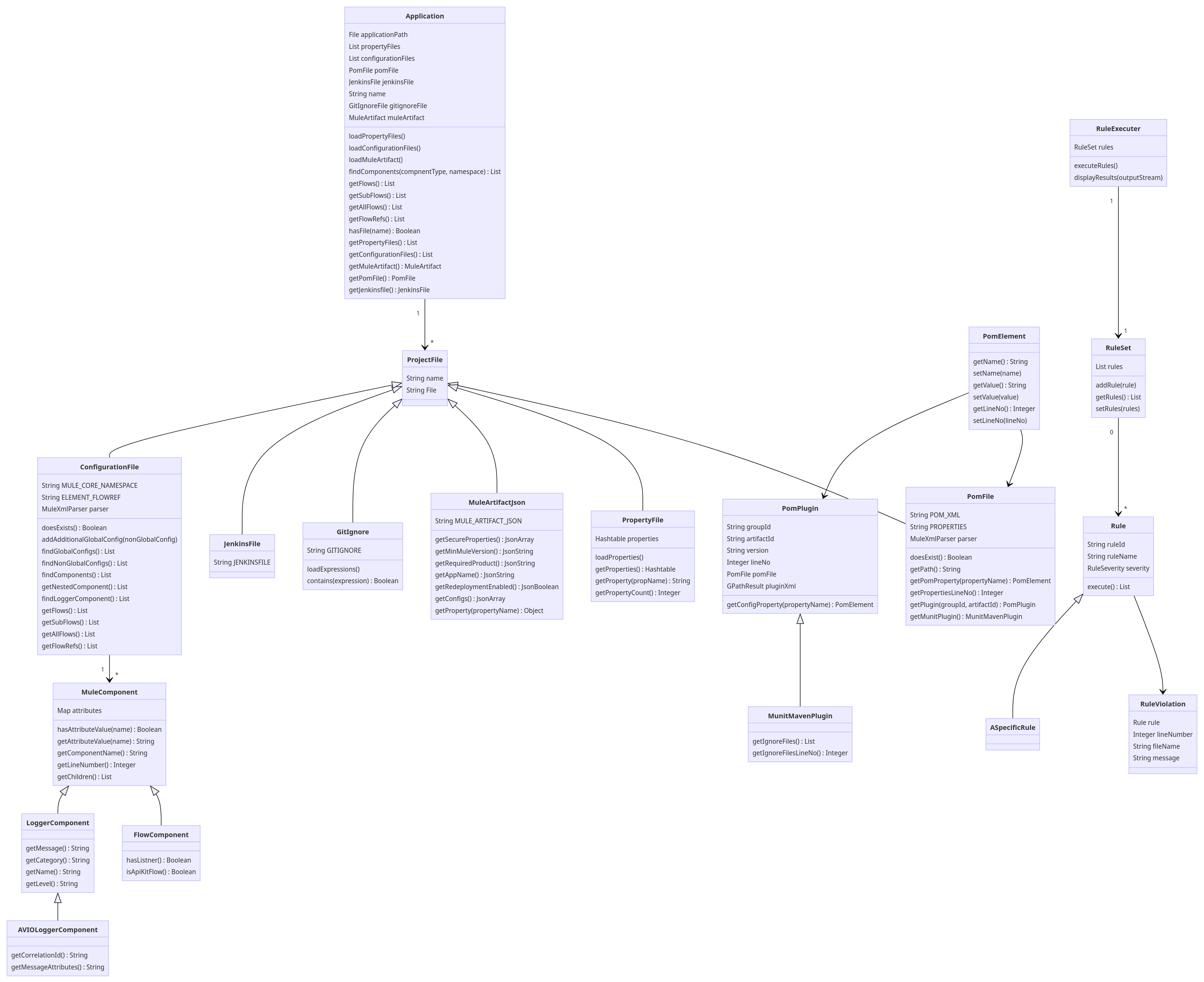
A linter is a tool that analyzes source code looking for patterns that don’t follow convention. Linting helps prevent errors and improve the overall quality of the code by following best practices. Lint tools are a form of static code analyzers. Some common code analyzers for Java are Checkstyle, FindBugs, and PMD.
The Mule Linter will enforce that all Mule projects are developed with a baseline set of rules. Some basic examples of rules that will be enforced, are the proper usage of property and pom files, useful logging messages, and standard project structure.
See Readme in mule-linter-maven-plugin module.
Project uses Gradle build system. Run following command to build all components in local -
./gradlew buildThe CLI distributions are generated in ./mule-linter-cli/build/distributions/.
Unzip/Untar the distribution. You can run the CLI from expanded files -
./bin/mule-linter-cliYou may move expanded distribution folder to other persistent location and add it on OS PATH, and then run cli from anywhere on the system.
When cloning add the 'recurse-submodules' flag
git clone --recurse-submodules
After cloning, update the submodules
git submodule update --remote
To build the project run -
./gradlew build
Generated Distribution and install in local -
./gradlew installDist
To release this module, follow these steps -
- Create a new branch from
mainwith naming convention -release/x.y.zeg.release/1.1.0 - Run one of the following command -
- Release current snapshot -
./gradlew -Dversion.prerelease= - Release next minor non-snapshot -
./gradlew -Dversion.prerelease= incrementMinor
- Commit the modified
version.propertiesmodified by above command - Create PR to main
- Once approved, JReleaser will release it to maven central
Rule Configuration uses a Groovy-DSL provided by Mule Linter. See AVIOGDSLRuleConfiguration.groovy for sample configuration.
Mule Linter Core is shipped with many rules. You can browse subpackages under com.avioconsulting.mule.linter.rule in https://avioconsulting.github.io/mule-linter/groovydoc/index.html.
Mule linter generates effective-pom.xml for the application using maven-invoker, and linter uses effective-pom.xml for executing the linter rulesets. Also, this requires Maven home location which can be passed using below options:
- Pass maven.home system variable when executing mule-linter
- Set MAVEN_HOME environment variable in the system executing mule-linter
Mule Linter's core library contains the GDSL file to support autocompletion in IntelliJ. To use that feature, com.avioconsulting.mule:mule-linter-core dependency must be added with provided scope in the project. provided scope will avoid maven packaging core into project artifact but still allow IntelliJ to detect the GDSL script from classpath.
Mule Linter provides a service provider interface (SPI) based mechanism to add custom rules and components. See SPI readme for details on how to use it. A Sample extension can be seen in mule-linter-spi-test module.
- Update code in mule-application-design.mmd and paste into live editor
- Click 'Download PNG' and save file into config/mermaid directory
CodeNarc is used to ensure quality in groovy code. The configuration file is located here. To execute run gradle check, and an output report will be generated.