Version 0.8.2 (available on the official R repository) fixes the issues reported with 0.8.0 and 0.8.1. Please make sure you are using the latest version!
The two following vignettes complement information found on this page:
summarytools is an R package providing tools to neatly and quickly summarize data. Its main purpose is to provide hassle-free functions that every R programmer once wished were included in base R:
- descriptive statistics with all common univariate statistics for numerical vectors.
- frequency tables with proportions, cumulative proportions and missing data information.
- cross-tabulations between two factors or any discrete data, with total, rows or columns proportions.
- Extensive data frame summaries that facilitate data cleaning and firsthand evaluation
One of its goals is to make it easier for newcomeRs who might be used to other statistical software which usually provide a wide range of functions and procedures out-of-the-box, making it very simple to create, with code or with a few point-and-click actions, thorough and well-formatted reports. For most tasks not relying on advanced statistical methods, summarytools allows you to do just that.
Here are some of the package's features:
- Variable and data frame labels are supported
- Sampling weights can be used in frequency tables and descriptive statistics
- Output files of various formats can be generated (plaintext, markdown and html)
- The html outputs are well integrated in RStudio (if an external browser is not your preferred method)
- You're looking for straightforward descriptive functions to get up and running in no time
- You're looking for flexibility in terms of outputs
To benefit from all the latests fixes, install it from GitHub:
install.packages("devtools")
library(devtools)
install_github('dcomtois/summarytools')To install the most recent version on the R-CRAN repository, just type into your R console:
install.packages("summarytools")For the most up-to-date version that has all the latest features but might also contain bugs (which can be fixed rapidly in most cases):
install.packages("devtools")
library(devtools)
install_github('dcomtois/summarytools', ref='dev-current')You can also see the source code and documentation on the official R site here.
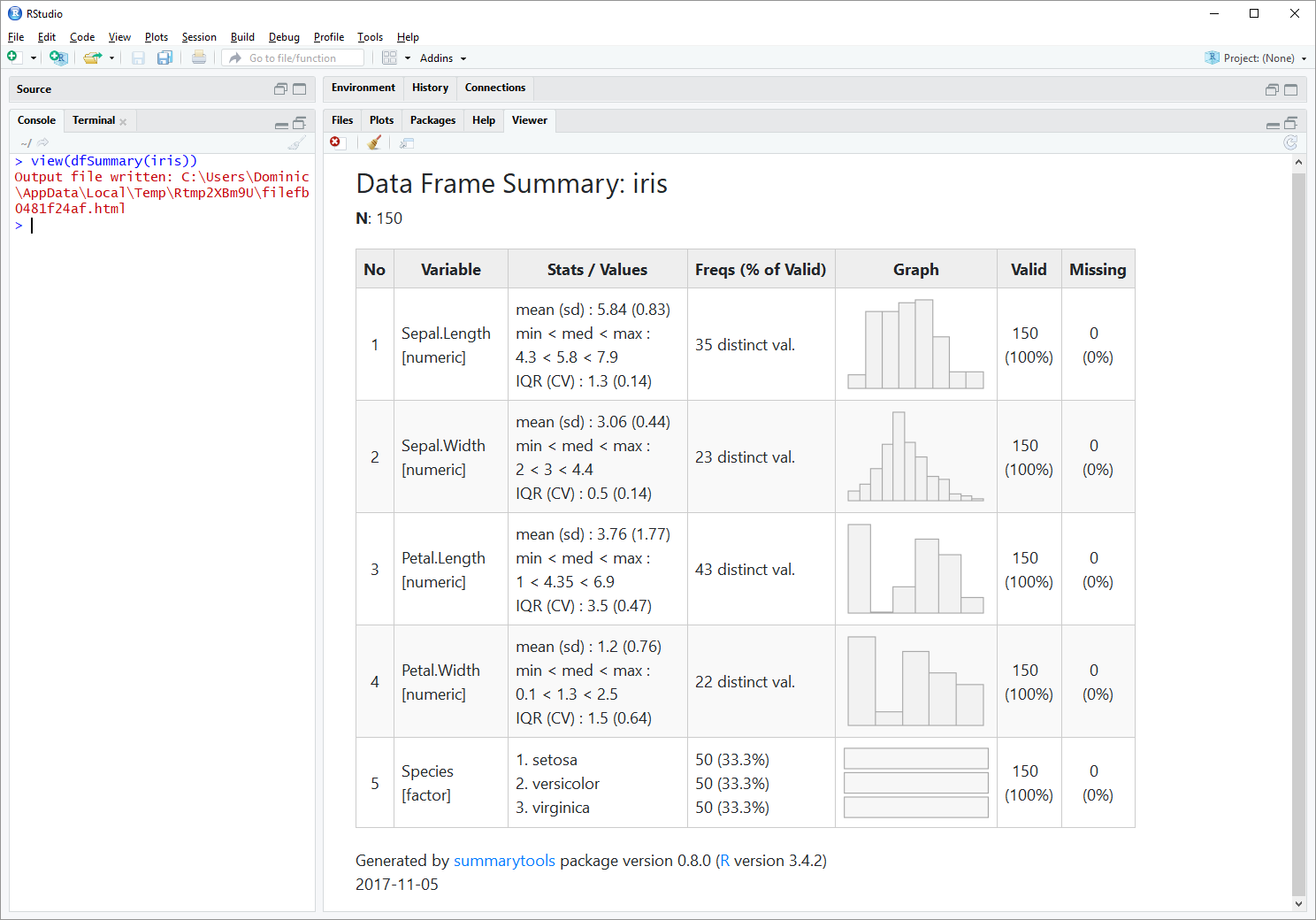
Using the iris sample data frame, we'll jump right to the most popular function in the package, dfSummary (Data Frame Summary).
With the following 2 lines of code, we'll generate a summary report for ''iris`` and have it displayed in RStudio's Viewer pane:
library(summarytools)
view(dfSummary(iris))Building on the strengths of pander and htmltools, the summary reports produced by summarytools can be:
- Displayed in plain text in the R console (default behaviour)
- Written to plain text files / markdown text files
- Written to html files that fire up in RStudio's Viewer pane or in your system's default browser
The freq() function generates a table of frequencies with counts and proportions.
library(summarytools)
freq(iris$Species)Frequencies
iris$Species
Type: Factor (unordered)
Freq % Valid % Valid Cum. % Total % Total Cum.
---------------- ------ --------- -------------- --------- --------------
setosa 50 33.33 33.33 33.33 33.33
versicolor 50 33.33 66.67 33.33 66.67
virginica 50 33.33 100.00 33.33 100.00
<NA> 0 0.00 100.00
Total 150 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00
The descr() function generates common central tendency statistics and measures of dispersion for numerical data. It can handle single vectors as well as dataframes, in which case it just ignores non-numerical columns.
We'll use the rmarkdown style for the next example:
descr(iris, style = "rmarkdown")N: 150
| Sepal.Length | Sepal.Width | Petal.Length | Petal.Width | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 5.84 | 3.06 | 3.76 | 1.20 |
| Std.Dev | 0.83 | 0.44 | 1.77 | 0.76 |
| Min | 4.30 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.10 |
| Median | 5.80 | 3.00 | 4.35 | 1.30 |
| Max | 7.90 | 4.40 | 6.90 | 2.50 |
| MAD | 1.04 | 0.44 | 1.85 | 1.04 |
| IQR | 1.30 | 0.50 | 3.50 | 1.50 |
| CV | 7.06 | 7.01 | 2.13 | 1.57 |
| Skewness | 0.31 | 0.31 | -0.27 | -0.10 |
| SE.Skewness | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Kurtosis | -0.61 | 0.14 | -1.42 | -1.36 |
| N.Valid | 150.00 | 150.00 | 150.00 | 150.00 |
| Pct.Valid | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
If your eyes/brain prefer seeing things the other way around, just use "transpose=TRUE". Here, we also select only the statistics we wish to see:
descr(iris, stats = c("mean", "sd", "min", "med", "max"), transpose = TRUE)N: 150
| Mean | Std.Dev | Min | Median | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sepal.Length | 5.84 | 0.83 | 4.30 | 5.80 | 7.90 |
| Sepal.Width | 3.06 | 0.44 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 4.40 |
| Petal.Length | 3.76 | 1.77 | 1.00 | 4.35 | 6.90 |
| Petal.Width | 1.20 | 0.76 | 0.10 | 1.30 | 2.50 |
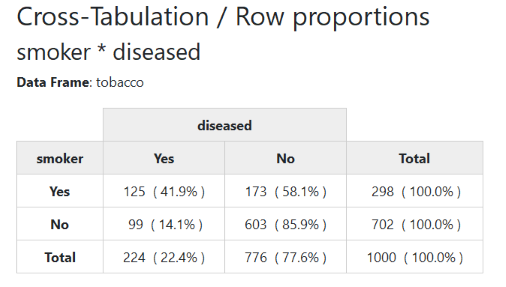
Here we'll use a sample data frame included in the package (tobacco), which contains simulated data. Say we want to cross-tabulate variables smoker and diseased. By default, ctable() gives row proportions, so we don't need to specify any additionnal parameter.
Here, instead of ctable(tobacco$smoker, tobacco$diseased), we'll make use of the with() (R-base) function:
data("tobacco")
with(tobacco, ctable(smoker, diseased))Cross-Tabulation / Row proportions
smoker * diseased
Data Frame: tobacco
-------- ---------- ------------- ------------- ---------------
diseased Yes No Total
smoker
Yes 125 (41.9%) 173 (58.1%) 298 (100.0%)
No 99 (14.1%) 603 (85.9%) 702 (100.0%)
Total 224 (22.4%) 776 (77.6%) 1000 (100.0%)
-------- ---------- ------------- ------------- ---------------
Note that markdown has no support (yet) for multi-line headers. Here is what the html version looks like:
view(with(tobacco, ctable(smoker, diseased)))It is possible to display column, total, or no proportions at all. We can also omit the marginal totals and proportions altogether, so at its simplest form, we have:
with(tobacco, ctable(smoker, diseased, prop = "n", totals = FALSE))Cross-Tabulation
smoker * diseased
Data Frame: tobacco
-------- ---------- ----- -----
diseased Yes No
smoker
Yes 125 173
No 99 603
-------- ---------- ----- -----
As seen earlier, the dfSummary() function gives information for all variables contained in a data frame. The objective in building this function was to fit as much relevant information as possible in a concise, legible table. Version 0.8.0 introduced graphs for both ascii and html outputs.
dfSummary(tobacco)Data Frame Summary: tobacco
N: 1000
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
No Variable Stats / Values Freqs (% of Valid) Text Graph Valid Missing
---- ---------------- ---------------------------- ---------------------- --------------------------- --------- ---------
1 gender 1. F 489 (50.0%) IIIIIIIIIIIIIIII 978 22
[factor] 2. M 489 (50.0%) IIIIIIIIIIIIIIII (97.8%) (2.2%)
2 age mean (sd) : 49.6 (18.29) 63 distinct val. . . . . : 975 25
[numeric] min < med < max : : . . : : : : : . : : (97.5%) (2.5%)
18 < 50 < 80 : : : : : : : : : : : :
IQR (CV) : 32 (0.37) : : : : : : : : : : : :
: : : : : : : : : : : :
: : : : : : : : : : : :
3 age.gr 1. 18-34 258 (26.5%) IIIIIIIIIIIII 975 25
[factor] 2. 35-50 241 (24.7%) IIIIIIIIIIII (97.5%) (2.5%)
3. 51-70 317 (32.5%) IIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
4. 71 + 159 (16.3%) IIIIIIII
4 BMI mean (sd) : 25.73 (4.49) 974 distinct val. : 974 26
[numeric] min < med < max : : : . (97.4%) (2.6%)
8.83 < 25.62 < 39.44 : : :
IQR (CV) : 5.72 (0.17) : : : : :
: : : : : .
. : : : : : : : .
5 smoker 1. Yes 298 (29.8%) IIIIII 1000 0
[factor] 2. No 702 (70.2%) IIIIIIIIIIIIIIII (100%) (0%)
6 cigs.per.day mean (sd) : 6.78 (11.88) 37 distinct val. : 965 35
[numeric] min < med < max : : (96.5%) (3.5%)
0 < 0 < 40 :
IQR (CV) : 11 (1.75) :
:
: . . .
7 diseased 1. Yes 224 (22.4%) IIII 1000 0
[factor] 2. No 776 (77.6%) IIIIIIIIIIIIIIII (100%) (0%)
8 disease 1. Hypertension 36 (16.2%) IIIIIIIIIIIIIIII 222 778
[character] 2. Cancer 34 (15.3%) IIIIIIIIIIIIIII (22.2%) (77.8%)
3. Cholesterol 21 ( 9.5%) IIIIIIIII
4. Heart 20 ( 9.0%) IIIIIIII
5. Pulmonary 20 ( 9.0%) IIIIIIII
6. Musculoskeletal 19 ( 8.6%) IIIIIIII
7. Diabetes 14 ( 6.3%) IIIIII
8. Hearing 14 ( 6.3%) IIIIII
9. Digestive 12 ( 5.4%) IIIII
10. Hypotension 11 ( 5.0%) IIII
[ 3 others ] 21 ( 9.4%) IIIIIIIII
9 samp.wgts mean (sd) : 1 (0.08) 0.86!: 267 (26.7%) IIIIIIIIIIIII 1000 0
[numeric] min < med < max : 1.04!: 249 (24.9%) IIIIIIIIIIII (100%) (0%)
0.86 < 1.04 < 1.06 1.05!: 324 (32.4%) IIIIIIIIIIIIIIII
IQR (CV) : 0.19 (0.08) 1.06!: 160 (16.0%) IIIIIII
! rounded
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
summarytools uses the pander package to generate ascii content. As a consequence, we can easily generate markdown content; We do this simply by specifying style="rmarkdown".
In the console, the output of a function using style = 'rmarkdown' looks like this:
## Frequencies
### iris$Species
**Type:** Factor (unordered)
| | Freq | % Valid | % Valid Cum. | % Total | % Total Cum. |
|---------------:|-----:|--------:|-------------:|--------:|-------------:|
| **setosa** | 50 | 33.33 | 33.33 | 33.33 | 33.33 |
| **versicolor** | 50 | 33.33 | 66.67 | 33.33 | 66.67 |
| **virginica** | 50 | 33.33 | 100.00 | 33.33 | 100.00 |
| **\<NA\>** | 0 | | | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| **Total** | 150 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
This ``ascii-plus-plus'' content needs an interpreted in order to be displayed as html. markdown documents can be converted to other formats as well, such as pdf or rtf.
To learn more about markdown and rmarkdown, see John MacFarlane's page and this RStudio's R Markdown Quicktour.
Version 0.8.0 of summarytools uses RStudio's htmltools package and version 4 of Bootstrap's cascading stylesheets.
It is also possible to include your own css if you wish to customize the look of the output tables.
summarytools has a generic print() method, print.summarytools. By default, its method argument is set to 'pander'. To easily display html outputs in RStudio's Viewer, we use the view() function, which acts as a wrapper around the generic print function, this time using method = 'viewer'. When used outside of RStudio, the method falls back on 'browser' and the report is opened in your system's default browser.
When using by() (with freq() or descr()) or lapply() (with freq()), R returns a list containing summarytools objects. Using the view() function with those objects is necessary in order to have non-redundant and clean section headings.
Example: Using the iris data frame, we will display descriptive statistics broken down by Species.
# First save the results
iris_stats_by_species <- by(data = iris,
INDICES = iris$Species,
FUN = descr, stats = c("mean", "sd", "min", "med", "max"),
transpose = TRUE)
# Then use view(), like so:
view(iris_stats_by_species, method = "pander")Non-numerical variable(s) ignored: Species
Descriptive Statistics: iris
Group: iris$Species = setosa
N: 50
Mean Std.Dev Min Median Max
------------------ ------ --------- ------ -------- ------
Sepal.Length 5.01 0.35 4.30 5.00 5.80
Sepal.Width 3.43 0.38 2.30 3.40 4.40
Petal.Length 1.46 0.17 1.00 1.50 1.90
Petal.Width 0.25 0.11 0.10 0.20 0.60
Group: iris$Species = versicolor
N: 50
Mean Std.Dev Min Median Max
------------------ ------ --------- ------ -------- ------
Sepal.Length 5.94 0.52 4.90 5.90 7.00
Sepal.Width 2.77 0.31 2.00 2.80 3.40
Petal.Length 4.26 0.47 3.00 4.35 5.10
Petal.Width 1.33 0.20 1.00 1.30 1.80
Group: iris$Species = virginica
N: 50
Mean Std.Dev Min Median Max
------------------ ------ --------- ------ -------- ------
Sepal.Length 6.59 0.64 4.90 6.50 7.90
Sepal.Width 2.97 0.32 2.20 3.00 3.80
Petal.Length 5.55 0.55 4.50 5.55 6.90
Petal.Width 2.03 0.27 1.40 2.00 2.50
To see an html version of these results, proceed like this:
view(iris_stats_by_species)The console will always tell you the location of the temporary html file that is created in the process. However, you can specify the name and location of that file explicitly if you need to reuse it later on:
view(iris_stats_by_species, file = "~/iris_stats_by_species.html")There is also an append = boolean parameter for adding content to existing reports.
When a summarytools object is stored, its formatting attributes are stored with it. However, you can override most of them when using the print() function.
Example:
data(tobacco)
bmi_stats <- descr(tobacco$BMI)
print(bmi_stats, Variable.label = "Body Mass Index")Descriptive Statistics: tobacco$BMI
Variable Label: Body Mass Index
N: 1000
BMI
----------------- --------
Mean 25.73
Std.Dev 4.49
Min 8.83
Median 25.62
Max 39.44
MAD 4.18
IQR 5.72
CV 5.73
Skewness 0.02
SE.Skewness 0.08
Kurtosis 0.26
N.Valid 974.00
Pct.Valid 97.40
Versions 0.5 and above support weights for freq() and descr().
- Putting together the object's class(es), type (typeof), mode, storage mode, length, dim and object.size, all in a single table
- Extending the
is()function in a way that the object is tested against all functions starting withis.-- see this post on StackOverflow for details; - Giving a list of the object's attributes names and length (c.g. rownames, dimnames, labels, etc.)
> what.is(c)
$properties
property value
1 class function
2 typeof builtin
3 mode function
4 storage.mode function
5 dim
6 length 1
7 object.size 56 Bytes
$extensive.is
[1] "is.function" "is.primitive" "is.recursive"
$function.type
[1] "primitive" "generic"
> what.is(NaN)
$properties
property value
1 class numeric
2 typeof double
3 mode numeric
4 storage.mode double
5 dim
6 length 1
7 object.size 48 Bytes
$extensive.is
[1] "is.atomic" "is.double" "is.na" "is.nan" "is.numeric" "is.vector"
$object.type
[1] "base"
I've been working on summarytools on and off over the last few months. Now I'm happy to introduce version 0.8. The most notable changes compared to 0.7 are:
- A cross-tabulation function,
ctable() - Improved support for
by(),with()andlapply()functions - Optional barplots and histograms in
dfSummary() - New layouts, most noticeable in html reports
- Improved flexibility on several fronts
- Support for Date / POSIX columns
The package comes with no guarantees. It is a work in progress and feedback / feature requests are welcome. Just send me an email (dominic.comtois (at) gmail.com), or open an Issue if you find a bug.
Also, the package grew significantly larger, and maintaining it all by myself is time consuming. If you would like to contribute, please get in touch, I'd greatly appreciate the help.