Fake or not: Detecting Manipulated Images Using Deep Learning
A video summarizing the project can be found here.
abstract
Digital images are essential to how humankind uses the internet, from saving and sharing memories to reporting news and serve as the cornerstone of e-commerce. Entire websites, based solely on image sharing, experience daily uploads of pictures surpassing the tenths of millions. However, this ubiquitous access to digital imagery online has enabled the upsurge of image tampering, helping societal issues, such as identity theft or fake news, to thrive more effectively. The public's trust in digital photography has, therefore, compelling reasons to have plummeted. We aim for a fast and reliable approach to detect whether an image has been manipulated. Our method starts with 22 thousand images from the famous subreddit PhotoshopBattles, which later are transformed with Error Level Analysis and used to train a Convolutional Neural Network. As a result, this pipeline achieves better and faster results compared to human performance, offering an improved way to detect image manipulation at scale.
data
Refer 2_report/1_report.pdf for detailed data wrangling and description.
introduction
Refer 2_report/1_report.pdf for detailed introduction.
background
Refer 2_report/1_report.pdf for detailed background.
methods
Refer 2_report/1_report.pdf for detailed methodology. The following is a list of methods that we tried:
- Human baseline score
- Error level analysis (ELA) and convolutional neural network (CNN).
- ManTra-Net and CNN
- VGGNet and dense network
result
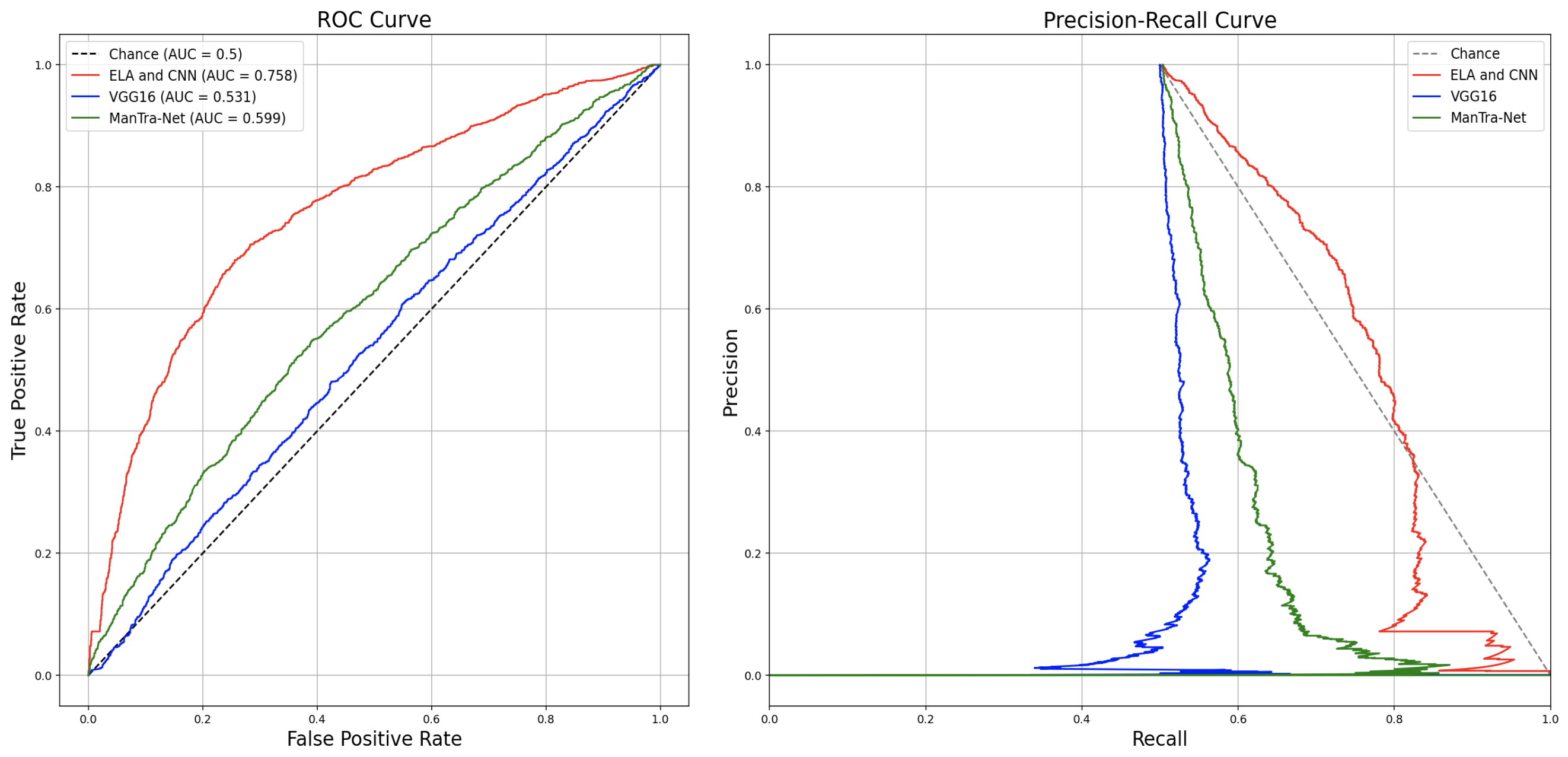
Refer 2_report/1_report.pdf for detailed results. The following table lists the accuracies and area under the curve of a ROC plot.
| Model | Accuracy | AUC |
|---|---|---|
| Human aggregate model (baseline) | 73.8 ± 8.16 (95% CI) | n/a |
| Human ensemble | 82.0% | n/a |
| ELA and CNN | 71.2% | 0.758 |
| VGG16 and dense net | 51.8% | 0.531 |
| ManTra-Net and CNN | 57.7% | 0.599 |
The ROC and precision-recall curve is shown below:
conclusion
After several iterations over diverse methods to accomplish the task proposed, the best method resulted to be the one integrating Error Level Analysis and Convolutional Neural Networks. The overall accuracy of the above model outperforms more complex transfer learning approaches but falls behind our custom human baseline. Nonetheless, it is important to mention that our human baseline for the PS-Battles dataset has potentially a high bias and a proofed wide confidence interval, since we did not calculate it using a rigorous statistical design as well as a well-formed sample of individuals. A more trustworthy metric to compare our model would the one presented by Nightingale et al. (2017), in which case our model improves human performance.
For further research, we would suggest using wavelet thresholding to remove the noisy components from the ELA-transformed images as well as trying to enhance ELA by using vertical and horizontal histograms, as noted in the literature review. Also, we would recommend implementing VGG16 with ELA-transformed images, as mentioned in the literature review, and see whether the results vary when we increase the resolution of the images significantly. In addition, we could try other methods popular for forgery detection tasks, such as RGB-N and J-LSTM (Wu et al., 2019). Lastly, it would be interesting to see how the results would vary if we run our models on the original dataset without a perfect balance between original and fake images. We suppose that having several derivatives of the original image would add randomness to our dataset and could lead to better generalization of our models. However, due to the limited time and computational power, we could not implement these suggestions.