Using Hexagonal (Ports & Adapters) Architecture & TDD
- Java 17
- AWS Lambda
- Amazon API Gateway
- Spring boot 2.6.14
- Micronaut 3.9.1
- Quarkus 3.1.0.Final
- Lombok
- Maven
- DynamoDB Local (docker container amazon/dynamodb-local:latest)
- org.testcontainers
- Junit 5
- npm
- jq (On Amazon Linux 2 run: 'sudo yum install jq' )
- Artillery (On Amazon Linux 2 run: 'npm install -g artillery@latest' )
- faker-js
- AWS SAM CLI
The Serverless Application Model Command Line Interface (SAM CLI) is an extension of the AWS CLI that adds functionality for building and testing Lambda applications. It uses Docker to run your functions in an Amazon Linux environment that matches Lambda. It can also emulate your application's build environment and API.
To use the SAM CLI, you need the following tools.
- SAM CLI - Install the SAM CLI
- Java 17 - Install the Java 17
- Maven - Install Maven
- Docker - Install Docker community edition
This application is a user microservice exposing REST endpoints for:
- Registering a new user,
- Fetching existing user details
A simple Springboot application version (demo-springboot-app) is provided as starting point. A corresponding initial architecture could be the following:
The purpose of this project is to compare the performance of this application deployed as a AWS Lambda function with the following targets:
- Springboot with serverless java container
- Springboot with lambda function handler
- Micronaut with lambda request handler
- Plain Java with lambda handler
The target architecture is the following:
For our AWS Lambda function, the default configuration is as following:
- Memory size: 256 MB
- Tiered compilation activated: -XX:+TieredCompilation -XX:TieredStopAtLevel=1
- Architecture: x86_64
- Reserved concurrency: 100
For each of the listed target, we will:
- Build the application
- Deploy on AWS Lambda
- Assess initial performances
- Apply Lambda Power Tuning Tool to find the right memory configuration
- Redeploy with memory optimization
- Assess performances
- Apply Java Snapstart for AWS Lambda
- Redeploy with Snapstart for AWS Lambda
- Assess performances
chmod 755 *.sh./deploy-all.sh AWS_REGION- Artillery
echo "Installing Artillery"
npm install -g artillery@latest
echo "Testing installation"
artillery dino- jq (On Amazon Linux 2)
sudo yum install jq- faker-js (only if needed, because generated node_modules resources are already provided in folder loadtest)
cd loadtest
npm init -y && npm install @faker-js/faker
cd ..stack_name = "workshop-java-lambda-optimizations"
s3_prefix = "workshop-java-lambda-optimizations"
Lambda functions:
- workshop-springboot-serverless-java-container
- workshop-springboot-lambda-function-handler
- workshop-quarkus-lambda-request-handler
- workshop-micronaut-lambda-request-handler
- workshop-plain-java-lambda-request-handler
./test-app.sh TARGET_APP AWS_REGION- With TARGET_APP values in ['plain-java', 'serverless-java-container', 'spring', 'micronaut', 'quarkus']
Load test configuration files are stored in folder loadtest.
You can run a benchmark per target (may be in parallel bash windows - by default 60 seconds per benchmark)
./benchmark.sh TARGET_APP AWS_REGION- With TARGET_APP values in
- plain-java
- serverless-java-container
- spring
- micronaut
- quarkus
OR
You can run your benchmarks all at once.
./run-all-benchmarks.sh AWS_REGIONThen go to CloudWatch Logs Insights:
- Select the appropriate log groups
- /aws/lambda/workshop-springboot-serverless-java-container
- /aws/lambda/workshop-springboot-lambda-function-handler
- /aws/lambda/workshop-quarkus-lambda-request-handler
- /aws/lambda/workshop-micronaut-lambda-request-handler
- /aws/lambda/workshop-plain-java-lambda-request-handler
- Collect your logs using this query:
filter @type = "REPORT"
| parse @log /\d+:\/aws\/lambda\/(?<function>.*)/
| parse @message /Restore Duration: (?<restoreDuration>.*?) ms/
| stats
count(*) as invocations,
pct(@duration+coalesce(@initDuration,0)+coalesce(restoreDuration,0), 0) as p0,
pct(@duration+coalesce(@initDuration,0)+coalesce(restoreDuration,0), 25) as p25,
pct(@duration+coalesce(@initDuration,0)+coalesce(restoreDuration,0), 50) as p50,
pct(@duration+coalesce(@initDuration,0)+coalesce(restoreDuration,0), 90) as p90,
pct(@duration+coalesce(@initDuration,0)+coalesce(restoreDuration,0), 95) as p95,
pct(@duration+coalesce(@initDuration,0)+coalesce(restoreDuration,0), 99) as p99,
pct(@duration+coalesce(@initDuration,0)+coalesce(restoreDuration,0), 100) as p100
group by function, (ispresent(@initDuration) or ispresent(restoreDuration)) as coldstart
| sort by coldstart desc
Install Lambda Power Tuning Tool
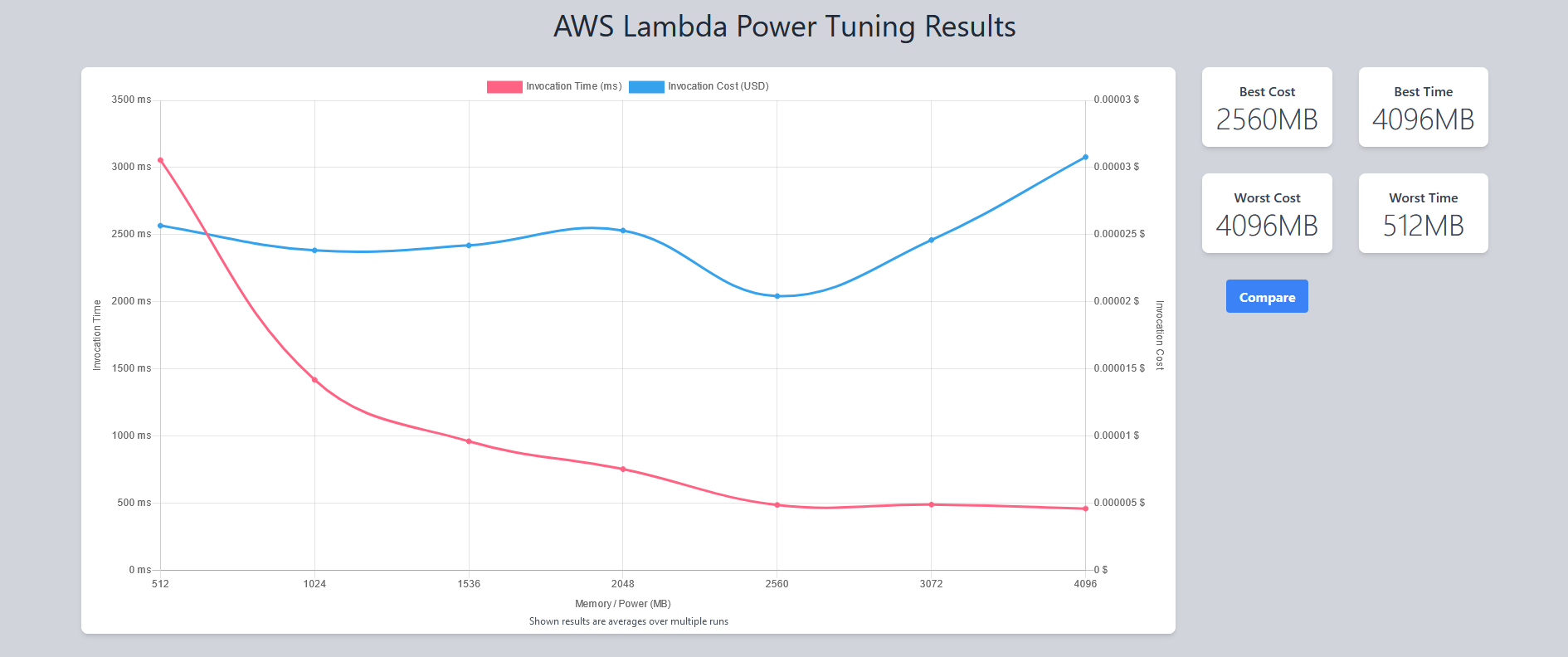
Execute the state machine to find the right memory configuration. The execution payloads are in folder payloads. We'll be looking for the best memory size with an acceptable cost.
{
"lambdaARN": "REPLACE_WITH_TARGET_LAMBDA_ARN",
"powerValues": [
512,
1024,
1536,
2048,
2560,
3072,
4096
],
"parallelInvocation": true,
"num": 5,
"payload": {
"resource": "/{proxy+}",
"path": "/REPLACE_WITH_ROOT_PATH/users",
"httpMethod": "POST",
"multiValueHeaders": {
"content-type": [
"application/json"
]
},
"pathParameters": {
"proxy": "REPLACE_WITH_ROOT_PATH/users"
},
"requestContext": {
"identity": {
"userAgent": "curl/7.64.1"
}
},
"body": "{\n \"firstName\": \"user\",\n \"lastName\": \"testing\",\n \"email\": \"user.testing@workshop.com\"}",
"isBase64Encoded": false
}
}Results will look like:
Update template.yaml to reflect your optimal memory choices.
- Global values
Globals:
Function:
Timeout: 30
Runtime: java17
# MemorySize: 512- For Serverless Java Container
SpringbootServerlessJavaContainer:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
CodeUri: .workshop-packages/demo-springboot-app-lambda-serverless-java-container-1.0.0-aws.jar
FunctionName: workshop-springboot-serverless-java-container
Handler: com.atn.digital.user.StreamLambdaHandler::handleRequest
MemorySize: 3072 #SET NEW VALUE HERE- For Spring Cloud Function
SpringbootLambdaFunctionHandler:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
CodeUri: .workshop-packages/demo-springboot-app-lambda-function-handler-1.0.0-aws.jar
FunctionName: workshop-springboot-lambda-function-handler
Handler: org.springframework.cloud.function.adapter.aws.FunctionInvoker::handleRequest
MemorySize: 2048 #SET NEW VALUE HERE- For Micronaut
MicronautLambdaRequestHandler:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
CodeUri: .workshop-packages/demo-micronaut-app-lambda-request-handler-1.0.0-aws.jar
FunctionName: workshop-micronaut-lambda-request-handler
Handler: com.atn.digital.user.adapters.in.handler.UserRequestHandler::handleRequest
MemorySize: 2560 #SET NEW VALUE HERE- For Plain java
PlainJavaLambdaRequestHandler:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
CodeUri: .workshop-packages/demo-plain-java-app-lambda-handler-1.0.0-aws.jar
FunctionName: workshop-plain-java-lambda-request-handler
Handler: com.atn.digital.user.adapters.in.handler.UserRequestHandler::handleRequest
MemorySize: 2560 #SET NEW VALUE HERE- For Quarkus
QuarkusLambdaRequestHandler:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
CodeUri: .workshop-packages/demo-quarkus-app-lambda-request-handler.zip
FunctionName: workshop-quarkus-lambda-request-handler
Handler: io.quarkus.amazon.lambda.runtime.QuarkusStreamHandler::handleRequest
MemorySize: 2048 #SET NEW VALUE HERE- If you changed something pertaining to your java code:
./deploy-all.sh UPLOAD_BUCKET AWS_REGION- If you didn't make any changes pertaining to your java code
./redeploy-all.sh AWS_REGION./test-app.sh TARGET_APP AWS_REGIONLoad test configuration files are stored in folder loadtest.
- Go to Cloudwatch
- Delete all the workshop function log groups
- Run you benchmark
./benchmark.sh TARGET_APP AWS_REGIONOR
./run-all-benchmarks.sh AWS_REGION- Then go to CloudWatch Logs Insights
- Select the appropriate log groups
- Collect your logs using the same query
Update template.yaml to enable SnapStart.
- Global values
Globals:
Function:
Timeout: 30
Runtime: java17
# MemorySize: 512
SnapStart:
ApplyOn: PublishedVersions- If you changed something pertaining to your java code:
./deploy-all.sh UPLOAD_BUCKET AWS_REGION- If you didn't make any changes pertaining to your java code
./redeploy-all.sh AWS_REGION./test-app.sh TARGET_APP AWS_REGIONLoad test configuration files are stored in folder loadtest.
- Go to Cloudwatch
- Delete all the workshop function log groups
- Run you benchmark
./benchmark.sh TARGET_APP AWS_REGIONOR
./run-all-benchmarks.sh AWS_REGION- Then go to CloudWatch Logs Insights
- Select the appropriate log groups
- Collect your logs using the same query
./cleanup-all.sh AWS_REGIONSee the AWS SAM developer guide for an introduction to SAM specification, the SAM CLI, and serverless application concepts.
Next, you can use AWS Serverless Application Repository to deploy ready to use Apps that go beyond hello world samples and learn how authors developed their applications: AWS Serverless Application Repository main page.
Official AWS workshop on Java on AWS Lambda.