- Container Instance
-
An AMI instance that is primed for running containers. By default, each Amazon instance uses Amazon ECS-Optimized Linux AMI. This is the recommended image to run ECS container service. The key components of this base image are:
-
Amazon Linux AMI
-
Amazon ECS Container Agent – manages containers lifecycle on behalf of ECS and allows them to connect to the cluster
-
Docker Engine
-
- Task
-
A task is defined as a JSON file and describes an application that contains one or more container definitions. This usually points to Docker images from a registry, port/volume mapping, etc.
- Service
-
ECS maintains the “desired state” of your application. This is achieved by creating a service. A service specifies the number of instances of a task definition that needs to run at a given time. If the task in a service becomes unhealthy or stop running, then the service scheduler will bounce the task. It ensures that the desired and actual state are match. This is what provides resilience in ECS.New tasks within a Service are balanced across Availability Zones in your cluster. Service scheduler figures out which container instances can meet the needs of a service and schedules it on a valid container instance in an optimal Availability Zone (one with the fewest number of tasks running).
This section will use AWS Console and show how to:
-
Create an ECS cluster
-
Create a task definition
-
Create a service using that task
-
Start tht service in the cluster
Let’s get started.
-
Go to AWS Console for ECS
-
Click on
Get Started, selectDeploy a sample application onto an Amazon ECS Cluster. This exercise does not require to deploy images to ECR and so unselect that. -
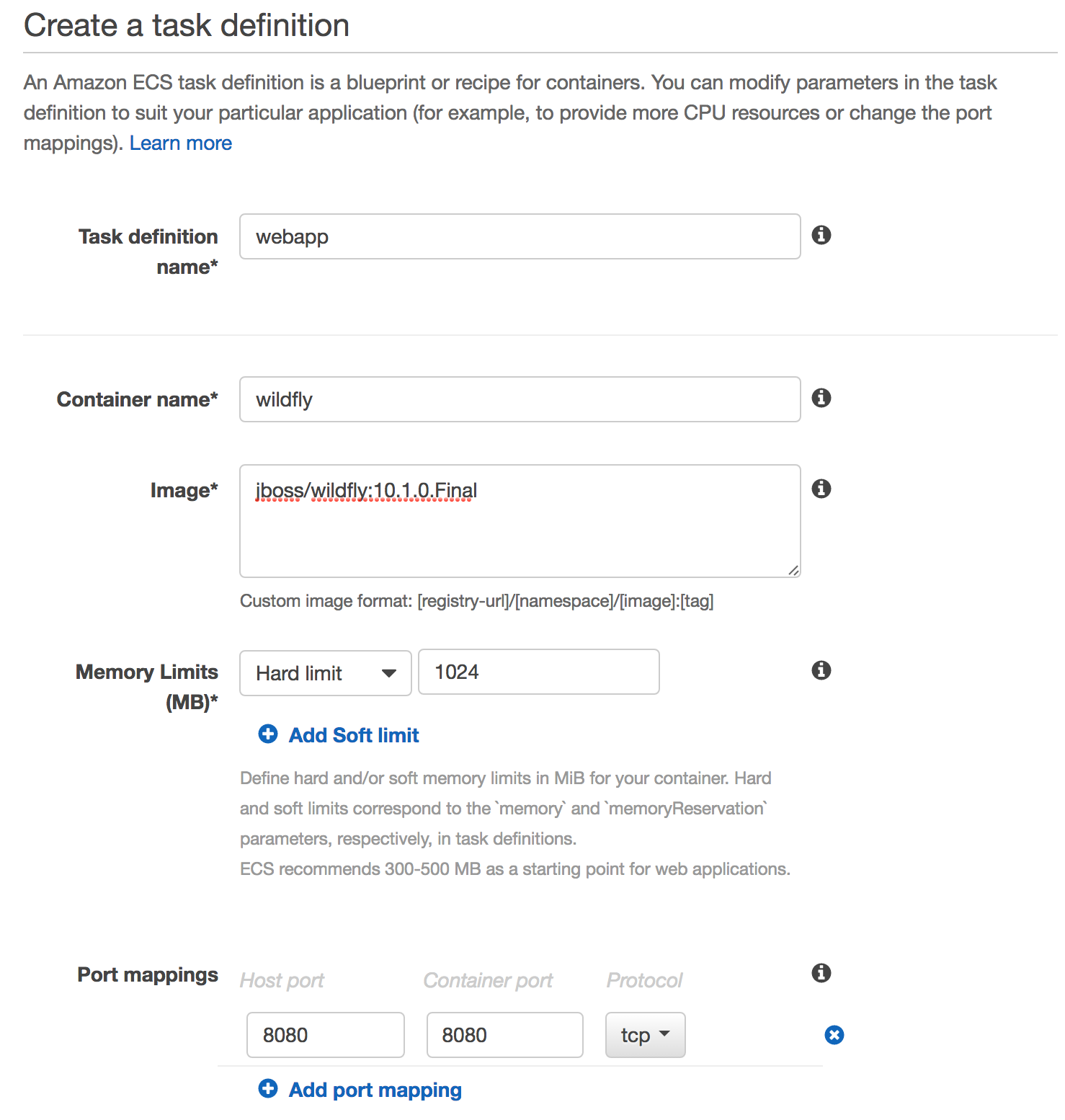
Create a task definition:
Click on
Next Step. -
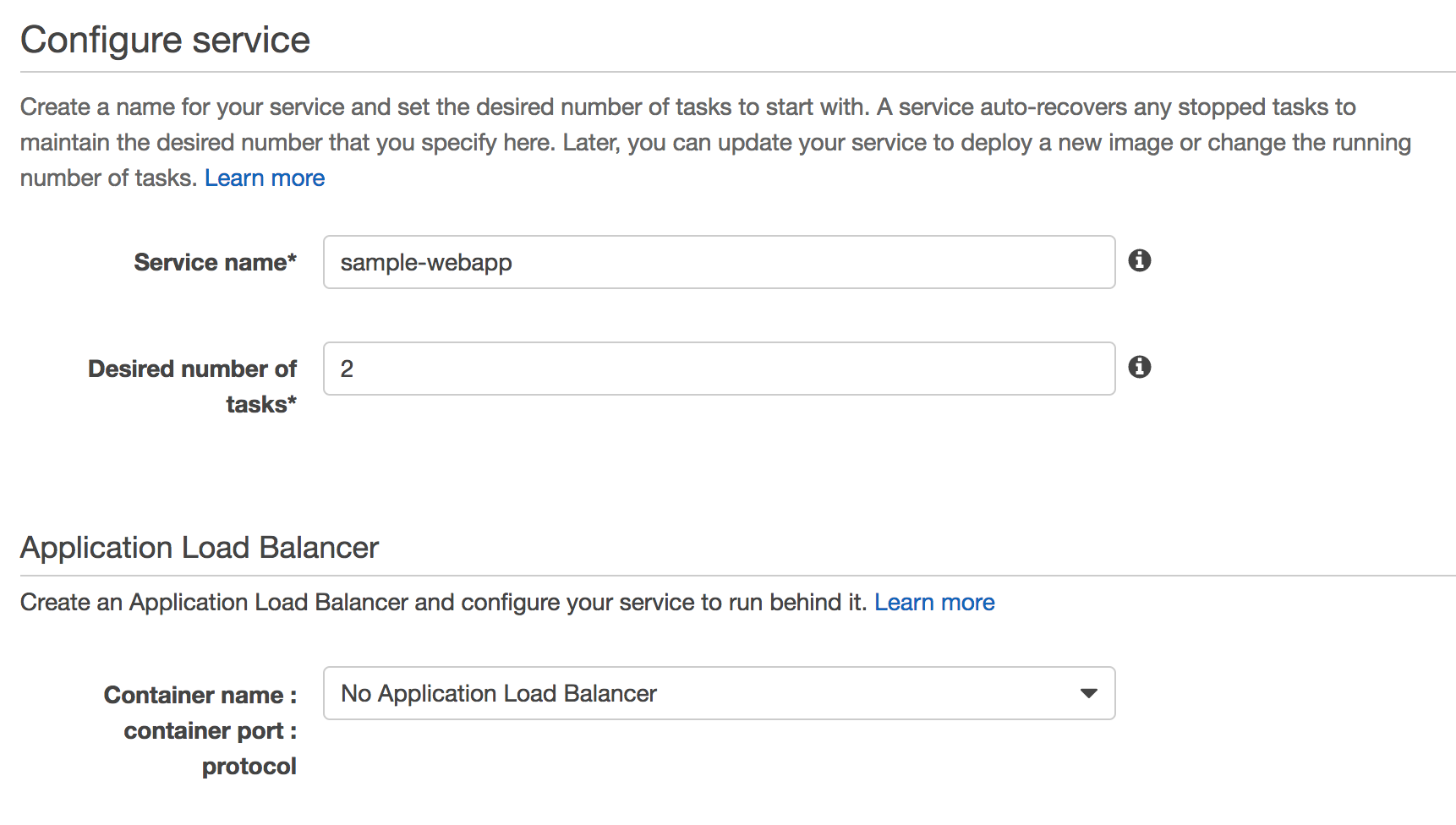
Create a service definition:
Click on
Next Step. -
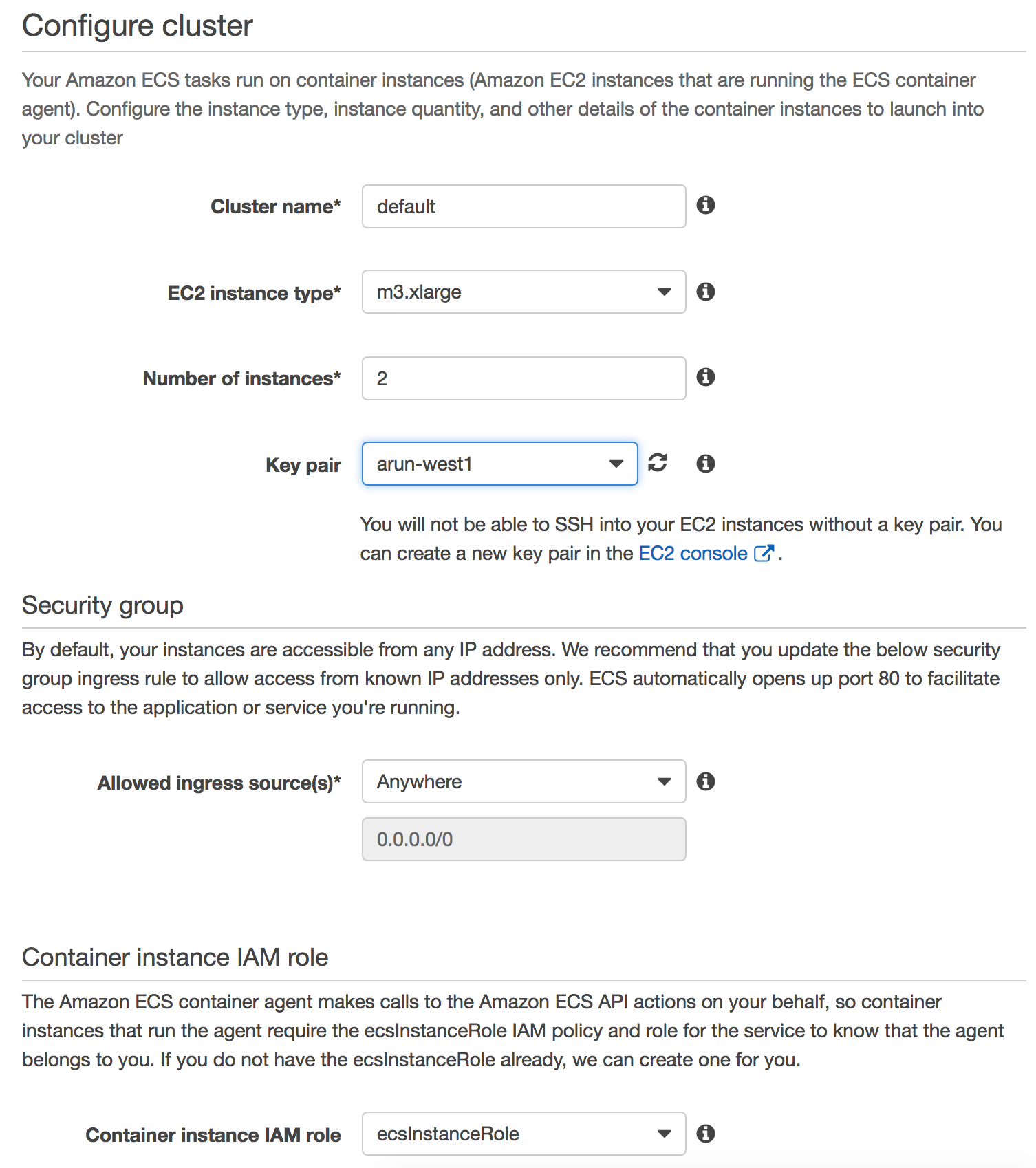
Configure cluster:
Click on
Review & Launch. -
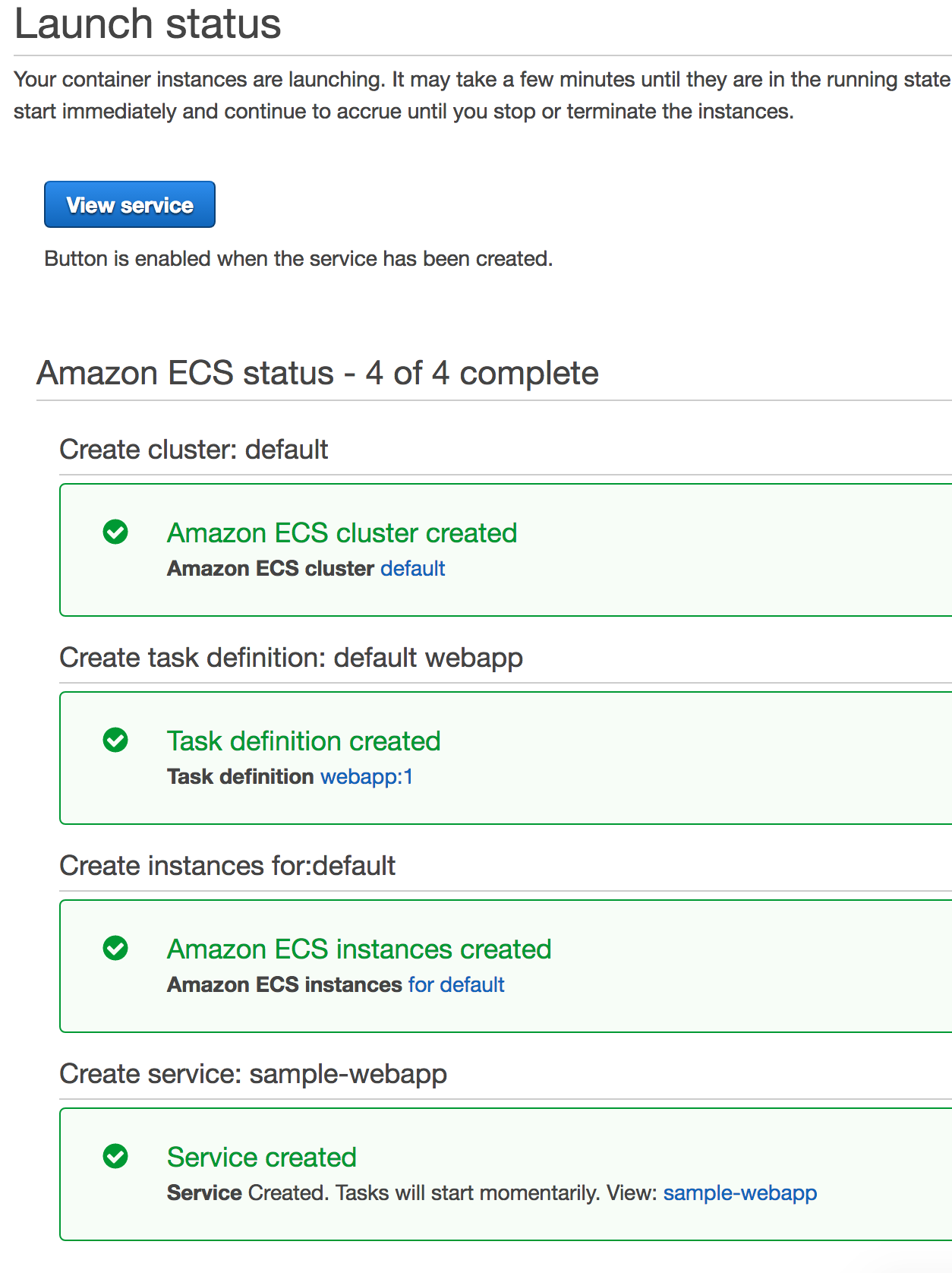
Click on
Launch instance & run service. It takes a few seconds for the cluster to be created and then it shows the following output: -
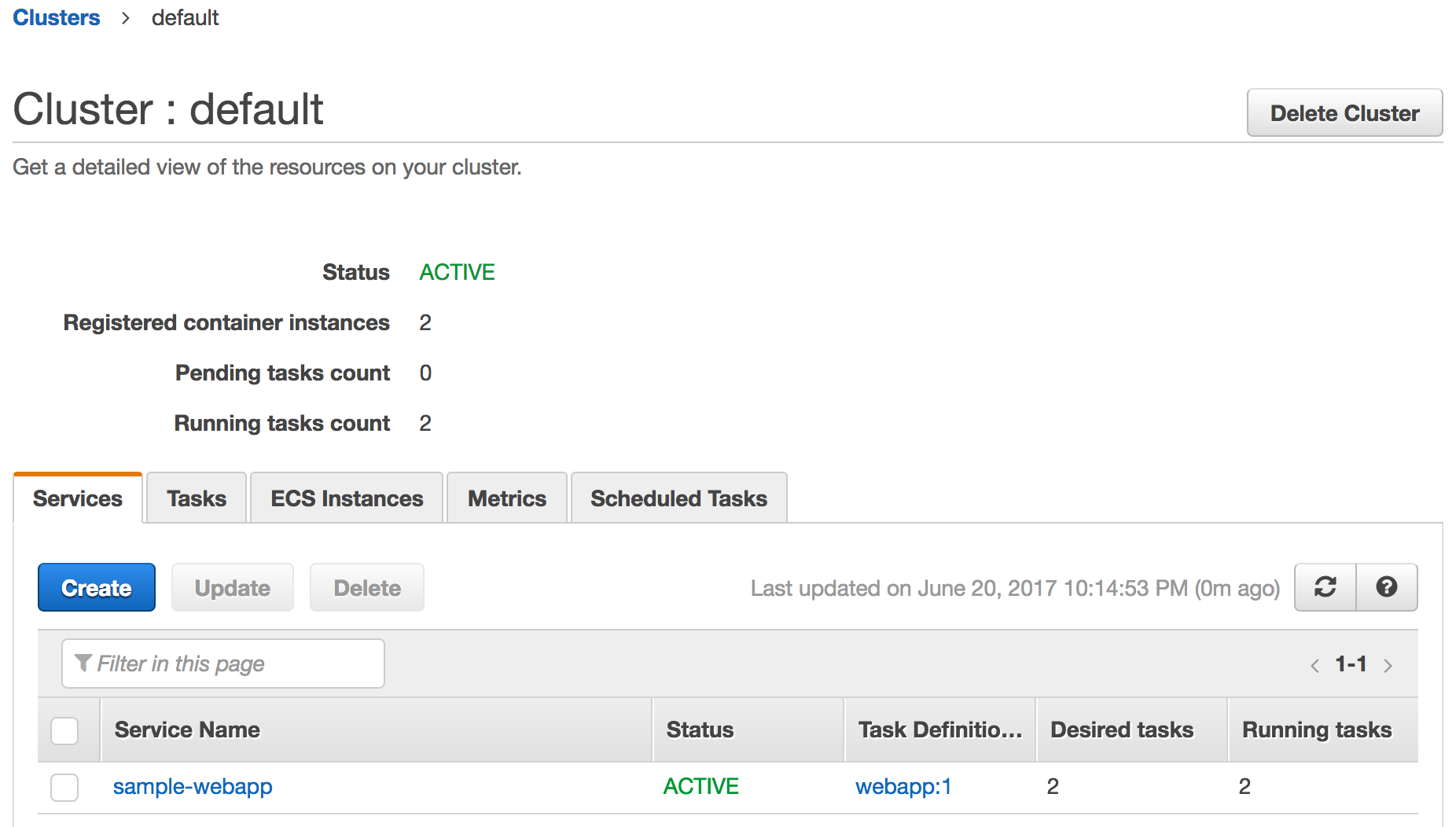
Wait for a few minutes for the Docker image to be downloaded to EC2 instances. Two task instances in the service are then started.
-
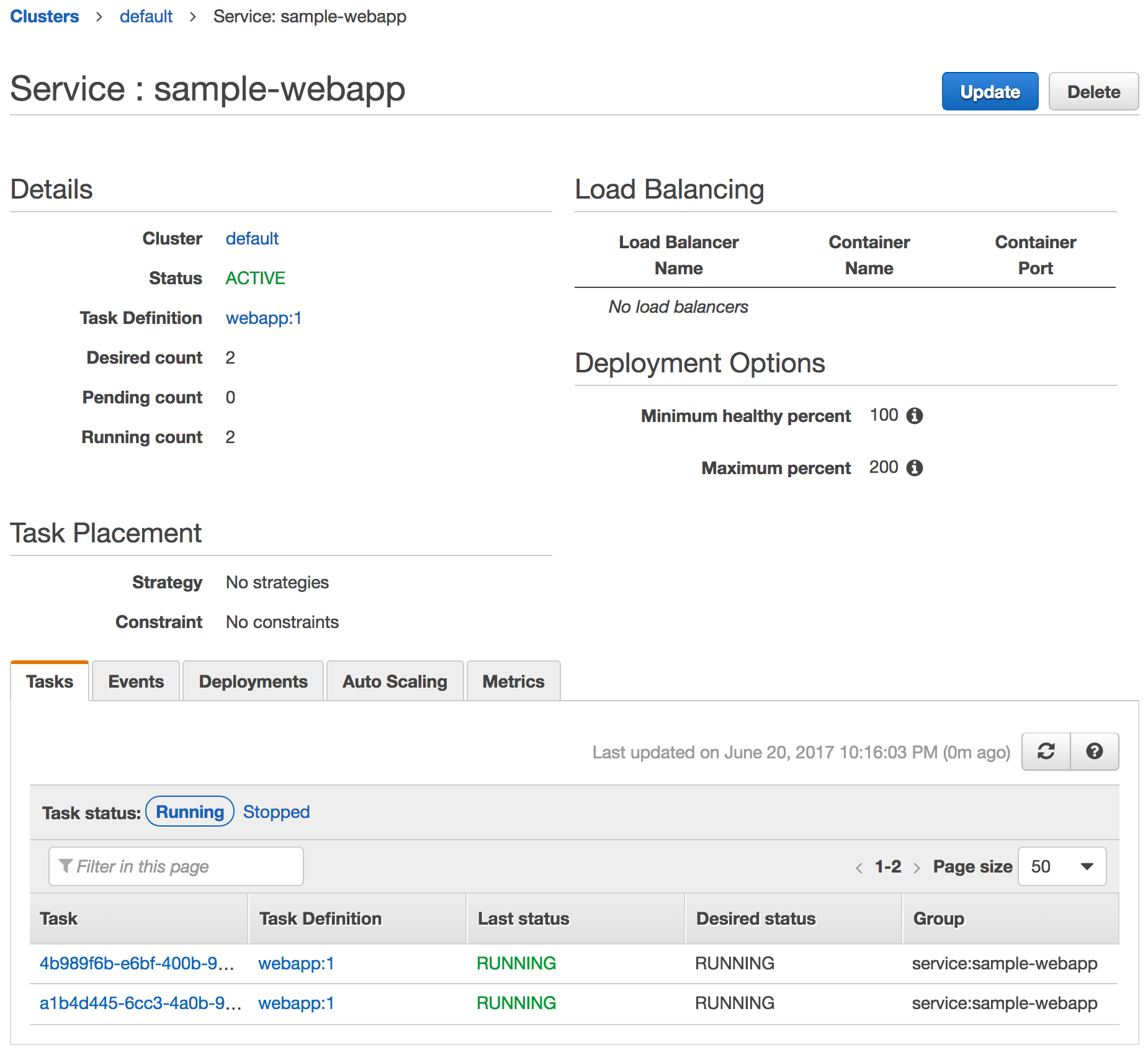
Click on the Service Name to see more details about the tasks running in this service:
-
Install AWS ECS CLI
curl -o ecs-cli https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazon-ecs-cli/ecs-cli-darwin-amd64-latest chmod +x ecs-cli-
Why there is no
brew install ecs-cli?
-
-
Create a cluster:
aws ecs create-cluster --cluster-name default ecs-cli configure --cluster default ecs-cli up --keypair arun-west1 --capability-iam --size 2 --port 8080 --instance-type m3.xlarge-
Why cluster create and configure is split between two CLIs?
aws ecs create-clusterfeels like a fake command. -
ecs-cliuses--helpwhere asaws ecsCLI useshelp -
Why
ecs-cli configureand thenecs-cli upinstead of adding--cluster-nameinup?
-
-
Register task definition:
aws ecs register-task-definition --cli-input-json file://./wildfly-task.json -
Create service:
aws ecs create-service --service-name webapp-service --task-definition webapp --desired-count 1 -
Get running count of the tasks in the service:
aws ecs describe-services --services webapp-service | jq .services[0].deployments[0].runningCount -
Scale service to 0:
aws ecs update-service --service webapp-service --desired-count 0 -
Delete service:
aws ecs delete-service --service webapp-service
Launch an automatically named ECS cluster in a region of your choice:
aws cloudformation deploy \
--template-file cloudformation/ecs-cluster.yml \
--region <region> \
--stack-name <stack name> \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAMCAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM allows to create IAM policies with names. This will create a CloudFormation stack and an ECS cluster with <stack name>.
A typical usage will be:
aws cloudformation deploy \
--template-file cloudformation/ecs-cluster.yml \
--stack-name default \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAMNote that the stack defaults to launching two micro instances. If you want to launch more instances or instances of a different type you must provide parameter overrides:
aws cloudformation deploy \
--template-file cloudformation/ecs-cluster.yml \
--parameter-overrides DesiredCapacity=3, MaxSize=5, InstanceType=m4.xlarge
--stack-name default \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAMFollow the steps from https://github.com/arun-gupta/ecs-workshop#create-service-and-task.
-
Build a Docker Image
-
Push and Pull images to EC2 Container Registry using Maven