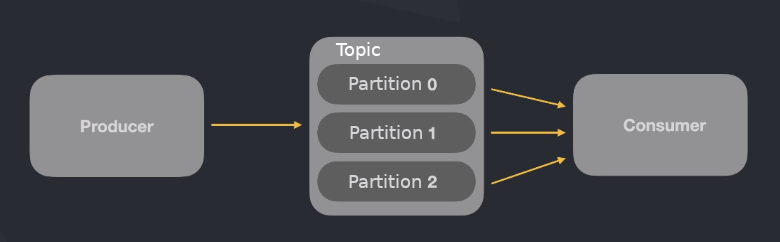
Each topic has associated partitions. Kafka saves messages sequentially to disk!
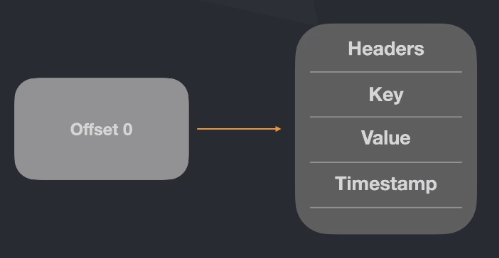
- Headers are metadata you can include in the message
- Key is used to send the same type of messages to the same partition
- Value is the payload itself
- Timestamp can be set by the producer or the kafka cluster when the message arrive
When you have Replication Factor greater than 1, Kafka will elect one of the partition replicas as the leader. That means the consumers will always read the leader messages.
This is useful because if one broker dies and it has a leader partition, Kafka will elect one of the partition replicas as the new leader.
Kafka comes with 3 types of message delivery guarantee:
- If you send a message with Ack 0, Kafka will return "None" instantly without delivery guarantee.
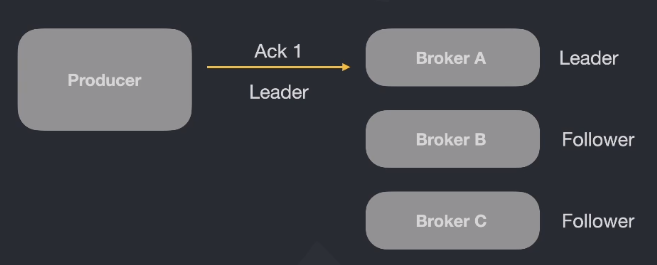
- If you send a message with Ack 1, Kafka will return "Leader" after the message is stored on it.
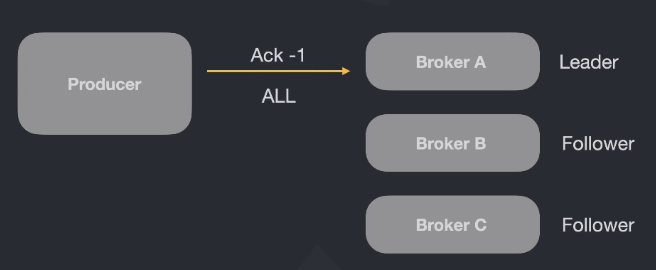
- If you send a message with Ack -1, Kafka will return "All" after the message is stored on the leader and the followers.
Kafka comes with other types of message delivery guarantee:
- "At most once" gives you the best performance but don't guarantee that all messages will be delivered.
- "At least once" gives you a moderate performance but can delivery two times the same message. So, you need to take care of not processing the same message in your system!
- "Exactly once" gives you the worst performance but delivery all messages exactly one time.
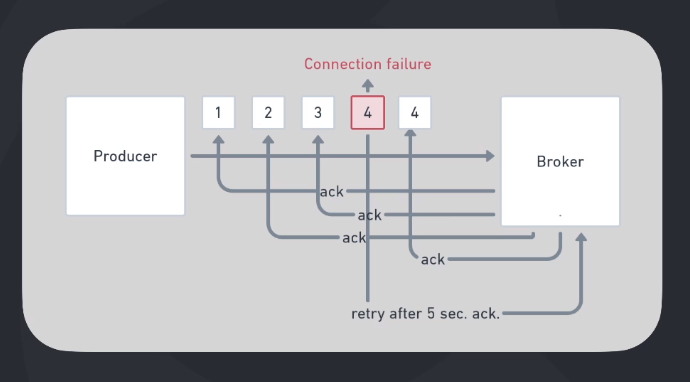
If a producer sends a message and it has a connectivity problem, maybe Kafka may have received and processed the message but the producer will send the message again when it come back.
This is a problem because the message will be duplicated. If you say a producer is idempotent, Kafka will notice the situation and discard one of the messages.
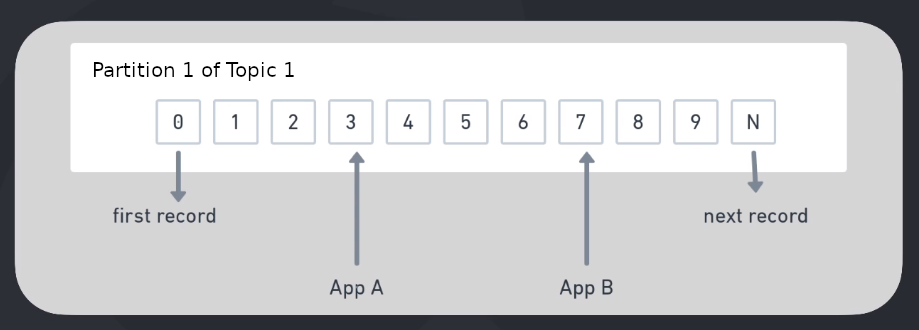
If only one consumer is consuming a topic, it will read from all partitions.
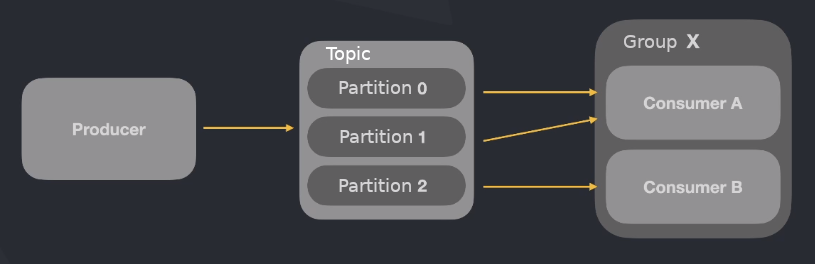
But you can create a group of consumers that read from the same topic. In this way, they divide the partitions between them.
docker-compose up -d
# After some minutes, go inside kafka container:
docker-compose exec kafka bashkafka-topics --bootstrap-server=localhost:9092 --create --topic=teste --partitions=3
kafka-topics --bootstrap-server=localhost:9092 --list
kafka-topics --bootstrap-server=localhost:9092 --describe --topic=testekafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server=localhost:9092 --topic=teste
# Let this terminal open. The consumer is listening to the topic!Open another terminal and run:
kafka-console-producer --bootstrap-server=localhost:9092 --topic=teste
# This will open a console that you can send messages via keyboard inputIf consumers are in the same group, they read different partitions of the same topic
To describe the consumer group, run:
kafka-consumer-groups --bootstrap-server=localhost:9092 --group=x --describeThe output should be similar to:
GROUP TOPIC PARTITION CURRENT-OFFSET LOG-END-OFFSET LAG CONSUMER-ID HOST CLIENT-ID
x teste 0 4 4 0 consumer-x-1-60e8ebe6-2814-4ec9-b5cd-b2283ce42ee3 /172.25.0.3 consumer-x-1
x teste 1 3 3 0 consumer-x-1-60e8ebe6-2814-4ec9-b5cd-b2283ce42ee3 /172.25.0.3 consumer-x-1
x teste 2 3 3 0 consumer-x-1-9a4a2b24-859f-4736-98b2-bb1988f90b3a /172.25.0.3 consumer-x-1
The Consumer IDs of the first two lines are equal (consumer-x-1-60e8ebe6-2814-4ec9-b5cd-b2283ce42ee3), so, the same consumer is reading from partition 0 and 1
kafka-topics --bootstrap-server=localhost:9092 --create --topic=goteste --partitions=3
kafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server=localhost:9092 --topic=gotestego get github.com/confluentinc/confluent-kafka-go/kafka
go mod tidy
go run cmd/producer/main.goAll consumer/producer properties: https://github.com/edenhill/librdkafka/blob/master/CONFIGURATION.md
Stop the consumer started with kafka-console-consumer and, in another terminal, run:
go run cmd/consumer/main.goIf you wanna test with multiple consumers, edit the client.id inside cmd/consumer/main.go and run another consumer.