Chinfuzz enables code coverage fuzzing for Tezos smart contracts
$ brew tap cuber/homebrew-libsecp256k1
$ brew install libsodium libsecp256k1 gmp pkg-config makegit clone https://github.com/ant4g0nist/chinfuzz
cd chinfuzz
makeRunning make will clone and build llvm and install it to ~/llvm-14.0.4 and install chinfuzz
If you already have a compiled version of llvm/clang, you could run:
LLVM_SYS=~/llvm-14.0.4 makeInstalling chinfuzz also installs chinstrap.
You can initialise a chinfuzz project by running chinfuzz init. This initialises a chinstrap project and creates an extra folder fuzz where we are going to write our fuzzers.
Folder structure:
.
|____originations
| |____1_samplecontract_origination.py
|____contracts
| |____SampleContract.py
|____tests
| |____sampleContractSmartPy.py
| |____samplecontractPytest.py
|____chinstrap-config.yml
|____.chinstrap
|____fuzz
| |____SampleContractFuzzer.py
|____.secretYou can find more details about chinstrap here: https://chinstrap.io/docs/usage
Chinfuzz takes a contract that has invariants and a fuzzer written in Python as input. Invariants are properties taht should always remain true for all inputs. If it can find some way to falsify the invariant, it saves the input that falsified the invariant.
For each invariant, it generates random inputs and call the entrypoint of contract as specified in the fuzzer and checks if the invariant holds true.
Invariants are expressed inside entrypoints that revert(FAILWITH) if falsified. In the following example, we have declared an invariant, sp.if name == "TEZOS":, to find if there is any name that matches that condition. If so, we trigger failwith(crash).
@sp.entry_point
def setName(self, name):
sp.if name == "TEZOS":
sp.failwith("Boom crash!!!")
self.data.name = nameLets modify our sample contract from
import smartpy as sp
class SampleContract(sp.Contract):
def __init__(self, value, owner):
self.init_type(sp.TRecord(counter=sp.TInt, owner=sp.TAddress))
self.init(counter=value, owner=owner)
@sp.entry_point
def increment(self, value):
sp.verify(sp.sender == self.data.owner, message="Only owner can increment")
self.data.counter += value
@sp.entry_point
def decrement(self, value):
sp.verify(sp.sender == self.data.owner, message="Only owner can decrement")
self.data.counter -= value
sp.add_compilation_target(
"SampleContract",
SampleContract(0, sp.address("tz1a9GCc4UU6d5Z9spyozgKTARngb8DZKbNe")),
)to
import smartpy as sp
class SampleContract(sp.Contract):
def __init__(self, value, owner, name):
self.init_type(sp.TRecord(counter=sp.TInt, name= sp.TString, owner=sp.TAddress))
self.init(counter=value, owner=owner, name=name)
@sp.entry_point
def increment(self, value):
sp.verify(sp.sender == self.data.owner, message="Only owner can increment")
self.data.counter += value
@sp.entry_point
def setName(self, name):
sp.if name == "TEZOS":
sp.failwith("Boom crash!!!")
self.data.name = name
@sp.entry_point
def decrement(self, value):
sp.verify(sp.sender == self.data.owner, message="Only owner can decrement")
self.data.counter -= value
sp.add_compilation_target(
"SampleContract",
SampleContract(0, sp.address("tz1a9GCc4UU6d5Z9spyozgKTARngb8DZKbNe"), "yolo"),
)We added one extra endpoint setName that takes a string as parameter.
Now, we compile the contract:
chinstrap compileNow we have to write our fuzzer. Inside the fuzz, chinfuzz init command should have added a file named SampleContractFuzzer.py with the following content:
from chinfuzz.core import fuzz
from chinstrap.tests import getContractInterface
owner = "tz1YtuZ4vhzzn7ssCt93Put8U9UJDdvCXci4"
def ChinfuzzFuzzerTestOneInput(data):
if len(data)>10:
return
fdp = fuzz.FuzzedDataProvider(data)
data = fdp.ConsumeString(100)
contract = getContractInterface("SampleContract")
storage = {"owner": owner, "counter": 0, "name": "yolo"}
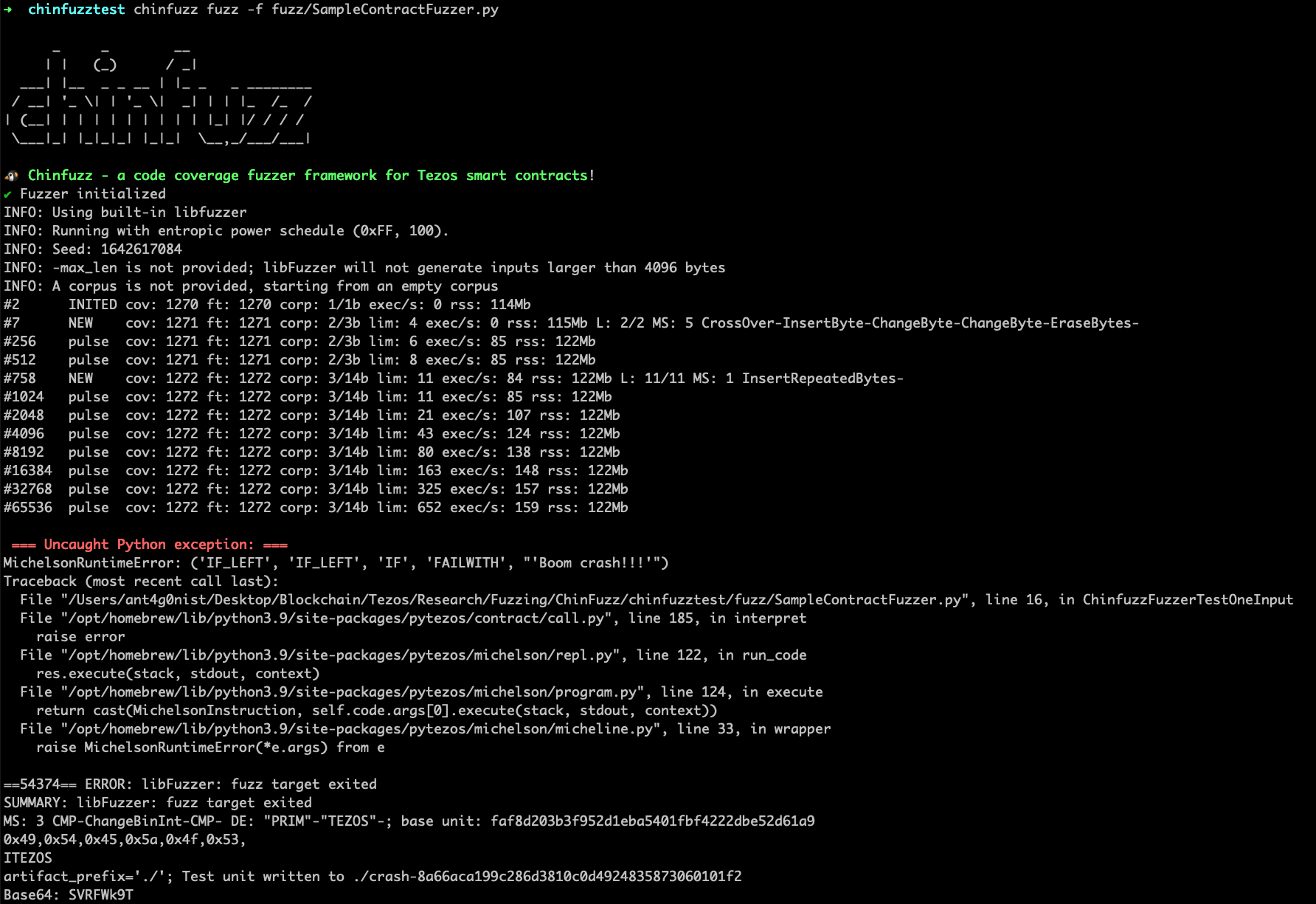
contract.setName(data.encode("ascii", "ignore").decode()).interpret(storage=storage, source=owner)To start fuzzing, we simply just run:
chinfuzz fuzz -f fuzz/SampleContractFuzzer.pyOften, a bytes object is not convenient input to your code being fuzzed. Similar to libFuzzer, we have a FuzzedDataProvider to translate these bytes into other input forms.
Functions available:
- fuzz.ConsumeUnicode(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeUnicodeNoSurrogates(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeBytes(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeString(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeInt(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeUInt(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeIntInRange(min, max)
- fuzz.ConsumeIntList(count, bytes)
- fuzz.ConsumeIntListInRange(count, min, max)
- fuzz.ConsumeFloat(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeRegularFloat(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeProbability(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeFloatInRange(min, max)
- fuzz.ConsumeFloatList(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeRegularFloatList(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeProbabilityList(count)
- fuzz.ConsumeFloatListInRange(count, min, max)
- fuzz.ConsumeBool(count)
Usage:
chinfuzz fuzz -f fuzz/SampleContractFuzzer.py -- -runs=1337LibFuzzer flags available:
- verbosity : 1 Verbosity level.
- seed : 0 Random seed. If 0, seed is generated.
- runs -: 1 Number of individual test runs (-1 for infinite runs).
- max_len : 0 Maximum length of the test input. If 0, libFuzzer tries to guess a good value based on the corpus and reports it.
- len_control 10: 0 Try generating small inputs first, then try larger inputs over time. Specifies the rate at which the length limit is increased (smaller == faster). If 0, immediately try inputs with size up to max_len. Default value is 0, if LLVMFuzzerCustomMutator is used.
- seed_inputs : 0 A comma-separated list of input files to use as an additional seed corpus. Alternatively, an "@" followed by the name of a file containing the comma-separated list.
- keep_seed : 0 If 1, keep seed inputs in the corpus even if they do not produce new coverage. When used with |reduce_inputs==1|, the seed inputs will never be reduced. This option can be useful when seeds arenot properly formed for the fuzz target but still have useful snippets.
- cross_over : 1 If 1, cross over inputs.
- cross_over_uniform_dist : 0 Experimental. If 1, use a uniform probability distribution when choosing inputs to cross over with. Some of the inputs in the corpus may never get chosen for mutation depending on the input mutation scheduling policy. With this flag, all inputs, regardless of the input mutation scheduling policy, can be chosen as an input to cross over with. This can be particularly useful with |keep_seed==1|; all the initial seed inputs, even though they do not increase coverage because they are not properly formed, will still be chosen as an input to cross over with.
- mutate_depth : 5 Apply this number of consecutive mutations to each input.
- reduce_depth : 0 Experimental/internal. Reduce depth if mutations lose unique features
- shuffle : 1 Shuffle inputs at startup
- prefer_small : 1 If 1, always prefer smaller inputs during the corpus shuffle.
- timeout 120: 0 Timeout in seconds (if positive). If one unit runs more than this number of seconds the process will abort.
- error_exitcode 7: 7 When libFuzzer itself reports a bug this exit code will be used.
- timeout_exitcode 7: 0 When libFuzzer reports a timeout this exit code will be used.
- max_total_time : 0 If positive, indicates the maximal total time in seconds to run the fuzzer.
- help : 0 Print help.
- fork : 0 Experimental mode where fuzzing happens in a subprocess
- fork_corpus_groups : 0 For fork mode, enable the corpus-group strategy, The main corpus will be grouped according to size, and each sub-process will randomly select seeds from different groups as the sub-corpus.
- ignore_timeouts : 1 Ignore timeouts in fork mode
- ignore_ooms : 1 Ignore OOMs in fork mode
- ignore_crashes : 0 Ignore crashes in fork mode
- merge : 0 If 1, the 2-nd, 3-rd, etc corpora will be merged into the 1-st corpus. Only interesting units will be taken. This flag can be used to minimize a corpus.
- set_cover_merge : 0 If 1, the 2-nd, 3-rd, etc corpora will be merged into the 1-st corpus. Same as the 'merge' flag, but uses the standard greedy algorithm for the set cover problem to compute an approximation of the minimum set of testcases that provide the same coverage as the initial corpora
- stop_file : 0 Stop fuzzing ASAP if this file exists
- merge_control_file : 0 Specify a control file used for the merge process. If a merge process gets killed it tries to leave this file in a state suitable for resuming the merge. By default a temporary file will be used.The same file can be used for multistep merge process.
- minimize_crash : 0 If 1, minimizes the provided crash input. Use with -runs=N or -max_total_time=N to limit the number attempts. Use with -exact_artifact_path to specify the output. Combine with ASAN_OPTIONS=dedup_token_length=3 (or similar) to ensure that the minimized input triggers the same crash.
- cleanse_crash : 0 If 1, tries to cleanse the provided crash input to make it contain fewer original bytes. Use with -exact_artifact_path to specify the output.
- mutation_graph_file : 0 Saves a graph (in DOT format) to mutation_graph_file. The graph contains a vertex for each input that has unique coverage; directed edges are provided between parents and children where the child has unique coverage, and are recorded with the type of mutation that caused the child.
- use_counters : 1 Use coverage counters
- use_memmem : 1 Use hints from intercepting memmem, strstr, etc
- use_value_profile : 0 Experimental. Use value profile to guide fuzzing.
- use_cmp : 1 Use CMP traces to guide mutations
- shrink : 0 Experimental. Try to shrink corpus inputs.
- reduce_inputs : 1 Try to reduce the size of inputs while preserving their full feature sets
- jobs : 0 Number of jobs to run. If jobs >= 1 we spawn this number of jobs in separate worker processes with stdout/stderr redirected to fuzz-JOB.log.
- workers : 0 Number of simultaneous worker processes to run the jobs. If zero, "min(jobs,NumberOfCpuCores()/2)" is used.
- reload : 1 Reload the main corpus every seconds to get new units discovered by other processes. If 0, disabled
- report_slow_units 1: 0 Report slowest units if they run for more than this number of seconds.
- only_ascii : 0 If 1, generate only ASCII (isprint+isspace) inputs.
- dict : 0 Experimental. Use the dictionary file.
- artifact_prefix : 0 Write fuzzing artifacts (crash, timeout, or slow inputs) as $(artifact_prefix)file
- exact_artifact_path : 0 Write the single artifact on failure (crash, timeout) as $(exact_artifact_path). This overrides -artifact_prefix and will not use checksum in the file name. Do not use the same path for several parallel processes.
- print_pcs : 0 If 1, print out newly covered PCs.
- print_funcs : 2 If >=1, print out at most this number of newly covered functions.
- print_final_stats : 0 If 1, print statistics at exit.
- print_corpus_stats : 0 If 1, print statistics on corpus elements at exit.
- print_coverage : 0 If 1, print coverage information as text at exit.
- print_full_coverage : 0 If 1, print full coverage information (all branches) as text at exit.
- dump_coverage : 0 Deprecated.
- handle_segv : 1 If 1, try to intercept SIGSEGV.
- handle_bus : 1 If 1, try to intercept SIGBUS.
- handle_abrt : 1 If 1, try to intercept SIGABRT.
- handle_ill : 1 If 1, try to intercept SIGILL.
- handle_fpe : 1 If 1, try to intercept SIGFPE.
- handle_int : 1 If 1, try to intercept SIGINT.
- handle_term : 1 If 1, try to intercept SIGTERM.
- handle_xfsz : 1 If 1, try to intercept SIGXFSZ.
- handle_usr1 : 1 If 1, try to intercept SIGUSR1.
- handle_usr2 : 1 If 1, try to intercept SIGUSR2.
- handle_winexcept : 1 If 1, try to intercept uncaught Windows Visual C++ Exceptions.
- close_fd_mask : 0 If 1, close stdout at startup; if 2, close stderr; if 3, close both. Be careful, this will also close e.g. stderr of asan.
- detect_leaks : 1 If 1, and if LeakSanitizer is enabled try to detect memory leaks during fuzzing (i.e. not only at shut down).
- purge_allocator_interval : 1 Purge allocator caches and quarantines every seconds. When rss_limit_mb is specified (>0), purging starts when RSS exceeds 50% of rss_limit_mb. Pass purge_allocator_interval=-1 to disable this functionality.
- trace_malloc : 0 If >= 1 will print all mallocs/frees. If >= 2 will also print stack traces.
- rss_limit_mb 204: 8 If non-zero, the fuzzer will exit uponreaching this limit of RSS memory usage.
- malloc_limit_mb : 0 If non-zero, the fuzzer will exit if the target tries to allocate this number of Mb with one malloc call. If zero (default) same limit as rss_limit_mb is applied.
- exit_on_src_pos : 0 Exit if a newly found PC originates from the given source location. Example: -exit_on_src_pos=foo.cc:123. Used primarily for testing libFuzzer itself.
- exit_on_item : 0 Exit if an item with a given sha1 sum was added to the corpus. Used primarily for testing libFuzzer itself.
- ignore_remaining_args : 0 If 1, ignore all arguments passed after this one. Useful for fuzzers that need to do their own argument parsing.
- focus_function : 0 Experimental. Fuzzing will focus on inputs that trigger calls to this function. If -focus_function=auto and -data_flow_trace is used, libFuzzer will choose the focus functions automatically. Disables -entropic when specified.
- entropic : 1 Enables entropic power schedule.
- entropic_feature_frequency_threshold 25: 5 Experimental. If entropic is enabled, all features which are observed less often than the specified value are considered as rare.
- entropic_number_of_rarest_features 10: 0 Experimental. If entropic is enabled, we keep track of the frequencies only for the Top-X least abundant features (union features that are considered as rare).
- entropic_scale_per_exec_time : 0 Experimental. If 1, the Entropic power schedule gets scaled based on the input execution time. Inputs with lower execution time get scheduled more (up to 30x). Note that, if 1, fuzzer stops from being deterministic even if a non-zero random seed is given.
- analyze_dict : 0 Experimental
- use_clang_coverage : 0 Deprecated; don't use
- data_flow_trace : 0 Experimental: use the data flow trace
- collect_data_flow : 0 Experimental: collect the data flow trace
- create_missing_dirs : 0 Automatically attempt to create directories for arguments that would normally expect them to already exist (i.e. artifact_prefix, exact_artifact_path, features_dir, corpus)
- Supports fuzzing on macOS and *nix
- Code coverage fuzzer
- Use Pytezos from thirdparty folder
- Rewrite the emulator in Rust
- Write documentation
- Add more examples and tests
- Support fork mode!