Process RINEX, SP3 and other GNSS files for orbit computation and geo-localization. Retrieve precise satellites and receptors position in a few lines of code.
This project will help you in your GNSS workflow. It provides tools for manipulating / converting GNSS dates (from datetime to Julian Day), readers for RINEX and SP3 for version 2 and 3.
Last but not least, gnsstools lets you correct GNSS orbits from raw files, and compute receptors' position.
| Development | Status | Feature |
|---|---|---|
| GNSS Time | finished |
|
| Rinex | in progress |
|
| Satellites | in progress |
|
The documentation is available online on readthedocs. You will find the code documentation of the whole package, examples and tutorials. Make sure you have read the documentation before opening an issue.
In addition of the examples and tutorials available on readthedocs, there is a list of jupyter notebooks. Each one focuses on a specific topic: reading files, retrieving orbits, computing receptor's position etc.
These instructions will show you the steps on how to install and use gnsstools straight from the box.
The package is available from PyPi. To install it, use:
pip install gnsstools
Alternatively, you can install the latest version from this repository. Download the package from github, then from the root folder:
python install .
To handles and convert time in different time system you should use the module gnsstime. It will create a time in the datetime.datetime format, and also process the provided arguments.
The gnsstime object behave exactly like a datetime one, as it inherits from it.
from gnsstools import gnsstime
# Create a datetime from GNSS information
# Year, Month, Day, Hour, Minute, Second, MicroSecond
date = gnsstime(18, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0)
date = gnsstime(2018, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0)However, the gnsstime is not type sensitive: you can provide arguments as a string, float or int.
If the argument is a string, it will convert it first as a float. Then, depending on the argument, it will extract the decimal and update the other arguments.
For example, if second=5.35, the number of seconds will be 5 and the number of microsecond 350000. Same for day=2.74 etc.
# Provide arguments as a string
date = gnsstime("18", "1", "1", "0", "0", "0")
date = gnsstime("2018", "01", "01", "00", "00", "00.000000")
# Provide argument as a float
date = gnsstime(2018, 1, 1, 5.933, 4.36, 33.231)You can also retrieve the number of days of the year, seconds of the day / weeks etc:
date = gnsstime(2018, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0)
doy = date.doy # Day of the year
woy = date.woy # Week of the year
sod = date.sod # Second of the day
sow = date.sow # Second of the weekYou can retrieve the number of seconds, days and weeks from a the GPS origin (GPS0) with:
date = gnsstime(2018, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0)
# From GPS0 defined at 1980-01-06T00:00:00 (UTC)
seconds0 = date.seconds0
days0 = date.days0
weeks0 = date.weeks0You can also retrieved the Julian Day:
date = gnsstime(2000, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0)
# Julian Day for year 2000
jd = date.jd
# Julian Day for year 1950
jd50 = date.jd50You can also create a gnsstime object from a Julian Day:
jd = 2451545.0
date = gnsstime.fromjd(jd)
jd50 = 2433282.5
date = gnsstime.fromjd50(jd50)Finally, you can extract modified Julian Day:
date = gnsstime(2000, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0)
# Modified Julian Day
mjd = date.mjdAgain, you can create a gnsstime object from a modified Julian Day:
mjd = 51544.5
date = gnsstime.frommjd(mjd)Load GNSS navigation and observation data as a pandas.DataFrame.
The supported format are:
.**o: Rinex 2 Observation,*O.rnx: Rinex 3 Observation,.**n,.**g: Rinex 2 Navigation,*N.rnx: Rinex 3 Navigation,.SP3: SP3
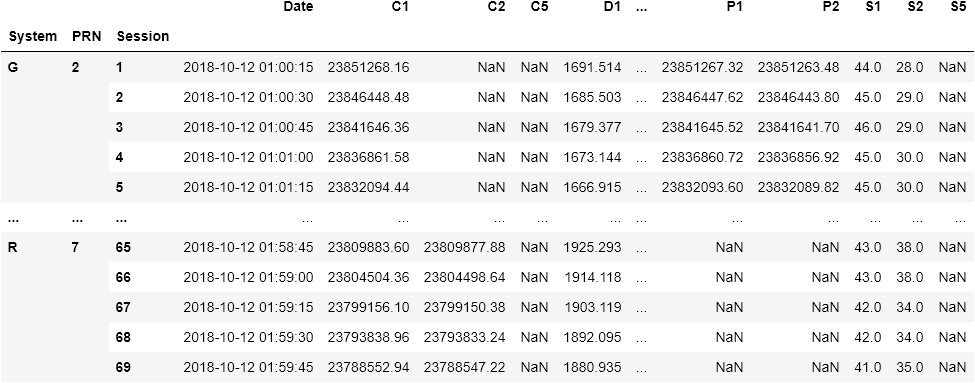
from gnsstools import rinex
filename = "data/edf1285b.18o"
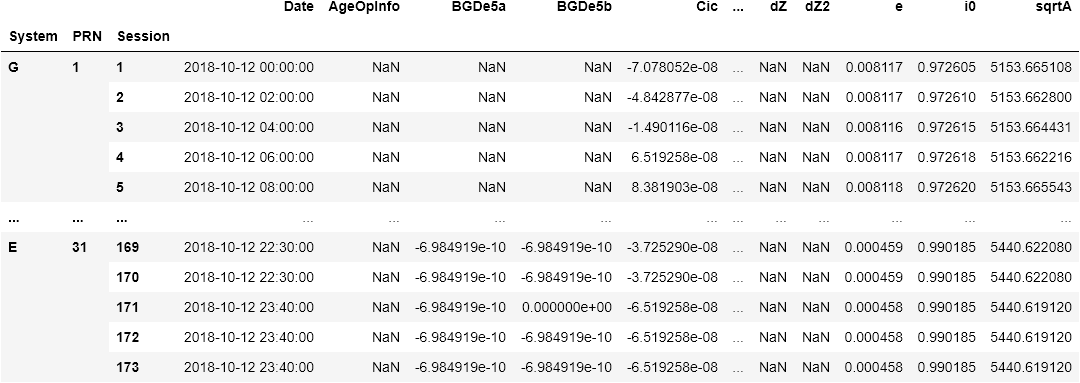
df = rinex.load(filename)from gnsstools import rinex
filename = "data/BRDC00IGS_R_20182850000_01D_MN.rnx"
df = rinex.load(filename)Once loaded, you select an ephemeris / satellite for a specific date with:
from gnsstools import gnsstime
date = gnsstime(2018, 10, 12, 0, 40, 15)
satellite = df.select("G", 2, date)If date is not part of the dataset df, it will return the closest satellite.
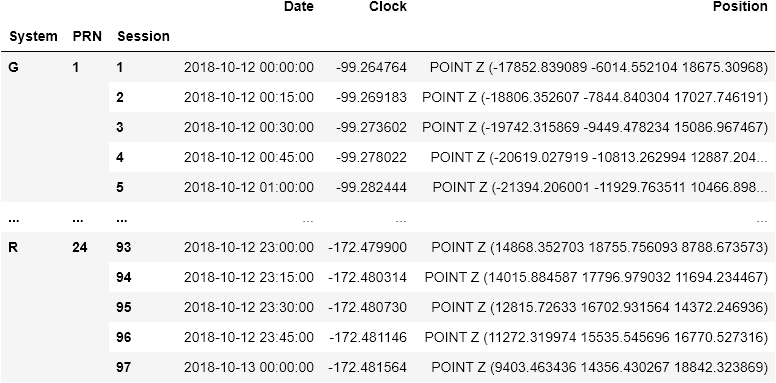
from gnsstools import rinex
filename = "data/COM20225_15M.SP3"
df = rinex.load(filename)Work in Progress
Work in Progress
- Hat tip to anyone whose code was used
- Inspiration
- References