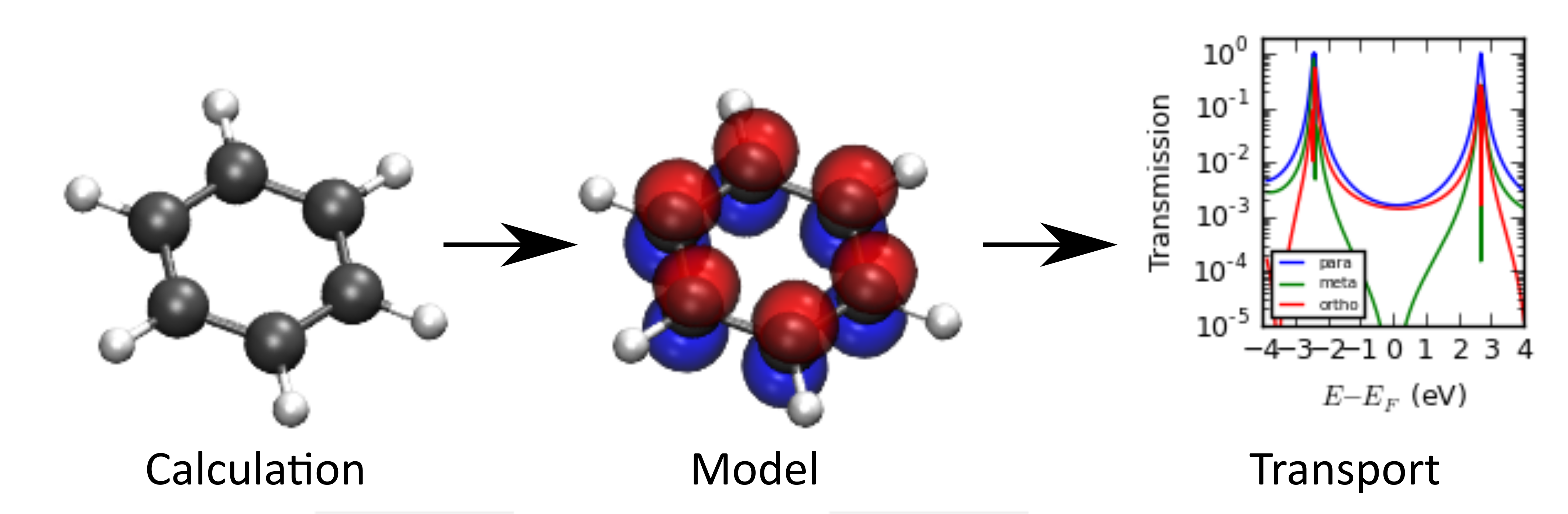
This implementation of natural orbitals can be used to e.g.:
- Extract parameters for Huckel-type/tight-binding models.
- Calculate the electrical conductance of a molecule from a gas phase calculation.
natural-orbitals is a Python class written to calculate different types of natural orbitals based on the output of electronic structure codes. It can also calculate effective Hamiltonians and calculate the electrical conductance on the basis of the Landauer formula.
Run an example file with python: python benzene_transport_example.py or go through the tutorial belown.
Supply the class with input extracted from DFT or HF calculations. Input from GPAW is used in the example but output from Gaussian09 is also possible.
The implementation of natural atomic orbitals (NAO) is based on:
Reed, A.; Weinstock, R.; Weinhold, F. J. Chem. Phys. 1985, 83 (1985), 735.
Note: Spherical symmetry is not implemented. As a result, the NAOs do not neccesarily resemble s, p or d-orbitals.
The implementation of natural hybrid orbitals is based on:
Foster, J. P.; Weinhold, F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102 (22), 7211.
Below I go through some of the features of the class.
The class can be initialized with the following parameters.
"""Arguments:
'h': (N,N) ndarray
Hamiltonian/Kohn-Sham operator in atom-centered basis.
's': (N,N) ndarray
Overlap matrix in atom-centered basis.
'ne': integer int
Number of electron pairs. It is assumed that the first 'ne' molecular eigenfunctions of h have occupations 2.0.
'mol':
Atoms object from e.g. Atomistic Simulation Environment (ASE).
'basis_dic': dict
Dictionary which links atom index to list of basis function indices. Basis function indices associated with each atom must be consequtive.
'NHO_model':
{False, Boolean}, optional
If True, an Atoms object (from ASE) will be saved. The ordering of the 'atoms' in this object will have the same ordering as the natural hybrids
obtained from get_natural_bonding_orbitals().
'NBO_model':
{False, Boolean}, optional
If True, an Atoms object (from ASE) will be saved. The ordering of the 'atoms' in this object will have the same ordering as the natural bonding orbitals
obtained from get_natural_bonding_orbitals().
'core_and_valence': {None, bool)
If input is for an all-electron calculation (like Gaussian): set this to True."""In principle, input from any electronic structure code can be used.
The tool dump_hamiltonian_parallel() can be used to save the Hamiltonian and overlap matrix to disk. If calc is a converged GPAW calculator and mol is an atoms object:
from gpaw.lcao.tools import dump_hamiltonian_parallel as dhp
calc.dump_hamiltonian_parallel('hs', mol)This will generate a pickle file. The library basis_dic can be generated with e.g. :
from gpaw.lcao.tools import get_bfi2
basis_dic = {}
for atom in mol:
basis_dic[atom.index]=get_bfi2(mol.get_chemical_symbols(), 'dzp', [atom.index])Obtaining input from Gaussian is slightly more tricky. One way to go about it is to save the read-write file (.rwf) by including the following lines in the beginning of the Gaussian input file (.com):
%rwf=mol.rwf
%save
The .rwf can then copied to the working directory. The script parse_g09.sh can then be used to extract the required input. The script takes the output file of the calculation as input. This script relies on the tool rwfdump. Use tool directly from the terminal:
python parse_g09.py mol.log
This will create a folder containing the necessary input. If using a Pople style basis set, the function get_basis_STOnG() which can be imported from NO.py does the exact same thing as GPAWs get_bfi2 and can be used in the same way to generate the library.
After the class has been initialized, different kinds of natural orbitals can be obtained as linear combination of the initial local basis.
By calling .get_NAO() you can get:
- natural molecular orbitals: (.NO)
- pre-natural atomic orbitals (.PNAO)
- natural atomic orbitals (.NAOs)
By calling .get_natural_bonding_orbitals() you can get:
- pre-natural hybrid orbitals (.PNHO)
- natural hybrid orbitals (.NHOs)
- natural bonding orbitals (.NBOs)
If you use GPAW, you can use the function plot_basis() to plot the orbitals obtained from GPAW calculations:
plot_basis(NO.NAOs, mol, pzs, basis = 'dzp', folder_name='./files_benzene/pzs') You can rotate matrix elements yourself:
h_NHO = np.dot(NO.NHOs.T.conj(), np.dot(NO.h, NO.NHOs))You can also find some handy matrices as attributes:
h_NHO = NO.h_NHOThe function .get_effective_Hamiltonian() can be used to construct energy-dependent effective Hamiltonians:
get_effective_Hamiltonian(self, indices, energies,h2=None, s2=None):
"""
Function to calculate energy-dependent effective Hamiltonian.
The Green's function of the effective Hamiltonian reproduces the corresponding retarded Green's function elements of the full non-interacting Hamiltonian.
"""The class can be used to calculate the Landauer transmission of gas phase molecules using the method get_transmission(). This requires specifying electrode self energies. Arbitrary Hamiltonians and overlap can be specified.
"""
Returns tranmission or partitioned tranmission (if partition!=None).
energies: list/1D-array of energies.
SigmaL/R: Left and right wide-band electrodes.
h2/s2: if None: Assume NAO.
eta: positive infinitesimal used to construct retarded Green's function.
rotate: array which defines unitary transformation. If!=None: SigmaL/SigmaR/h/s will be rotated to basis.
partition: List of lists. E.g. [ [0,10], [20,40] ]
If!=None: will return partitioned transmission as sum of terms
GammaL_ij Gr_jk GammaR_kl Ga_li where i,j,k,l are indices in one of the lists.
"""