This repository contains the development source of the GNU Radio-based satellite receiver. See the Wiki for setup and configuration information.
Go to the #blockstream-satellite IRC channel on freenode for additional help.
This is an initial release and regular improvements will be made to make Blockstream Satellite more user friendly and less technically complex.
Blockstream Satellite currently covers nearly 2/3rds of the Earth's landmass. To see if you are in the coverage area, use our Interactive Coverage Map
To utilize the Blockstream Satellite network, you must have the following hardware at a minimum. These items are available from resellers around the world and we are currently working with a vendor to provide complete kits and components.
Following is a list of all the hardware required:
- 45cm Ku Band Satellite Dish (antenna)
- PLL LNB (linear polarization) w/ < = 200kHz LO stability
- LNB Power Supply
- LNB Mounting Bracket
- Software Defined Radio interface
- Cables, Connectors, and Mounting Hardware
Blockstream Satellite is designed to work with small antennas only 45cm or larger in diameter. However, a larger antenna is always better. When possible, we recommend installing an antenna larger than 45cm if one is readily available. 60cm, 90cm, and 1.2m antennas are readily available.
Other than size, the only other requirement is that the antenna will work with Ku band and higher frequencies.
Blockstream Satellite operates in Ku band.
C band: 3.4 GHZ - 4.2 GHz
Ku band: 11.7 GHz to 12.7 GHz
Ka band: 17.7 GHz - 21.2 GHz
You can always use antennas designed for higher frequencies. For example, an antenna designed for Ka band will work as it is designed for higher frequencies than Blockstream Satellite which operated in Ku band.
However, a C band antenna will not work as it is designed for frequencies lower than Ku band.
The type of LNB used is critical. There are 3 parameters of an LNB that must be met to use Blockstream Satellite:
First you must verify that the Blockstream Satellite coverage in your area operates within the LNB frequency range. You can check the coverage area and satellite frequencies on our Network Status page.
For example, if you are located in North America and are using the Galaxy 18 satellite, your frequency is 12.178 GHz. Thus an LNB that operates from 11.7 GHz to 12.2 GHz would work. However, if your LNB operates from 10.7 GHz to 11.7 GHz would NOT work.
Note on “Universal” LNB. A Universal LNB supports multiple frequency bands, however it requires a 22kHz tone to be sent to the LNB to activate the switch. If the default frequency band (without the 22khz tone) is the same frequency band that will work for your satellite, a universal LNB should work. However, if the LNB requires the tone to activate the correct frequency band, then Blockstream Satellite will not work as it would require an SDR with transmit capability.
Blockstream Satellite requires a LNB with Linear Polarization. While most Ku LNBs are linearly polarized, some popular satellite TV services use circular polarization. A circularly polarized LNB will NOT work with Blockstream satellite.
If an LNB is described as horizontal or vertical polarization, than it is linear.
However, if an LNB is described as Right Hand or Left Hand, then it is circular and will NOT work with Blockstream Satellite.
Blockstream Satellite requires a highly stable LNB. Most LNBs will have a stability parameter referred to as either “Stability” or “L.O. Stability” measured in +/- XX kHz or MHz.
Blockstream Satellite requires the LNB have at stability measurement of <= +/- 200kHz. Any higher and the system may not operate reliably.
Most LNBs require anywhere from 13 vdc to 30vdc to be injected on the coaxial port to power the LNB. As this is a common requirement, many power injectors exist for this purpose.
Be sure to check the power requirement of your LNB and ensure that your power injector matches.
While the dish likely comes with a mounting bracket, you’ll need one designed to accept a universal LNB. These attach to the feed arm of the antenna and have a circular ring that will accept a universal LNB.
There exist many different Software Defined Radio (SDR) interfaces. Currently, Blockstream Satellite is confirmed to work with an RTL SDR model R820T2.
SDRs other than the RTL may be used, but it must be supported by the GNUradio project and be able to receive frequencies from 950MHz to 1450MHz. Additional custom configuration will be required to use non-RTL SDRs.
You’ll need to connect your SDR to the LNB power supply. The powered output of the power supply is then connected to the LNB. You’ll need to ensure that you have the necessary coaxial cable and connectors to make these interfaces.
Note: Not every RTL SDR has the same interface connector. Some use the SMA connector and some use MCX. Be sure to order the correct cable and adaptors to make the necessary connections.
Many antennas will come with mounting hardware, but you may need additional or different hardware depending on your installation. Check with the antenna manufacturer for the correct mounting hardware.
Three software components are needed to utilize Blockstream Satellite:
Bitcoin Fibre: http://bitcoinfibre.org
GNUradio: http://gnuradio.org (Version 3.7.10 or greater)
gr-osmosdr: https://github.com/osmocom/gr-osmosdr
Blockstream Satellite Receiver: https://github.com/Blockstream/satellite
After building and installing Bitcoin Fibre, GNUradio and the gr-osmosdr, using this repository, run the following:
-
Install the gr-framers gnuradio modules:
./install_gr_framers.sh -
Install the Blockstream GNUradio modules:
./install_mods.sh
Possible Issues:
Ensure that your PYTHONPATH environment variable is set to the installed location of gr-framers and gr-mods. Usually >/usr/local/lib64/python2.7/site-packages on redhat/fedora or /usr/local/lib64/python2.7/dist-packages on ubuntu.
Ensure your LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable is set. Typically /usr/local/lib64
Aligning a satellite antenna is a precise procedure. Remember that the satellites are over 35,000 km (22,000 mi) away. A tenth of a degree of error will miss the satellite by more than 3500 km.
Before mounting your satellite antenna, it is important to ensure you find the ideal mounting location.
To find the ideal location to place your antenna, first use the following tool to find the correct azimuth and elevation. http://blockstream.com/satellite/satellite (click on the satellite dish icon in the upper right).
After entering your address or latitude/longitude, this tool will give you three parameters:
The azimuth is the side to side adjustment on your antenna. The antenna aiming tool will provide the compass heading your dish will need to point.
The elevation is the up and down adjustment of your antenna. The antenna aiming tool provides the number of degrees above the horizon your antenna must point. 0 degrees represents pointing at the horizon and 90 degrees is pointing straight up.
The polarization parameter is how many degrees your LNB will need to be rotated. Many LNBs will provide a scale of degrees to assist in setting the LNB skew.
Once you have your azimuth, elevation, and polarization, you can identify the general direction your antenna must point. Using a compass or smartphone, visually check the general direction your antenna must point. Ensure that there are no obstacles such as trees or buildings in the path between your antenna location and the area of the sky that your antenna will point. It is important that you have clear line of sight to that area of the sky.
There are many useful smartphone apps available for android and ios that will aid in pointing your antenna. Some even have augmented reality features that allow you to see the satellite in the sky so that you can ensure you have good line of sight.
Now that you have verified you have clear line of sight, it is time to mount your antenna. Install the satellite antenna according to the directions accompanying it, or have it done professionally.
If you install it yourself, confirm the following: Check to be certain the pole the dish is mounted on is completely level. Set the elevation of the antenna to the parameter provided by the antenna aiming tool (above). This is the up and down angle. Many antenna will have an elevation scale on the back of the dish that you can use to set the approximate elevation.
Set the LNB polarization to the parameter provided by the antenna aiming tool. This involves rotating the LNB. There is typically a polarization rotation scale on the LNB or the LNB mounting bracket.
To locate the Blockstream Satellite signal and perform fine adjustment of your antenna alignment, you will need the following:
- Computer with SDR interface and previously downloaded Blockstream Satellite Receiver and GNUradio.
- LNB power supply with electricity to power it.
- Coax cable to connect LNB to LNB power supply.
- SMA to F connector cable to connect the SDR to the LNB power supply.
Note: This process is performed easiest with a laptop than can be watched while moving the antenna. If you are not able to have a computer at the antenna, you’ll need two people: one to move the antenna and one to monitor the laptop.
a. With power disconnected from the LNB power supply, connect the SDR to the non-powered port on the LNB power supply using the SMA to F connector cable.
IMPORTANT: Do NOT connect the powered port of the LNB power supply to the SDR interface. Permanent damage may occur to your SDR and/or your computer.
b. Connect the powered port of the LNB power supply to the LNB using coaxial cable.
Once you have your azimuth, elevation, and polarization skew you can place your antenna in the approximate position. You’ll need to use a computer and your SDR to identify the optimal position for your antenna.
Ensure RTL SDR is connected to the LNB power supply and the powered output of the LNB power supply is connected to the LNB. Then run:
python rx_gui.py --freq 1276150000 --gain 40
Possible Issues:
Ensure that your PYTHONPATH environment variable is set to the installed location of gr-framers and gr-mods. Usually >/usr/local/lib64/python2.7/site-packages on redhat/fedora or /usr/local/lib64/python2.7/dist-packages on ubuntu.
Ensure your LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable is set. Typically /usr/local/lib64
The frequency should be your satellite's frequency - LNB's LO frequency.
To find your frequency, first go to http://blockstream.com/satellite/satellite and find your satellite. You should see the frequency listed in MHz.
Then adjust for your LNB LO frequency. For example, if your LNB has an LO frequency of 10750 MHz and you're connecting to Eutelsat 113 at 12026.15 MHz, the frequency is 12026.15 - 10750 = 1276.15 MHz.
Note: When running, the frequency parameter is specified in Hz. So 1276.15 MHz would be specified as 1276150000 Hz.
The gain parameter is a value between 0 and 50. Higher gain values may be required for long cable runs or LNBs with weak output. Until we implement signal to noise ratio measurement, some experimentation may be required to identify the best value for your application.
-
After running rx_gui.py (above), click on the
FLL Intab in the GUI. -
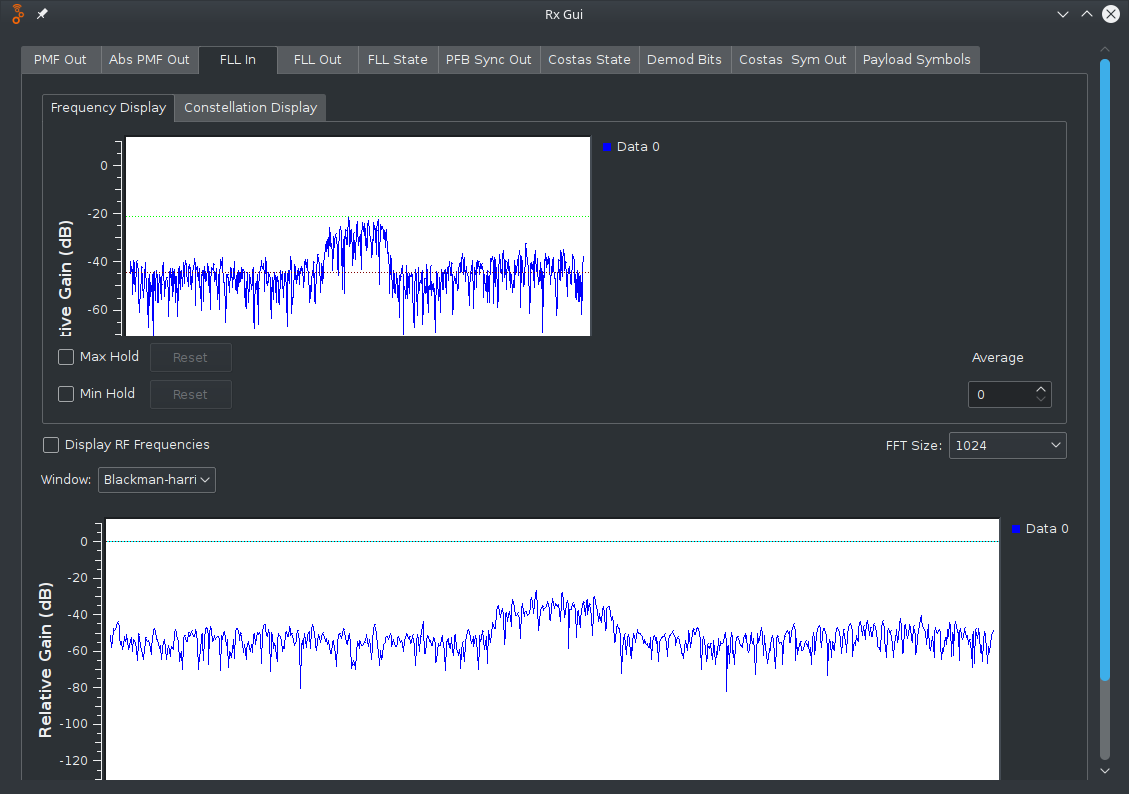
Very slowly move the antenna side to side (azimuth), until you begin to see a pattern that looks like this:
Notice the wide peak that is above the noise floor.
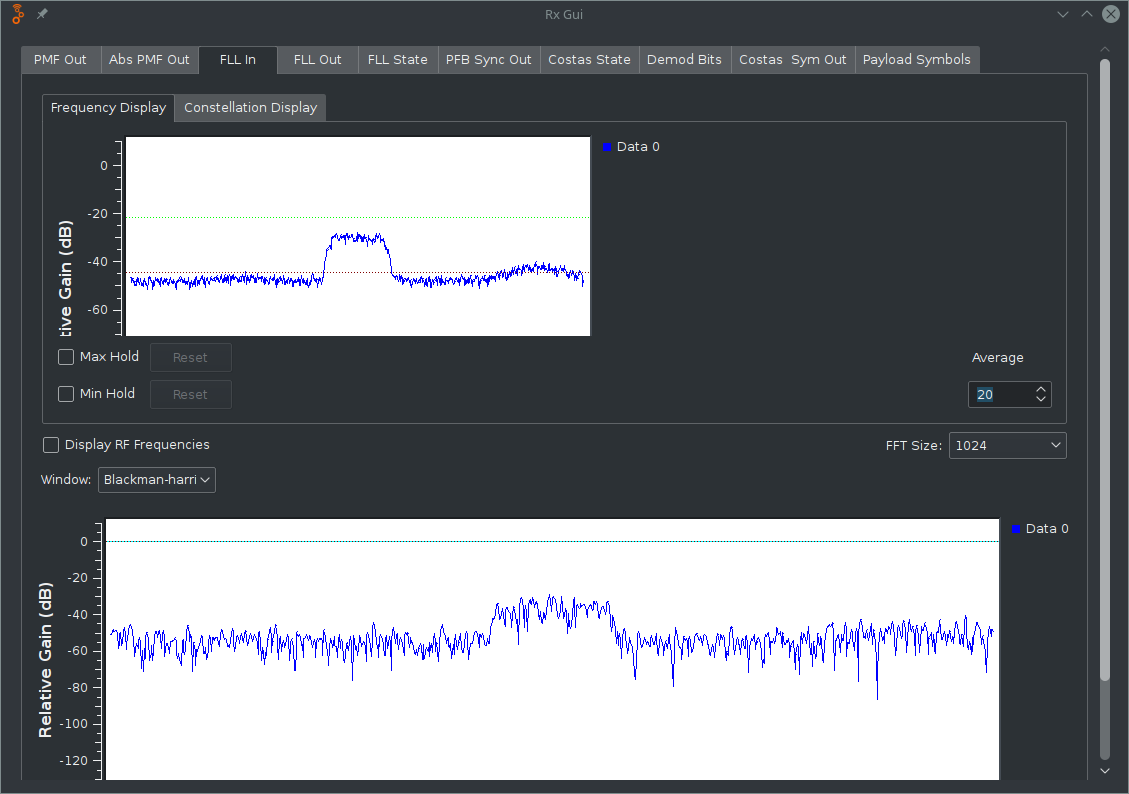
If you increase the average value on the right side of the graph, this peak can be easier to see, however, you'll have to make slower movements of your antenna to allow the graph to update.
If after moving your antenna left and right across a wide range of azimuth over which you expect to see the signal, you find that you still need to adjust your elevation, increase your elevation by 1 degree, and then sweep the antenna left and right through a wide azimuth range again. You may need to repeat this increasing by several degrees and decreasing by several degrees of elevation before you are able to find the signal.
Remember, even though a single degree may seem like a minuscule movement, each degree is tens of thousands of kilometers over the 36,000 kilometers to geosynchronous orbit.
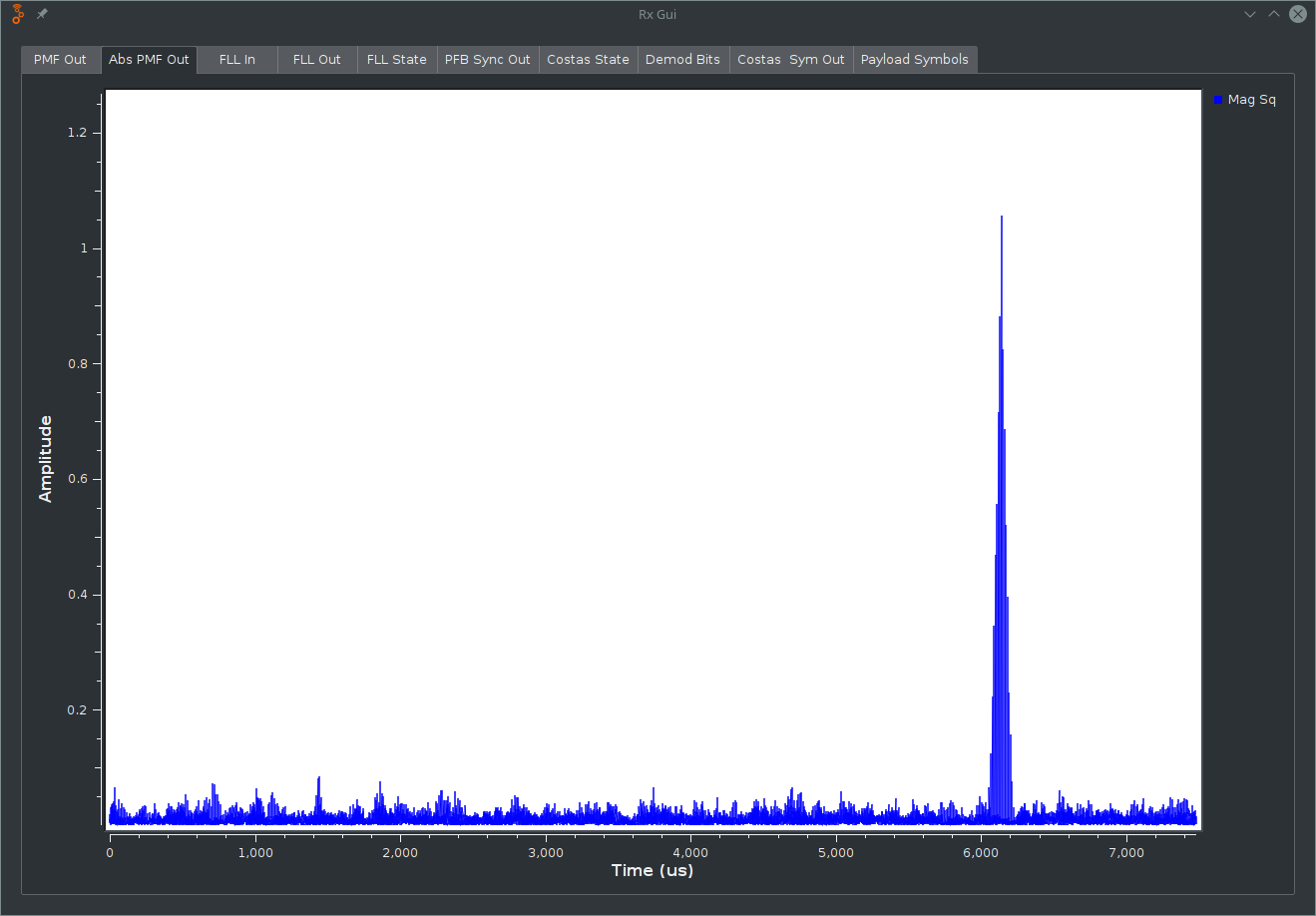
Once you have located the signal, adjust the azimuth, elevation, and rotation of your LNB until you the peak is at its maximum. You can confirm you have a good signal by looking at the Abs PMF Out tab and Costas Sym Out tab.
The Abs PMF Out screen should have one very strong peak and it should remain in place. It can be in any position, but it must remain in the same position for the system to be reliable.
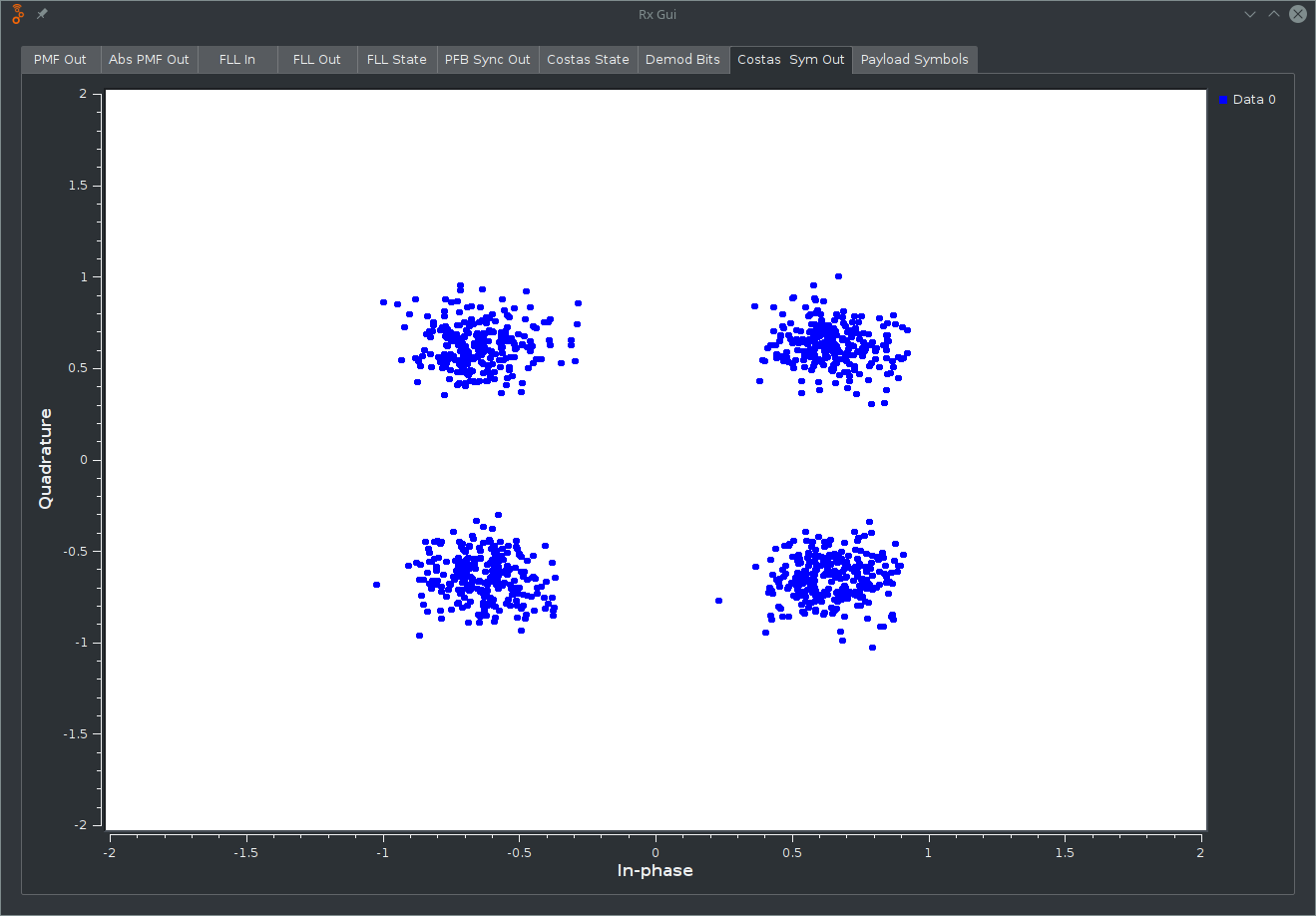
Finally, look at the Costas Sym Out tab and you should see a constellation of 4 point clouds. The more compact the point clouds are, the better your signal quality:
After successfully aiming your antenna, ensure that all connections are made and run the following:
./grc/rx.py --freq 1276150000 --gain 40
The frequency should be the difference between your satellite's frequency and the LNB's LO frequency (the former minus the latter). For example, if your LNB has an LO frequency of 10750 MHz and you're connecting to Eutelsat 113 at 12026.15 MHz, the frequency is 12026.15 - 10750 = 1276.15 MHz.
Note: When running, the frequency parameter is specified in Hz. So 1276.15 MHz would be specified as 1276150000 Hz.
The gain parameter is a value between 0 and 50. Higher gain values may be required for long cable runs or LNBs with weak output. Until we implement signal to noise ratio measurement, some experimentation may be required to identify the best value for your application.
Bitcoin Fibre uses the same bitcoin.conf configuration file as Bitcoin Core. Configure as needed and start bitcoind with the following parameters after the receiver (above) is running:
./bitcoind -fecreaddevice=/tmp/async_rx
Note: The Blockstream Satellite receiver will create /tmp/async_rx
Once the Blockstream Satellite Receiver and Bitcoin Fibre is running, your node will stay in sync!