This is a BOSH release for spinning Kubernetes 1.14.0, using BOSH to orchestrate the "physical" nodes that comprise the various roles of a Kubernetes cluster (master and worker).
This is, at present, an investigative project, wherein I am attempting to learn how to assemble a working, highly-available Kubernetes cluster from first principles.
I am following Kelsey Hightower's Kubernetes the Hard Way write-up.
I am aware of other efforts to BOSH-ify Kubernetes, like kubo. This project does not aim to replace those other projects in any way, and if you find joy in using those projects, please continue using them.
This repository comes with some sample manifests to illustrate how one might configure a k8s deployment in the wild.
-
tinynetes - A single-VM instance, all-in-one k8s "cluster", suitable for experimentation or CI/CD.

-
labernetes - A multi-node cluster of combined master+worker nodes, suitable for shared lab exercises.
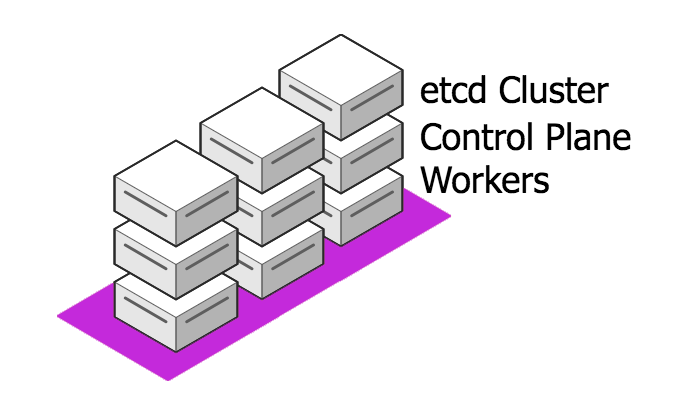
-
prodernetes - A proper cluster with master and worker nodes on separate VMs, allowing one to scale the workers separately from the control plane. All aspects of the control plane are co-located (etcd, api, scheduler, and cmgr). Suitable for (possibly) some real-world prod use.
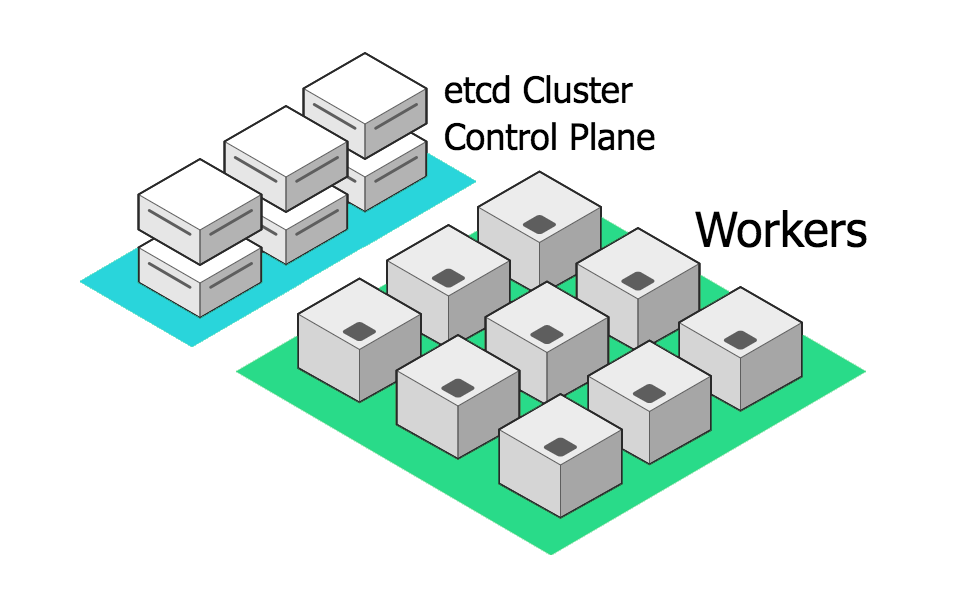
-
hugernetes - A REALLY BIG CLUSTER that splits the etcd component out onto its own multi-node cluster, leaving the control plane VMs to run api, scheduler, and the controller manager. Suitable for (possibly) some real-world prod use.
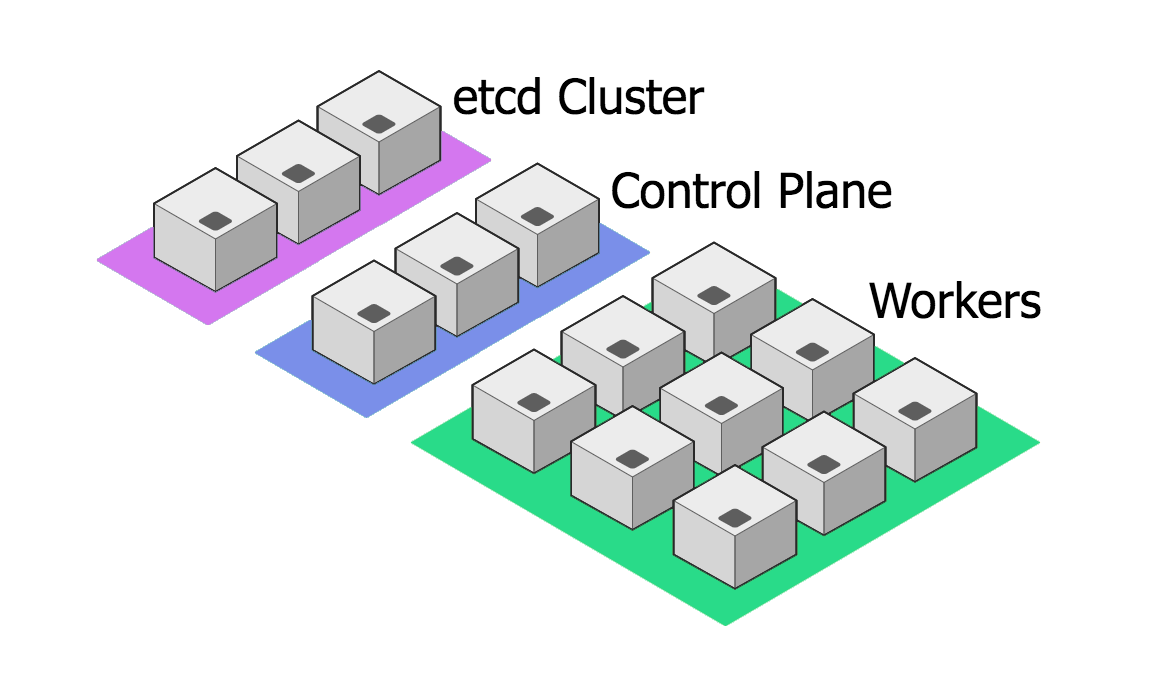
These are found in the manifests/ directory, and can be deployed
without further pre-processing (no Spruce... yet).
In order to perform activites on the pods which require DNS lookups, such as kubectl exec or kubectl pods, BOSH DNS must be deployed. The easiest way of doing this is by adding BOSH DNS to your Runtime Config. An example of a Runtime Config with BOSH DNS can be found here at bosh.io.
Once Kubernetes is deployed you will likely want to connect to it with kubectl from a jumpbox or laptop but you need a configuration for that. Fortunately there is a jumpbox script which generates the configuration. From one of the control instances run the following as root:
. /var/vcap/jobs/jumpbox/envrc
This will generate a long-lived cluster cert, user client cert and client key and make these available in an environment variable named KUBECONFIG. From this control node you are now authenticated and kubectl is also added to the PATH for the current BOSH SSH session.
Get the contents of this variable on the control instance by running:
cat $KUBECONFIG
On your jumpbox or anywhere else you need a kubectl configuration file, write out the contents to a file (such as my-bosh-deployed-k8s-config-file.yaml) and then source the file similar to:
export KUBECONFIG=$PWD/my-bosh-deployed-k8s-config-file.yaml
I am not currently accepting unrequested PR's or other contributions to this repository. As I said, this is a personal project, for exploring the world of Kubernetes through the lens of a BOSH director.
If you find this, and manage to get it to work for you, great! I'd love to hear from you, of your successes and struggles.