This is a fork of Emily Bache's repository, which can be found here. The tests have been updated to use assertj.
Can you spot any code smells in this code? I'll give you a clue - a spot of Pol(l)ymorphism should improve matters!
Refactor this code, take small steps, run the tests often. See how small and beautiful you can make it.
This code is heavily inspired by one of the examples in Martin Fowler's book "Refactoring". It's a classic, and if it's not on your bookshelf already I suggest you treat yourself to a copy!
For this exercise you are going to get another opportunity to practice the refactoring rhythm. You'll also learn the steps to replacing the Switch Statement or Repeated Switches code smell.
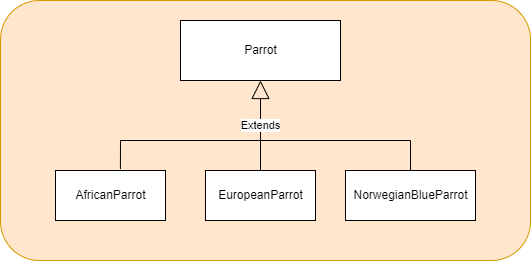
- Refactor into a polymorphic solution (see diagram below).
- Take small steps and run the tests often.
- Use automated refactorings as much as possible.
These are the steps to remove the Switch Statement (or Repeated Switches) code smell. They consist of two refacotrings. Replace Type Code with Subclasses & Replace Conditional with Polymorphism.
- Introduce a static creation method on the
Parrot Classthat wraps the construction of the parrot. Call it instead of the Parrot constructor from the tests. (You can use find and replace in a single step for this). - Make
typea self encapsulated field (a getter for the fieldtype). Look for the refactoring in the IntelliJ Refactoring Menu - Create sublcass for Parrot type (auotmated subclass creation is available from context actions menu off of the class name).
- Override type getter on the subclass, return the hardcoded type enum value.
- Create instance of subclass in creation method by checking provided type parameter in Parrot creation method.
- Repeat the previous three stps for the other two Parrot types.
- Remove creation of base Parrot in creation method (it is dead code now).
- Make Parrot class
abstract - Make
getType()methodabstract - Remove dead code (using Safe Delete from context actions menu)
What can get pushed down into child classes, what needs to stay in the parent Parrot class?
- Change access modifer for
getBaseSpeed()toprotected - Override
getSpeed()method inEuropeanParrotclass - Paste code from base class
getSpeed()European case into overridden method on child class. - Delete case code from switch in base class.
- Repeat the previous three steps for the other two parrot types (what methods and fields can be pushed down into base classes?)
- Push down fields and methods before overriding
getSpeed()in the child class (Push Members Down refactoring is available from the Refactoring Menu) - Remove dead code (context action menu has the Safe Delete refactoring)
- Make
getSpeed()abstract on the base Parrot class (requires makingParrotbase class abstract). - Remove dead code from classes (context action menu Safe Delete)
- Make sure to get rid of the
getType()method, thetypefield, and the corresponding overrides.
- Make sure to get rid of the
You Did it!