(Again, I am showing everyone how untalented I am in naming things)
A set of convenience tools for my work with JupyterLab.
They mostly deal with Pandas, RDKit and Cell Painting.
There are also utilities for displaying HTML tables and grids of molecules.
Main list of tools. Please have a look at the included documentation.
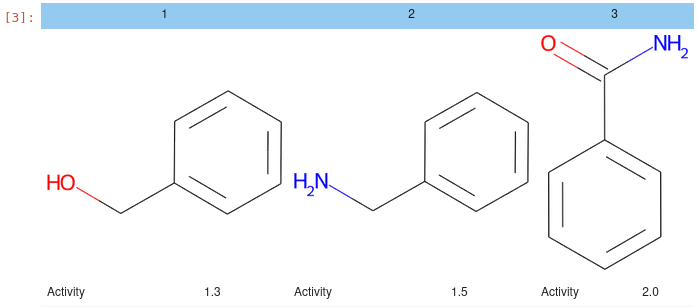
Utilities for displaying HTML tables and grids of molecules, e.g.:
from jupy_tools import mol_view as mv
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
"Compound_Id": [1, 2, 3],
"Smiles": ["c1ccccc1CO", "c1ccccc1CN", "c1ccccc1C(=O)N"],
"Activity": [1.3, 1.5, 2.0]
}
)
mv.mol_grid(df)
# mv.write_mol_grid(df) # Saves the grid as one HTML file to disk,
# without external dependencies
# (images are embedded and no dependency on external Javascript)- stand_struct.py: A Python script for standardizing structure files. The input can be either SD files OR CSV or TSV files which contain the structures as
Smiles. The output is always a TSV file, various options are available, please have a look at the help in the file. - calc_pmi.py: Script for calculating PMI values.
- extract_nps_from_sqlite.py: Script to extract the Natural Products from ChEMBL. Both the SQLite db and the standardized ChEMBL (using
stand_struct.py) data are required to be available in the same folder where this script is run. Run withextract_nps_from_sqlite.py <ChEMBL_version>.
$ stand_struct --help
usage: stand_struct [-h] [--canon {none,rdkit,cxcalc,legacy}] [--idcol IDCOL] [--nocanon] [--min_heavy_atoms MIN_HEAVY_ATOMS]
[--max_heavy_atoms MAX_HEAVY_ATOMS] [-d] [-c COLUMNS] [-n N] [--deglyco] [-v]
in_file {full,fullrac,medchem,medchemrac,fullmurcko,medchemmurcko,fullracmurcko,medchemracmurcko}
Standardize structures. Input files can be CSV, TSV with the structures in a `Smiles` column
or an SD file. The files may be gzipped.
All entries with failed molecules will be removed.
By default, duplicate entries will be removed by InChIKey (can be turned off with the `--keep_dupl` option)
and structure canonicalization using the RDKit will be performed (can be turned with the `--canon=none` option).
Omitting structure canonicalization drastically reduces the runtime of the script.
Structures that fail the deglycosylation step WILL NOT BE REMOVED and the original structure is kept.
The output will be a tab-separated text file with SMILES.
Example:
Standardize the ChEMBL SDF download (gzipped), keep only MedChem atoms
and molecules between 3-50 heavy atoms, do not perform canonicalization:
$ ./stand_struct.py chembl_29.sdf.gz medchemrac --canon=none
positional arguments:
in_file The optionally gzipped input file (CSV, TSV or SDF). Can also be a comma-separated list of file names.
{full,fullrac,medchem,medchemrac,fullmurcko,medchemmurcko,fullracmurcko,medchemracmurcko}
The output type. 'full': Full dataset, only standardized; 'fullrac': Like 'full', but with stereochemistry removed; 'fullmurcko',
'fullracmurcko: Like 'full' or 'fullrac', but structures are reduced to their Murcko scaffolds; 'medchem': Dataset with MedChem
filters applied, bounds for the number of heavy atoms can be optionally given; 'medchemrac': Like 'medchem', but with
stereochemistry removed; 'medchemmurcko', 'medchemracmurcko': Like 'medchem' or 'medchemrac', but structures are reduced to their
Murcko scaffolds; (all filters, canonicalization and duplicate checks are applied after Murcko generation).
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--canon {none,rdkit,cxcalc,legacy}
Select an algorithm for tautomer generation. `rdkit` uses the new C++ implementation from `rdMolStandardize.TautomerEnumerator`,
`legacy` uses the older canonicalizer from `MolStandardize.tautomer`. `cxcalc` requires the ChemAxon cxcalc tool to be installed.
--idcol IDCOL Name of the column that contains a unique identifier for the dataset. Required for canonicalization with `cxcalc`.
--nocanon Do not perform canonicalization. DEPRECATED - use `--canon=none` instead.
--min_heavy_atoms MIN_HEAVY_ATOMS
The minimum number of heavy atoms for a molecule to be kept (default: 3).
--max_heavy_atoms MAX_HEAVY_ATOMS
The maximum number of heavy atoms for a molecule to be kept (default: 50).
-d, --keep_duplicates
Keep duplicates.
-c COLUMNS, --columns COLUMNS
Comma-separated list of columns to keep (default: all).
-n N Show info every `N` records (default: 1000).
--deglyco deglycosylate structures. Requires jupy_tools.
-v Turn on verbose status output.
- Download the repository
- Change into the dowloaded directory
- Create and activate a Python virtual environment, e.g. with conda
- Pip-install the dependencies and the package
git clone https://github.com/apahl/jupy_tools
cd jupy_tools
conda create -n chem python=3.11
conda activate chem
pip install .Or install the dependencies also with conda and then pip-install just the package:
git clone https://github.com/apahl/jupy_tools
cd jupy_tools
conda create -n chem python=3.11 rdkit pillow cairocffi pandas matplotlib seaborn networkx python-graphviz scikit-learn scipy
pip install .