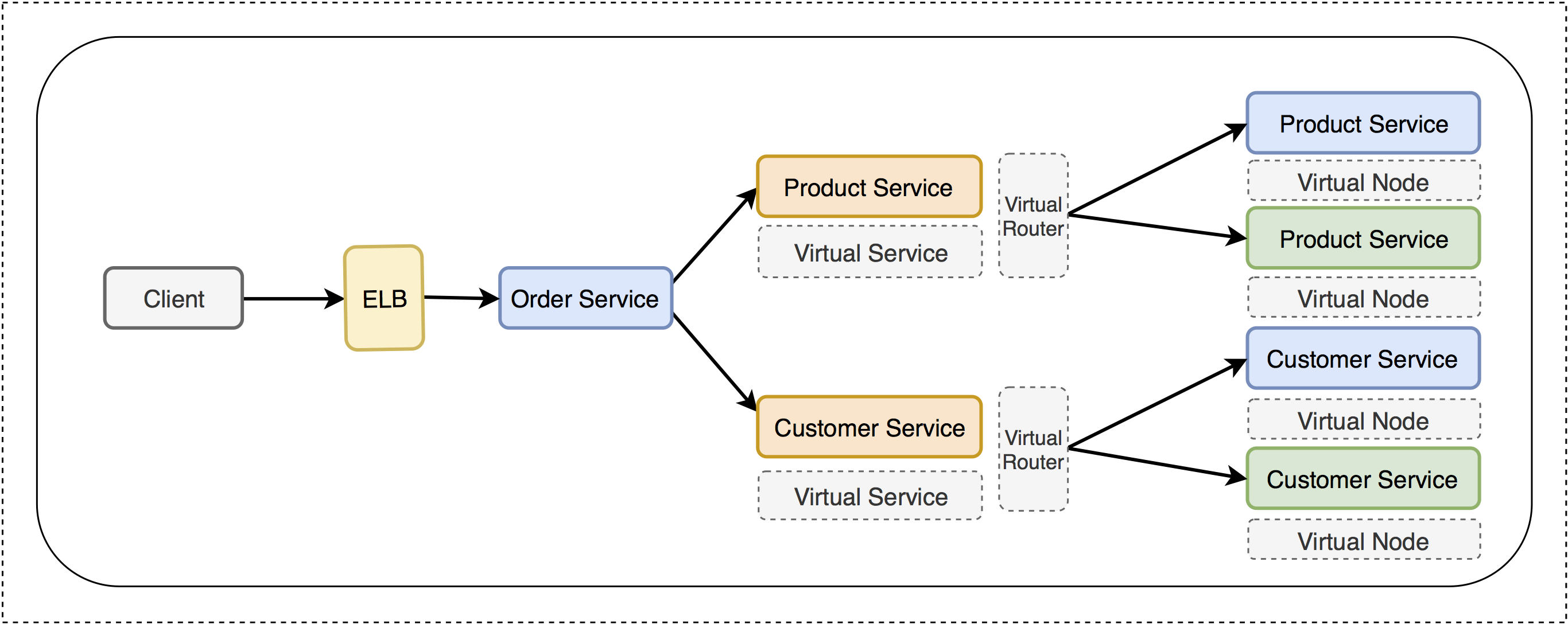
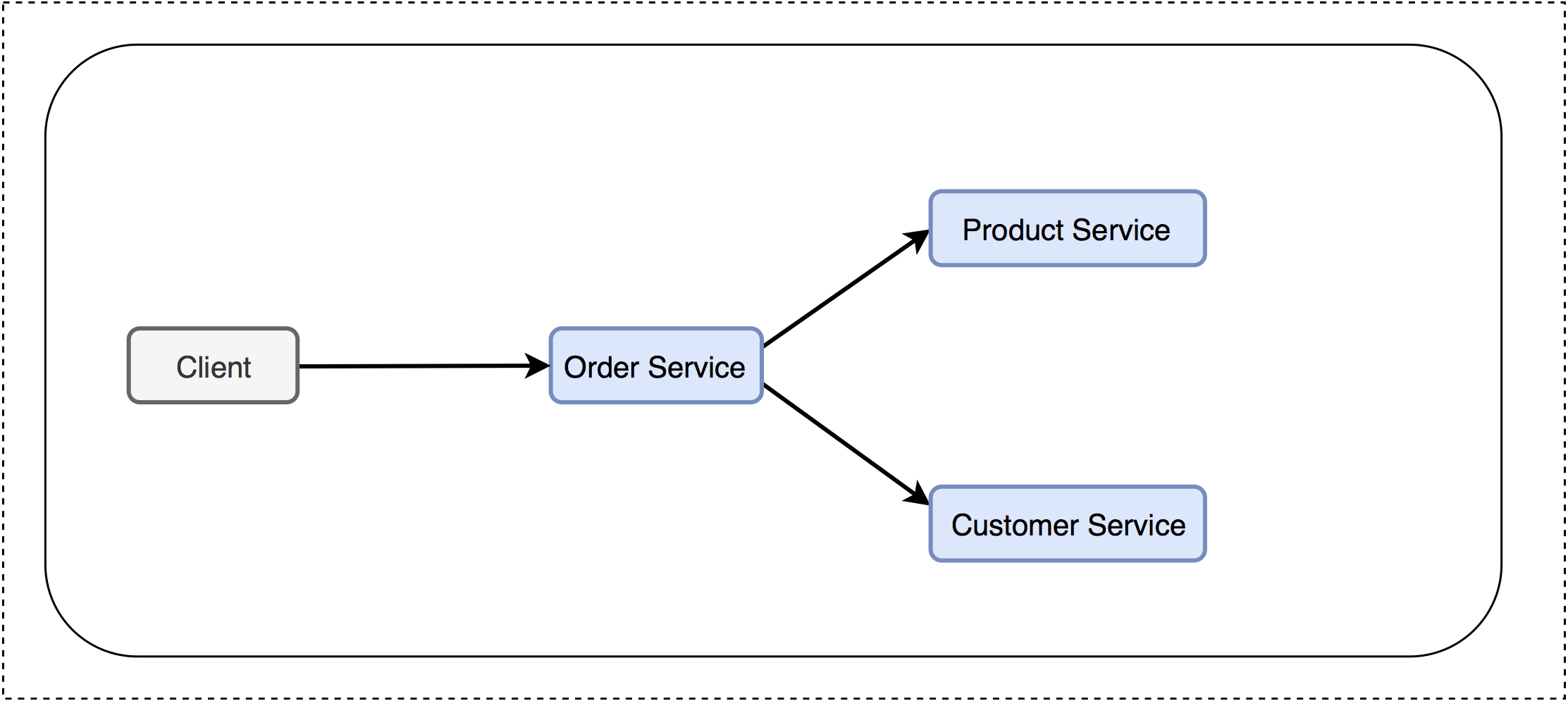
Reference Architecture of Canary Deployment with Amazon EKS and AWS Step Functions
(Diagram A)
- Order Service - A public-facing service API that query product service and customer service and response to the client
- Product Service - Internal service for product info lookup.
- Customer Service - Internal service for customer info lookup.
(Diagram B)
cd ./mesh
bash 01-create_mesh.sh This will create demomesh as the service mesh and virtual node, virtual router, and route for 3 services. And 2 virtual services for customer service and product service will be created as well.
Now we're gonna deploy v1 of the 3 services into the Amazon EKS cluster.
cd ../k8s
bash deploy_v1.sh
Response
deployment.extensions/product created
service/product created
deployment.extensions/customer created
service/customer created
deployment.extensions/order created
service/order created
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/customer ClusterIP 10.100.113.89 <none> 8080/TCP 4s
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.100.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 23h
service/order LoadBalancer 10.100.27.80 <pending> 80:31888/TCP 2s
service/product ClusterIP 10.100.230.95 <none> 8080/TCP 6s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.extensions/customer 1 1 1 0 4s
deployment.extensions/order 1 1 1 0 2s
deployment.extensions/product 1 1 1 1 6s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/customer-7976f6c89c-snwvg 0/2 PodInitializing 0 4s
pod/order-868bb64dcf-dx6pt 0/2 PodInitializing 0 2s
pod/product-74b96c4f46-g5rwr 2/2 Running 0 6s
The product and customer services will be exposed as ClusterIP while order service will be exposed with LoadBalancer type. It might take a few minutes before the ELB is ready.
Let's test the product service with kubectl port-forward like this:
$ kubectl port-forward deployment/product 8080:8080
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 8080
Forwarding from [::1]:8080 -> 8080
Open another terminal and cURL on localhost:8080
$ curl localhost:8080/
{"service":"Product","version":"1.0"}
Ctrl-c to terminate the port-forward terminal and test customer service
$ kubectl port-forward deployment/customer 8080:8080
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 8080
Forwarding from [::1]:8080 -> 8080
$ curl localhost:8080/
{"service":"Customer","version":"1.0"}
Both Product and Customer services are running with version 1.0 now.
Finally, let's test the Order service agains the ELB.
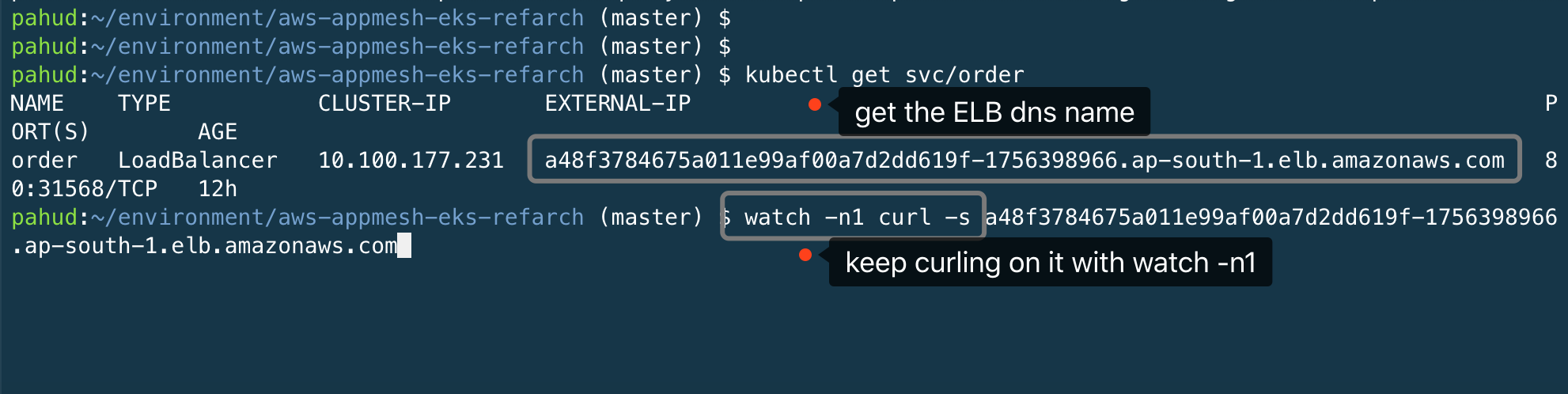
$ kubectl get svc/order
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
order LoadBalancer 10.100.27.80 a8d4ac145757e11e99af00a7d2dd619f-1485101703.ap-south-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:31888/TCP 6m7s
(please note your ELB DNS name should be different from above)
$ curl a8d4ac145757e11e99af00a7d2dd619f-1485101703.ap-south-1.elb.amazonaws.com
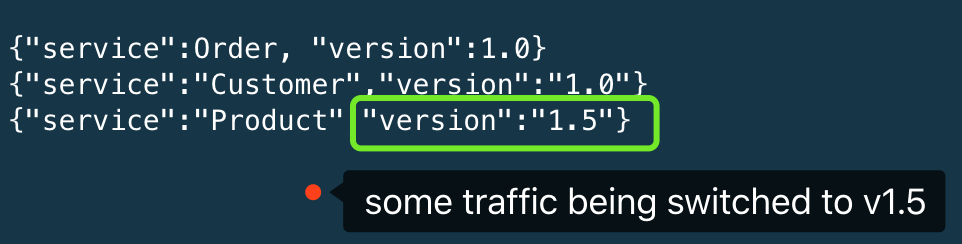
{"service":Order, "version":1.0}
{"service":"Product","version":"1.0"}
{"service":"Customer","version":"1.0"}
Behind the scene, the order service on receiving the request will call Product and Customer services in parallel and return all the response to the client. Make sure they all return version 1.0
Let's run this command with watch -n1 and keep this terminal open.
$ watch -n1 curl -s a8d4ac145757e11e99af00a7d2dd619f-1485101703.ap-south-1.elb.amazonaws.com
(This will execute the curl command every 1 second. You will see the respose is very consistent with all 1.0 version )
Let's say if we are planing to upgrade the product service to 1.5. So we deploy another 1.5 deployment:
Open another terminal and run:
cd ../k8s
bash deploy_product_v15.sh
Response
deployment.extensions/product-v15 created
service/product-v15 created
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/customer ClusterIP 10.100.113.89 <none> 8080/TCP 12m
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.100.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 23h
service/order LoadBalancer 10.100.27.80 a8d4ac145757e11e99af00a7d2dd619f-1485101703.ap-south-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:31888/TCP 12m
service/product ClusterIP 10.100.230.95 <none> 8080/TCP 12m
service/product-v15 ClusterIP 10.100.82.11 <none> 8080/TCP 2s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.extensions/customer 1 1 1 1 12m
deployment.extensions/order 1 1 1 1 12m
deployment.extensions/product 1 1 1 1 12m
deployment.extensions/product-v15 1 1 1 0 2s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/customer-7976f6c89c-snwvg 2/2 Running 0 12m
pod/order-868bb64dcf-dx6pt 2/2 Running 0 12m
pod/product-74b96c4f46-g5rwr 2/2 Running 0 12m
pod/product-v15-6db9ccbc58-tfmz2 0/2 PodInitializing 0 2s
A new standalone deployment named product-v15 is being deployed.
OK now we have product-v1 running with live traffic while product-v15 is also ready. Let's create a virtual node for product-v15 and start the canary deployment on it.
cd ../mesh
bash 02-update-mesh-v15.sh
(this will create a virtual node called product-v15-vn for the product-v15 service)
bash 03-deploy-prod-v15-canary.sh
This will update the product vertiaul route between v1 and v15 with different traffic weight.
"weightedTargets": [
{
"virtualNode": "product-vn",
"weight": 75
},
{
"virtualNode": "product-v15-vn",
"weight": 25
}
]
check ./mesh/v15/product-canary.json for details. You may update product-canary.json and run bash 03-deploy-prod-v15-canary.sh agan to apply the new traffic weight.
Now, let's switch 100% traffic to v1.5.
bash 04-deploy-prod-full.sh
Now the Product version is being steady at 1.5 because we've change the virtual route to switch 100% traffic onto product-v15.
Similarily, let's deploy a v2 for customer service with kubectl and canary deploy on it.
cd ../k8s
bash deploy_customer_v2.sh
Response
deployment.extensions/customer-v2 created
service/customer-v2 created
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.extensions/customer 1 1 1 1 28m
deployment.extensions/customer-v2 1 1 1 0 2s
deployment.extensions/order 1 1 1 1 27m
deployment.extensions/product 1 1 1 1 28m
deployment.extensions/product-v15 1 1 1 1 15m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/customer ClusterIP 10.100.113.89 <none> 8080/TCP 28m
service/customer-v2 ClusterIP 10.100.102.79 <none> 8080/TCP 2s
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.100.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 23h
service/order LoadBalancer 10.100.27.80 a8d4ac145757e11e99af00a7d2dd619f-1485101703.ap-south-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:31888/TCP 27m
service/product ClusterIP 10.100.230.95 <none> 8080/TCP 28m
service/product-v15 ClusterIP 10.100.82.11 <none> 8080/TCP 15m
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/customer-7976f6c89c-snwvg 2/2 Running 0 28m
pod/customer-v2-5648d668df-wfpgc 0/2 PodInitializing 0 2s
pod/order-868bb64dcf-dx6pt 2/2 Running 0 27m
pod/product-74b96c4f46-g5rwr 2/2 Running 0 28m
pod/product-v15-6db9ccbc58-tfmz2 2/2 Running 0 15m
Create a customer-v2 virtual node for it.
cd ../mesh
bash 05-update-mesh-v2.sh
Update the virtual route to canary deploy the v2.
bash 06-deploy-customer-v2-canary.sh
You might also update ./v2/customer-canary.json to set different weight of traffic and run again.
When you are ready, switch 100% traffic to customer service v2 now:
bash 07-deploy-customer-full.sh
Now we have 100% traiffic going to order v1.0, customer v2.0 and product v1.5 with zero impact on the service. All traffic is being routed as expected.
Chances are we might need an immediate rollback to previous all v1.0 version. We can just do it like this:
$ bash 08-rollback-v1.sh
This will update the virtual route of product and cutomer services to set 100% traffic going to the v1 virtual node. Immediately all traffic goes to 1.0 as below:
{"service":Order, "version":1.0}
{"service":"Product","version":"1.0"}
{"service":"Customer","version":"1.0"}
I hope you enjoy this demo. Moving forward, you may consider using aws/aws-app-mesh-inject to auto inject the sidecar proxy into your deployment to simplified the YAML configuration.
delete the mesh
bash 99-delete_mesh.sh
delete the k8s deployment
cd ../k8s
bash delete_all.sh
Response
deployment.extensions "product" deleted
service "product" deleted
deployment.extensions "customer" deleted
service "customer" deleted
deployment.extensions "order" deleted
service "order" deleted
deployment.extensions "product-v15" deleted
service "product-v15" deleted
deployment.extensions "customer-v2" deleted
service "customer-v2" deleted
That's all.
Have fun!
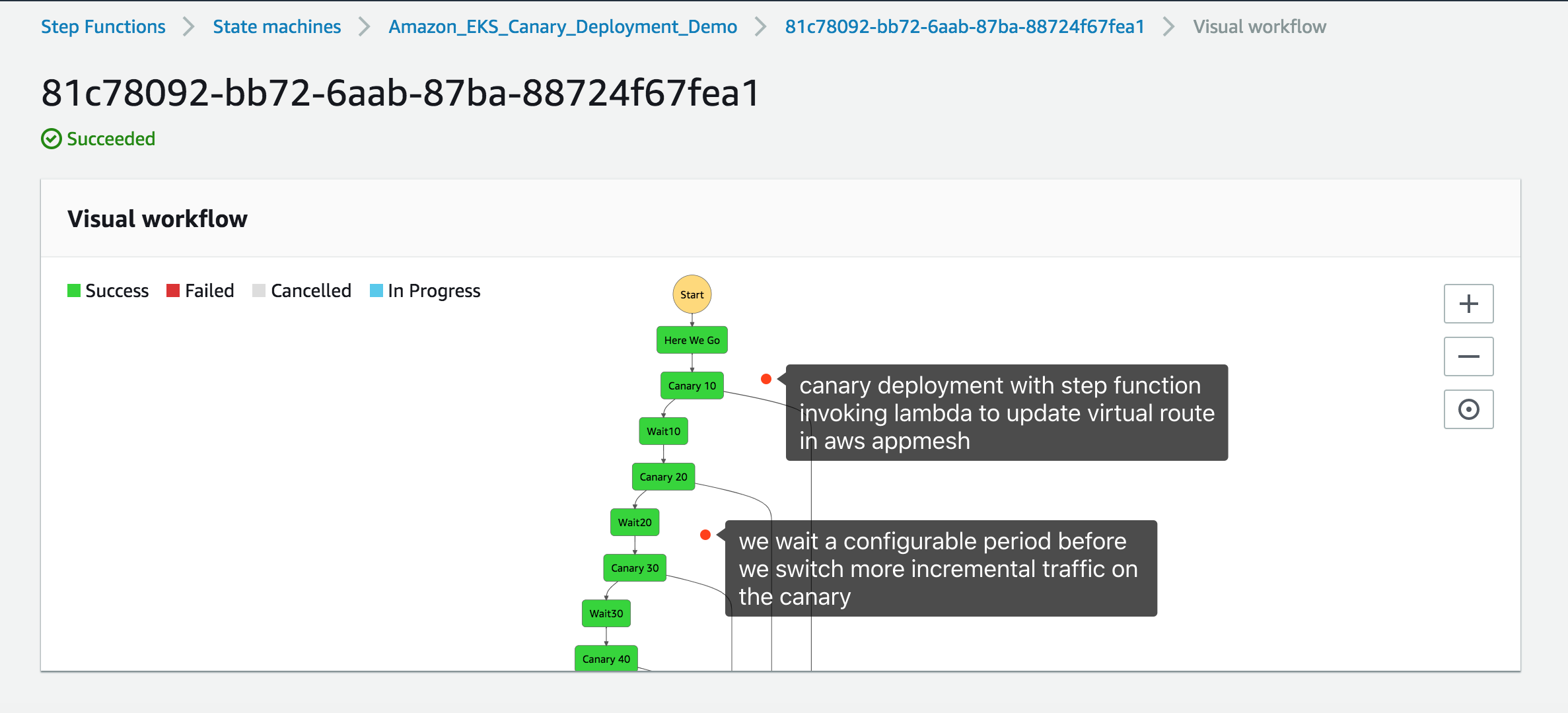
You may build your state machine with AWS Step Function for automated canary deployment. For example, 10% incremental traffic every 10 minutes until 100% or 10% initial canary traffic for 5min and immediately switch 100% after 10 minutes. AWS Step Functions gives you flexibility to define your canary deployment strategy while Lambda function being invoked by AWS Step Function can update the virtual route on AWS App Mesh for you.
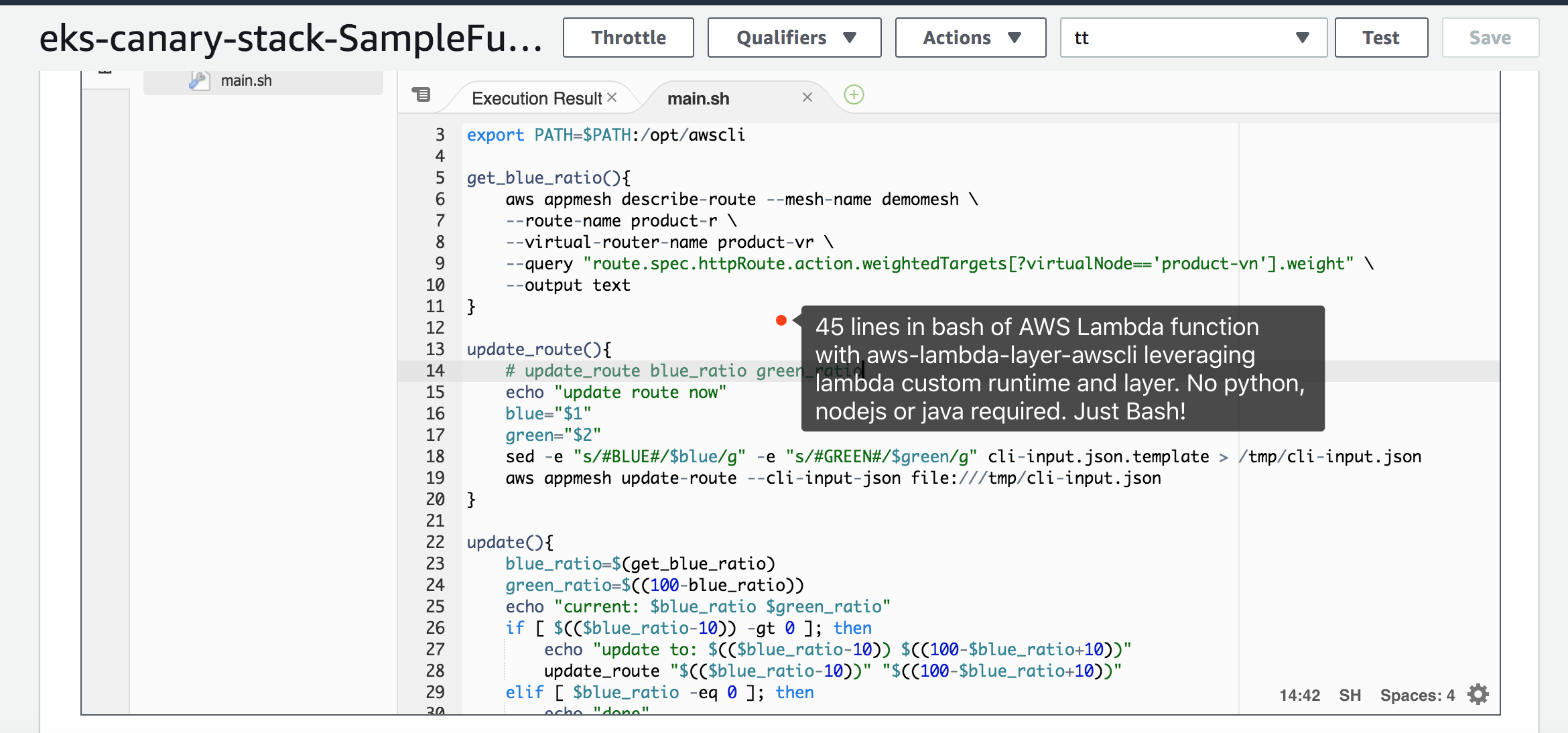
We are going to build our own aws-lambda-layer-awscli from scratch
cd stepfunc/lambda/
make build layer-zip layer-upload layer-publish
Response
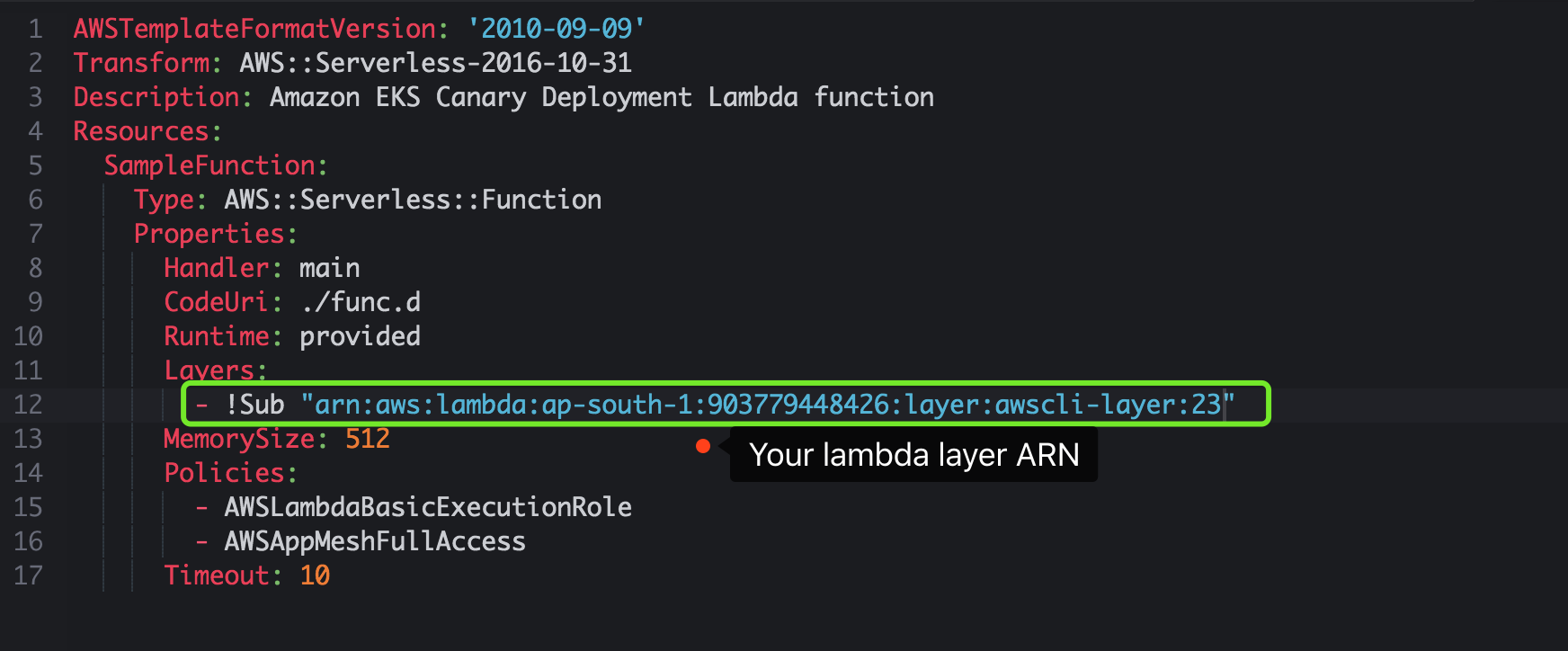
{
"LayerVersionArn": "arn:aws:lambda:ap-south-1:903779448426:layer:awscli-layer:23",
"Description": "awscli-layer",
"CreatedDate": "2019-05-14T05:18:40.388+0000",
"LayerArn": "arn:aws:lambda:ap-south-1:903779448426:layer:awscli-layer",
"Content": {
"CodeSize": 22977865,
"CodeSha256": "Tg6Yjr99B1MXRSs0uGhSWaTZKdLtob3nHPugfn0eIAs=",
"Location": "..."
},
"Version": 23,
"CompatibleRuntimes": [
"provided"
],
"LicenseInfo": "MIT"
}
Copy the LayerVersionArn value string.
update sam.yaml and configure the Layers with LayerVersionArn provided above.
OK. Let's publish our Lambda function.
update the Makefile and define your own parameters such as S3BUCKET and LAMBDA_REGION. Make sure your current IAM identity has read/write to S3BUCKET bucket and LAMBDA_REGION is the correct AWS region you are deploying to.
make sam-package sam-deploy
Response
Successfully packaged artifacts and wrote output template to file packaged.yaml.
Execute the following command to deploy the packaged template
aws cloudformation deploy --template-file /home/samcli/workdir/packaged.yaml --stack-name <YOUR STACK NAME>
Waiting for changeset to be created..
Waiting for stack create/update to complete
Successfully created/updated stack - eks-canary-stack
# print the cloudformation stack outputs
aws --region ap-south-1 cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name "eks-canary-stack" --query 'Stacks[0].Outputs'
[
{
"Description": "Function ARN",
"OutputKey": "FunctionArn",
"OutputValue": "arn:aws:lambda:ap-south-1:903779448426:function:eks-canary-stack-Function-8BYBEJIPXV6D"
}
]
Now your lambda function is deployed. Copy the FunctionArn value above.
Create a new step function with the provided spec JSON here. Make sure update the Task Resource arn to your own Lambda function arn above.
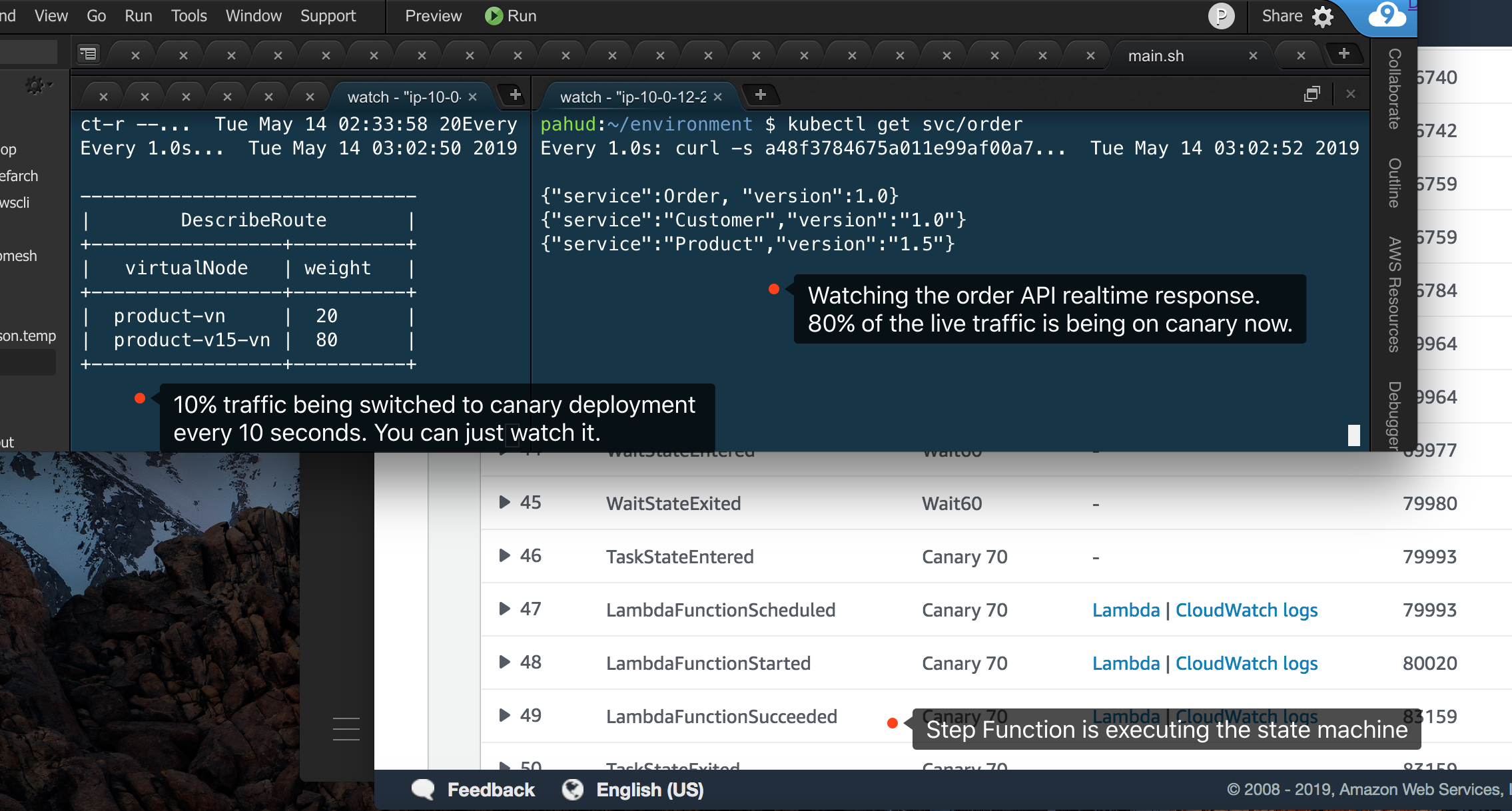
Before we execute the state machine, let's monitor our application with two seperate tabs or windows.
In the 1st tab we monitor the different weighted targets in the product virtual route with watch -n1. The result will refresh every second.
$ watch -n1 aws appmesh describe-route --mesh-name demomesh --route-name product-r --virtual-router-name product-vr --query "route.spec.httpRoute.action.weightedTargets" --output table
------------------------------
| DescribeRoute |
+-----------------+----------+
| virtualNode | weight |
+-----------------+----------+
| product-vn | 100 |
| product-v15-vn | 0 |
+-----------------+----------+
In the 2nd tab we keep curling on the ELB of the order service.
OK let's execute the state machine in step function. Watch the state machine in the step function console.
And also watch the changes of the two tabs.
In this demo, we walks you through how to build a customized Amaozn EKS canary deployment with AWS Step Function, AWS Lambda and AWS App Mesh. I hope you enjoy it and customize your own deployment logic based on it.