Data Structures and Algorithms
by Artem Moshnin as part of my studies of Computer Science Degree
Data Structures
A data structure is a particular way of organizing and storing data in a computer so that it can be accessed and modified efficiently. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the functions or operations that can be applied to the data.
B - Beginner, A - Advanced
Algorithms
An algorithm is an unambiguous specification of how to solve a class of problems. It is a set of rules that precisely define a sequence of operations.
B - Beginner, A - Advanced
Algorithms by Topic
- Strings
ALevenshtein Distance - minimum edit distance between two sequences
Useful Information
References
▶ Data Structures and Algorithms on YouTube
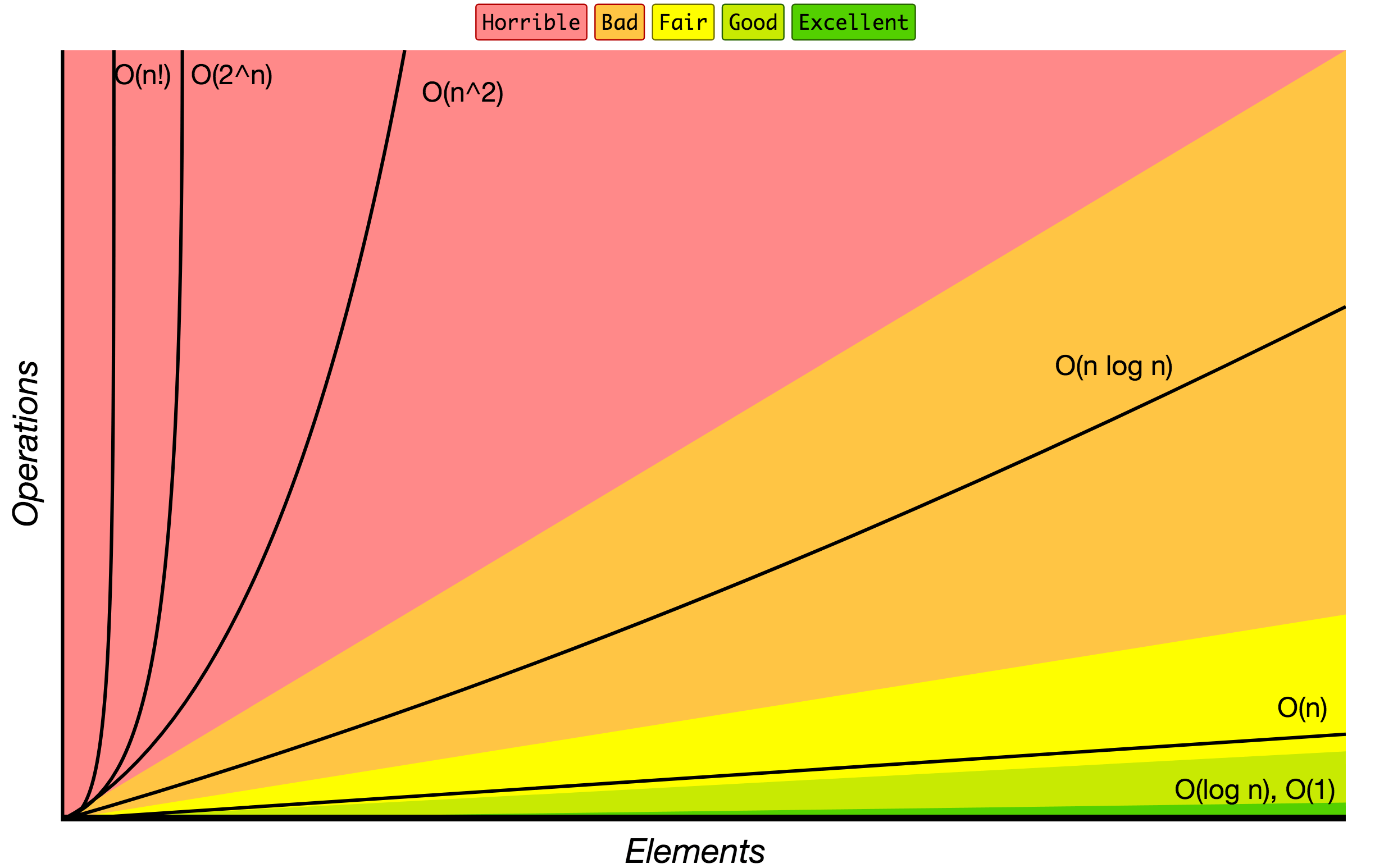
Big O Notation
Big O notation is used to classify algorithms according to how their running time or space requirements grow as the input size grows. On the chart below you may find most common orders of growth of algorithms specified in Big O notation.
Source: Big O Cheat Sheet.
Below is the list of some of the most used Big O notations and their performance comparisons against different sizes of the input data.
| Big O Notation | Computations for 10 elements | Computations for 100 elements | Computations for 1000 elements |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(1) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| O(log N) | 3 | 6 | 9 |
| O(N) | 10 | 100 | 1000 |
| O(N log N) | 30 | 600 | 9000 |
| O(N^2) | 100 | 10000 | 1000000 |
| O(2^N) | 1024 | 1.26e+29 | 1.07e+301 |
| O(N!) | 3628800 | 9.3e+157 | 4.02e+2567 |
Data Structure Operations Complexity
| Data Structure | Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Array | 1 | n | n | n | |
| Stack | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Queue | n | n | 1 | 1 | |
| Linked List | n | n | 1 | n | |
| Hash Table | - | n | n | n | In case of perfect hash function costs would be O(1) |
| Binary Search Tree | n | n | n | n | In case of balanced tree costs would be O(log(n)) |
| B-Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| Red-Black Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| AVL Tree | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | log(n) | |
| Bloom Filter | - | 1 | 1 | - | False positives are possible while searching |
Array Sorting Algorithms Complexity
| Name | Best | Average | Worst | Memory | Stable | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bubble sort | n | n2 | n2 | 1 | Yes | |
| Insertion sort | n | n2 | n2 | 1 | Yes | |
| Selection sort | n2 | n2 | n2 | 1 | No | |
| Heap sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | 1 | No | |
| Merge sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n log(n) | n | Yes | |
| Quick sort | n log(n) | n log(n) | n2 | log(n) | No | Quicksort is usually done in-place with O(log(n)) stack space |
| Shell sort | n log(n) | depends on gap sequence | n (log(n))2 | 1 | No | |
| Counting sort | n + r | n + r | n + r | n + r | Yes | r - biggest number in array |
| Radix sort | n * k | n * k | n * k | n + k | Yes | k - length of longest key |