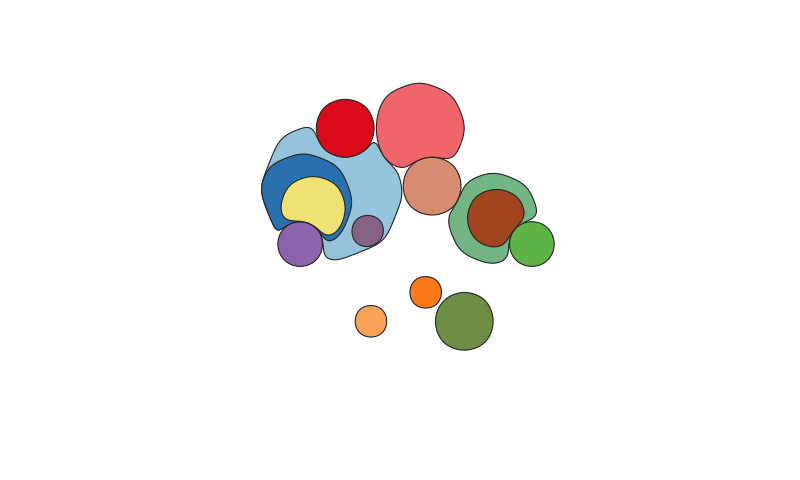
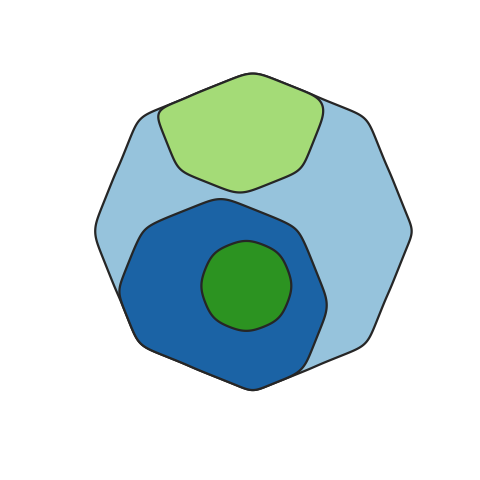
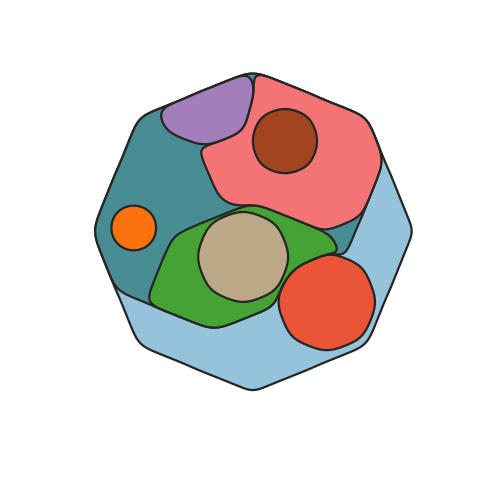
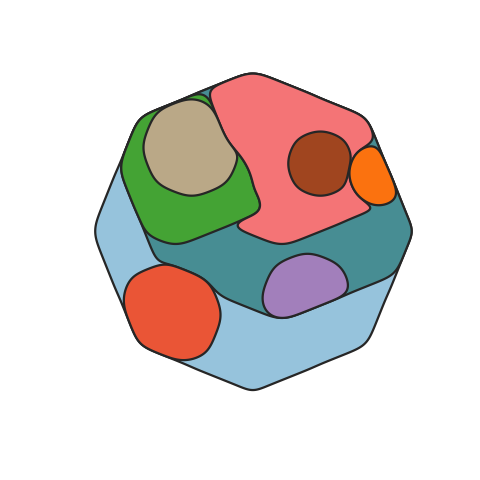
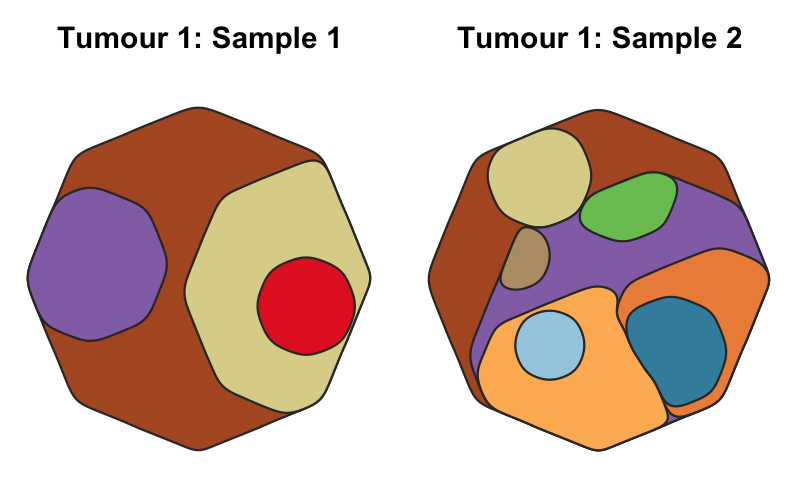
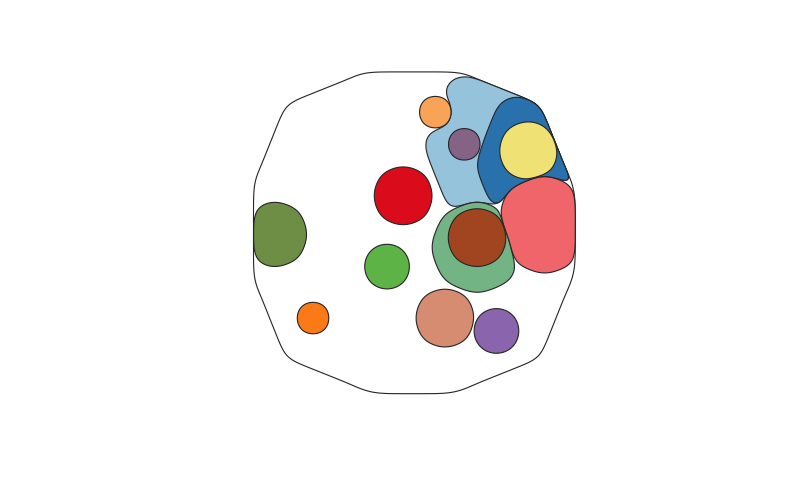
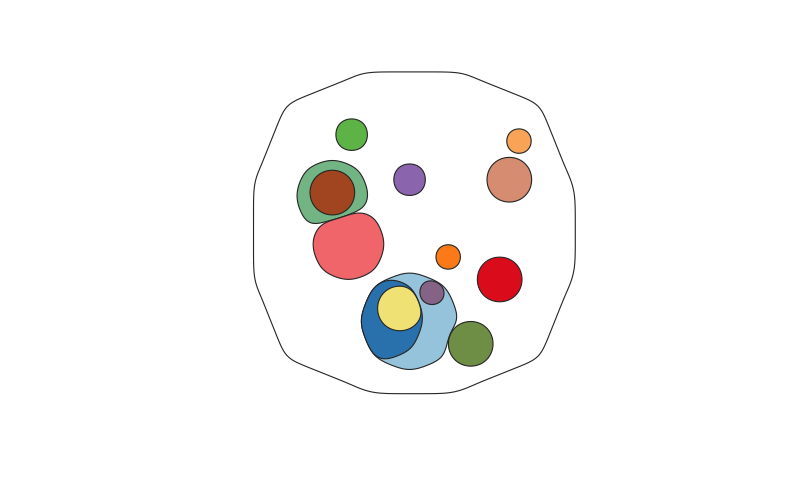
A function to map the distribution of somatic clones in sample or set of samples, accounting for the clone size(s), ie the Cancer Cell Fraction (CCF), and phylogenetic relationships between clones. Clone positions are semi-randomised in the plot while maintaining the two formally described factors.
Unfortunately the R package Rgeos which is required for cloneMaps has been archieved on CRAN. Therefore install geos using homebrew and install the R package using R-Forge:
brew install geos
install.packages("rgeos", repos="http://R-Forge.R-project.org", type="source”)You can then use devtools::install_github() to install cloneMap from this repository:
devtools::install_github("amf71/cloneMap")`load package:
library(cloneMap)tree_example_1, tree_example_2, tree_example, CCFs_example_1, CCFs_example_2, and clone_colours_example are loaded into the R environment (hidden) upon package loading and also are defined below:
Example CCF tables, these could be from the same tumour
CCFs_example_1 <- data.frame( clones = c( 1, 2, 3, 4 ),
CCF = c( 1, 0.4, 0.2, 0.1 ),
stringsAsFactors = F)
CCFs_example_2 <- data.frame( clones = c( 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 ),
CCF = c( 1, 0.1, 0.7, 0.2, 0.25, 0.03, 0.06, 0.1, 0.05 ),
stringsAsFactors = F )Example tree matricies are written with each relationship as a row, the parent as the first column and child as the second
tree_example_1 <- matrix( c(1, 2,
1, 3,
2, 4 ), ncol = 2, byrow = TRUE )
tree_example_2 <- matrix( c(1, 2,
1, 3,
3, 5,
3, 6,
3, 7,
3, 8,
5, 9,
6, 10 ), ncol = 2, byrow = TRUE )
tree_example <- matrix( c(1, 2,
1, 3,
2, 4,
3, 5,
3, 6,
3, 7,
3, 8,
5, 9,
6, 10 ), ncol = 2, byrow = TRUE )Example colours are define using a named vector of hexidecimal colours with clones as names
clone.names <- unique( c( tree_example[,1], tree_example[,2] ) )
clone_colours_example <- c( "#B15928", "#DDD399", "#9471B4", "#ED8F47", "#FDB762",
"#E52829", "#B89B74", "#79C360", "#3F8EAA", "#A6CEE3" )
names(clone_colours_example) <- clone.namesAdditionally a function is provided to make clone colour input objects using a specified RColourBrewer pallete (default = "Paired" palette)
clone.names <- unique( c( tree_example[,1], tree_example[,2] ) )
clone_colours_example_2 <- make_clone_col_input( clone.names )Simple map:
cloneMap( tree_example_1, CCFs_example_1 )More complex map:
cloneMap( tree_example_2, CCFs_example_2 )Use a clone_map object to plot cloneMaps reproducably and much faster:
clone_map_eg <- cloneMap( tree_example_2, CCFs_example_2, output.Clone.map.obj = TRUE, plot.data = FALSE )
cloneMap( clone_map = clone_map_eg )Specify the same clone colours accross several plots:
cloneMap( tree_example, CCFs_example_1, clone.cols = clone_colours_example )
cloneMap( tree_example, CCFs_example_2, clone.cols = clone_colours_example )cloneMaps will also plot unrooted trees - i.e. where some clones are not related to each other. This is common in data derived from normal tissues, rather than tumours, which are dominated by small unrelated clones.
If a clone has no parents or daughters it is specified as clone name (parent) -> clone name (child) as for clones 1, 2, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 in the example below.
tree_example_poly, CCF_example_poly are loaded into the R environment (hidden) upon package loading and also are defined below:
Example CCF table for unrooted data
CCF_example_poly <- data.frame( clones = c( 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 ),
CCF = c( 0.03, 0.05, 0.2, 0.1, 0.02, 0.05, 0.1, 0.05, 0.1, 0.05, 0.02, 0.02, 0.05, 0.03 ),
stringsAsFactors = F )Example tree matrix for unrooted data. Each relationship is specified as a row, the parent as the first column and child as the second
tree_example_poly <- matrix( c(1, 1,
2, 2,
3, 4,
3, 5,
4, 6,
7, 8,
9, 9,
10, 10,
11, 11,
12, 12,
13, 13,
14, 14), ncol = 2, byrow = TRUE )
Plot map of polyclonal data similar to that found in normal tissues.
cloneMap( tree.mat = tree_example_poly,
CCF.data = CCF_example_poly )Plot map of polyclonal data similar to that found in normal tissues with border around the plot area. This makes clearer the % of the tissue containing mutant clones.
cloneMap( tree.mat = tree_example_poly,
CCF.data = CCF_example_poly,
tissue_border = TRUE)Plot map of polyclonal data similar to that found in normal tissues with border with sparsely
spaced clones. Here space_fraction indicates that 70% of the plot area should be white space
indicating that only 70% of cells are wildtype.
cloneMap( tree.mat = tree_example_poly,
CCF.data = CCF_example_poly,
tissue_border = TRUE,
space_fraction = 0.7 )