This repository contains a CDK template for deploying an Ethereum execution client, such as Geth or Erigon, and an Ethereum consensus client, such as Lighthouse or Prysm, on an EKS cluster across a configurable set of Availability Zones. This repository also demonstrates how to deploy a Prometheus metrics server and provision a Grafana dashboard with Amazon Managed Service for Grafana.
Two Grafana dashboards, and an Amazon CloudWatch dashboard are deployed to provide insights into the health of the EKS cluster, and the Ethereum clients.
The cluster nodes are deployed on r7g Graviton instances which provide the best performance to cost ratio for running Ethereum clients on AWS. Client storage is on Amazon EBS gp3 volumes. These settings can be easily configured within the deployment template. A Bastion host is also deployed from which we manage the EKS cluster. The EKS cluster is deployed in private subnets, while the Bastion host is in a public subnet.
A couple of things to note. First, in order to provision the Grafana dashboard, your AWS account needs to be part of an Organization, with IAM Identity Center enabled. Instructions to do these can be found below.
Second, the CDK creates an SSH key that you will use to connect to the Bastion host. The key is saved in Parameter Store. For security considerations, it's advised that you delete the key from Parameter Store after you have downloaded it.
Third, the walkthrough deploys this CDK in us-east-1 in Availability Zones us-east-1a, us-east-1b, and us-east-1c.
Fourth, due to the size of the Ethereum blockchain, client sync time can take a day, to a week, or even longer. The example below installs the Geth client which can be synced within a day using its snap sync feature.
With all that behind us, let's move on to deploying the solution.
The diagram below shows the primary components involved in the solution.
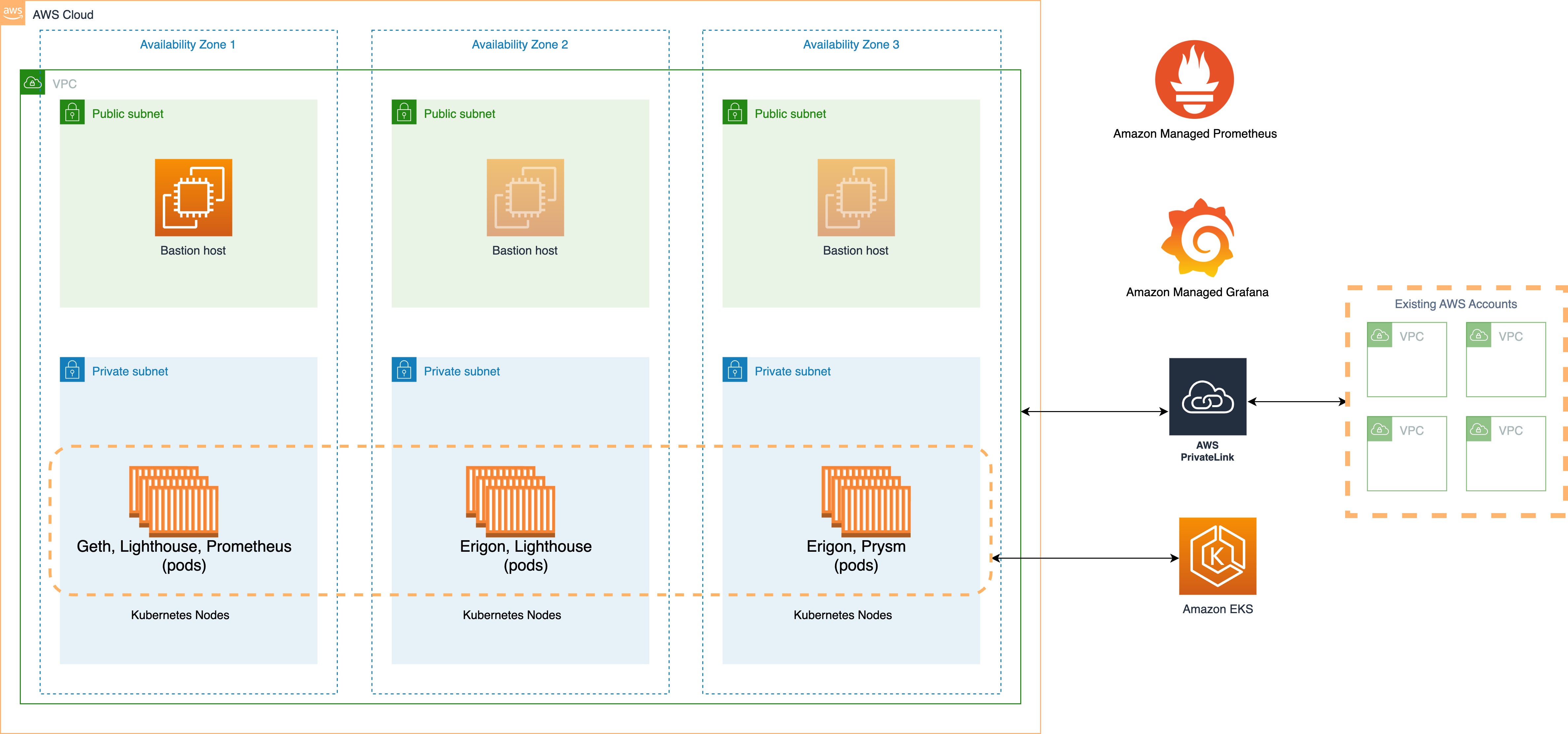
Before deploying, ensure your local environment is configured with your AWS credentials and the region to deploy to. See the CDK docs for more information.
git clone <this repo>
cd <this repo>
npm install
You need to have the CDK cli installed locally. Follow the steps here to install it. Note: version 2.81 of the CDK has a known issue that prevents all the stacks from being deployed at once. Please use version 2.71. If you are installing via npm, you can run npm install -g aws-cdk@v2.71.0.
Follow the steps here to configure your AWS credentials.
If this is the first time CDK is being deployed in this account, you need to bootstrap the account:
cdk bootstrap
An Organization is required to use Amazon Managed Service for Grafana. If the AWS account is not already part of an Organzation, you can create one on the Organization page.
In order to log into the Grafana dashboard, you need to create a user from the IAM Identity Center. Visit here to enable Identity Center, and to create a user.
cdk deploy -c cluster_name=ethereum-staking-cluster -c availability_zones=us-east-1a,us-east-1b,us-east-1c --app "npx ts-node --prefer-ts-exts bin/app.ts" --all --require-approval never
This will deploy multiple Cloudformation stacks. This will take around one hour to complete. Once the stacks have deployed, we can deploy the Ethereum clients.
We need to communicate with our EKS cluster from our Bastion host, as the cluster is not accessible via the public internet. We can either connect to the Bastion Host via Session Manager, or ssh from our local environment. In this walk through we will connect from our local environment.
- Download the ssh key we created in the solution. The key is in Parameter Store and has a naming convention like
/ec2/keypair/key-123abc... - Click the key name, and then click Show.
- On your local device,
cd ~/.sshand create a new file calledbastionHostKeyPair.pem. For example, withvi:vi bastionHostKeyPair.pem - Add the contents of the key you copied from Parameter Store into
bastionHostKeyPair.pemand save the file. - Set the correct file permissions:
chmod 400 bastionHostKeyPair.pem - Connect to the Bastion Host. You can find the public IP address of your Bastion Host on the EC2 console. You can find an example of how to connect on the
Connectpage of theEKS/BastionEKSHostinstance. It will be something like this:ssh -i ~/.ssh/bastionHostKeyPair.pem ec2-user@<public ip address of Bastion host>
In order to access the EKS cluster, we must first authorize our local environment. The Outputs tab of our EKS Cloudformation stack includes the command we can run to authorize our local environment to work with the cluster.
- From the Cloudformation Console, open the
EKSstack you just deployed, and browse the Outputs tab. Look for a Key calledEKSClusterConfigCommand. Copy the value. - From the Bastion host, paste this value, and click enter.
Your local environment is now authorized to communicate with your EKS cluster.
Next we need to configure your local environment's kubeconfig file for kubectl. We need to supply the name of our EKS cluster to the command below. The EKS cluster name can be found within the command you ran above for updating the kubeconfig file. You can also find it on the EKS console: aws eks update-kubeconfig --name <ethereum-staking-cluster-name> --region us-east-1
Helm should already be installed on the Bastion host. If you need to install it, you can follow the steps on the Helm website.
At this point we have a running EKS cluster and a Bastion host that is authorized to manage the cluster. Pat yourself on the back, you've already come a long way. From here on out, we are going to be installing the Ethereum clients.
We use Helm charts from Stakewise to deploy the clients.
From the Bastion host:
- We need to create our
storageClassthat our clients will use. We create a storageclass forgp3volumes. Copy the contents of thelib/storageClass.yamlfile into an identically named file, on the Bastion host, and then run:kubectl apply -f storageClass.yaml
- The execution and consensus client share a JWT to authenticate. We generate and set one in our environment.
export JWT=`openssl rand -hex 32`
We install three replicas of the Geth client.
helm repo add stakewise https://charts.stakewise.io
helm repo update
helm upgrade --debug --install geth stakewise/geth \
--set='global.replicaCount=3' \
--set='global.network=mainnet' \
--set='global.metrics.enabled=true' \
--set='global.metrics.serviceMonitor.enabled=true' \
--set='global.metrics.prometheusRule.enabled=true' \
--set='global.livenessProbe.enabled=false' \
--set='global.readinessProbe.enabled=false' \
--set='persistence.storageClassName=ebs-gp3-storageclass' \
--set='metrics.serviceMonitor.namespace=monitoring' \
--set='metrics.serviceMonitor.additionalLabels.release=kube-prometheus' \
--set='global.JWTSecret='${JWT} \
--create-namespace \
--namespace chain
Install Lighthouse, once the geth pods are up and running.
helm upgrade --debug --install lighthouse stakewise/lighthouse \
--set='global.network=mainnet' \
--set='global.JWTSecret='${JWT} \
--set='global.executionEndpoints[0]=http://geth-0.geth.chain:8551' \
--set='global.executionEndpoints[1]=http://geth-1.geth.chain:8551' \
--set='global.executionEndpoints[2]=http://geth-2.geth.chain:8551' \
--set='global.metrics.enabled=true' \
--set='global.metrics.serviceMonitor.enabled=true' \
--set='global.metrics.prometheusRule.enabled=true' \
--set='global.livenessProbe.enabled=false' \
--set='global.readinessProbe.enabled=false' \
--set='checkpointSyncUrl=https://beaconstate.ethstaker.cc/' \
--set='persistence.storageClassName=ebs-gp3-storageclass' \
--set='metrics.serviceMonitor.namespace=monitoring' \
--set='metrics.serviceMonitor.additionalLabels.release=kube-prometheus' \
--create-namespace \
--namespace chain
To monitor the pods and logs, these commands may be helpful:
kubectl get pods -A
kubectl logs geth-0 -n chain
kubectl describe pod geth-0 -n chain
kubectl exec -i -t geth-0 --container geth -n chain -- sh -- connect to the Container
Check /aws/containerinsights/<ethereum-staking-cluster-name>/application CloudWatch log group for the client logs. For checking EKS/System logs, check the following logs groups:
/aws/containerinsights/<ethereum-staking-cluster-name>/host
/aws/containerinsights/<ethereum-staking-cluster-name>/dataplane
For accessing Grafana, follow the steps here to configure AWS IAM Identity Center users/user groups.
Once you setup the users & obtain the access to Grafana dashboard, add the Amazon Prometheus as a data source by following the steps here.
Follow the steps here to import the following dashboards to visualize EKS & Geth metrics:
| Dashboard | ID/Json |
|---|---|
| Geth System Resources | dashboard.json |
| Geth Transaction Processing | dashboard.json |
| Lighthouse Consensus | dashboard.json |
| k8s-views-global | 15757 |
| k8s-views-namespaces | 15758 |
| k8s-views-nodes | 15759 |
| k8s-views-pods | 15760 |
| k8s-system-api-server | 15761 |
| k8s-system-coredns | 15762 |
| k8s-addons-prometheus | 19105 |
See CONTRIBUTING for more information.
This library is licensed under the MIT-0 License. See the LICENSE file.