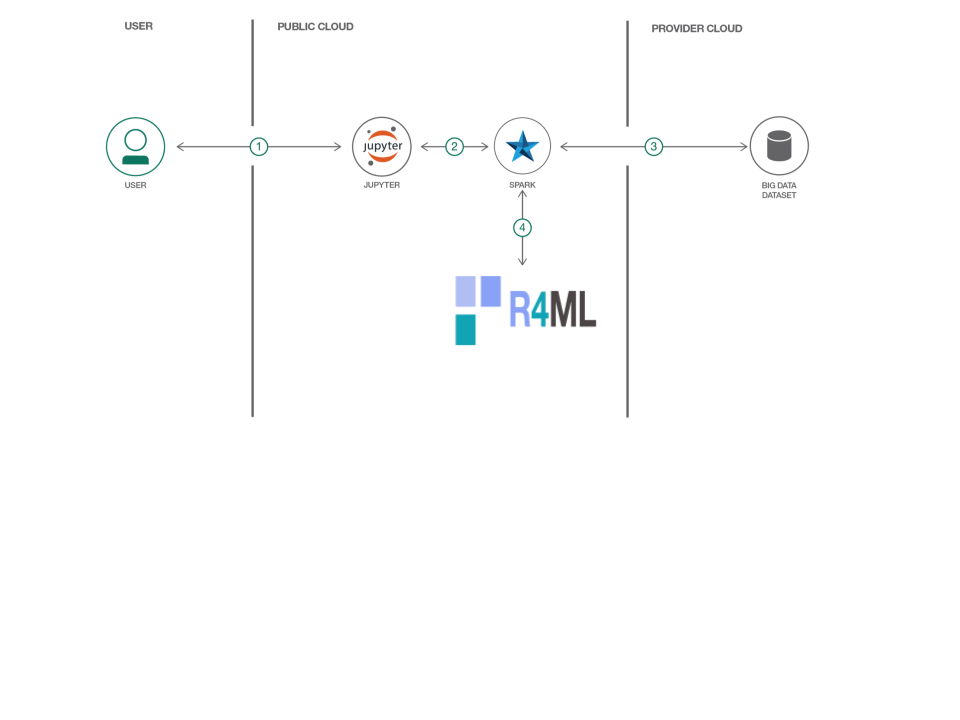
In this developer journey we will use R4ML, a scalable R package, running on IBM Data Science Experience (DSX) to perform various Machine Learning exercises. For those users who are unfamiliar with the Data Science Experience, DSX is an interactive, collaborative, cloud-based environment where data scientists, developers, and others interested in data science can use tools (e.g., RStudio, Jupyter Notebooks, Spark, etc.) to collaborate, share, and gather insight from their data.
When the reader has completed this journey, they will understand how to:
- Use Jupyter Notebooks to load, visualize, and analyze data.
- Run Notebooks in IBM Data Science Experience.
- Leverage R4ML to conduct preprocessing and exploratory analysis with big data
The Intended audience of this code pattern is data scientists, who wish to apply scalable machine learning algorithms using R. R4ML provides various out of the box algorithms to experiments with. This specific Code Pattern will provide a SVM (Suport Vector Machine) example to demonstrate the ease and power of R4ML in implementing the scalable classification. For more information about additional functionality support, documentation, and the roadmap, please vist R4ML
-
We use the Airline On-Time Statistics and Delay Causes from RITA A 1% sample of the "airline" dataset available at http://stat-computing.org/dataexpo/2009/the-data.html This data originally comes from RITA (http://www.rita.dot.gov) and is in the public domain.
-
For this example, we will use, a subset of above dataset, which is shipped with R4ML
-
User can use the bigger dataset from RITA and our code will work with that.
- Load the provided notebook onto the IBM Data Science Experience platform.
- The notebook interacts with an Apache Spark instance.
- A sample big data dataset is loaded into the Jupyter Notebook.
- To perform machine learning, R4ML is used atop Apache Spark.
- Large Scale Model Training for classification using a Support Vector Machine
- Large Scale Model Tuning using Cross validation
Included Components:
- IBM Data Science Experience: Analyze data using RStudio, Jupyter, and Python in a configured, collaborative environment that includes IBM value-adds, such as managed Spark.
- IBM Analytics for Apache Spark: An open source cluster computing framework optimized for extremely fast and large scale data processing.
- Bluemix Object Storage: Build and deliver cost effective apps and services with high reliability and fast speed to market in an unstructured cloud data store.
- Jupyter Notebooks: An open source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations and explanatory text.
- R4ML: R4ML is a scalable, hybrid approach to ML/Stats using R, Apache SystemML, and Apache Spark
-
R4ML is a git downloadable open source R package from IBM
-
Created on top of SparkR and Apache SystemML (so it supports features from both)
-
Acts as a R bridge between SparkR and Apache SystemML
-
Provides a collection of canned algorithms
-
Provides the ability to create custom ML algorithms
-
Provides both SparkR and Apache SystemML functionality
-
APIs are friendlier to the R user
-
We will first load the package and data and do the initial transformation of the dataset
-
Then we will use the inbuilt SVM algorithm from R4ML to predict whether airline will be delayed or not
-
Then we will observe the output accuracy and confusion matrix
-
We will use Cross Validation to improve the accuracy of the classifications.
-
More details are in the notebook.
Follow these steps to setup and run this developer journey. These steps are described in detail below.
Sign up for IBM's Data Science Experience. By signing up for the Data Science Experience, two services will be created in your Bluemix account: DSX-Spark and DSX-ObjectStore. If these services do not exist, or if you are already using them for some other application, you will need to create new instances.
To create these services:
- Login or create your Bluemix account.
- Create your Spark service by selecting the service type Apache Spark. If the name has not already been used, name your service
DSX-Sparkso that you can keep track of it. - Create your Object Storage service by selecting the service type Cloud Object Storage. If the name has not already been used, name your service
DSX-ObjectStorageso that you can keep track of it.
Note: When creating your Object Storage service, select the
Swiftstorage type in order to avoid having to pay an upgrade fee.
Take note of your service names as you will need to select them in the following steps.
First you must create a new Project:
- From the IBM Data Science Experience page either click the
Get Startedtab at the top or scroll down toRecently updated projects. - Click on
New projectunderRecently updated projects. - Enter a
Nameand optionalDescription. - For
Spark Service, select your Apache Spark service name. - For
Storage Type, select theObject Storage (Swift API)option. - For
Target Object Storage Instance, select your Object Storage service name. - Click
Create.
Create Notebook 1:
- Click on your project to open up the project details panel.
- Click
add notebooks. - Click the tab for
From URLand enter aNameand optionalDescription. - Select Language 'R'
- Select Spark version 2.1
- For
Notebook URLenter: https://github.com/aloknsingh/ibm_r4ml_svm_classification/notebooks/R4ML_Classification_modeling_using_SVM.ipynb - For
Spark Service, select your Apache Spark service name. - Click
Create Notebook.
When a notebook is executed, what is actually happening is that each code cell in the notebook is executed, in order, from top to bottom.
Each code cell is selectable and is preceded by a tag in the left margin. The tag
format is In [x]:. Depending on the state of the notebook, the x can be:
- A blank, this indicates that the cell has never been executed.
- A number, this number represents the relative order this code step was executed.
- A
*, which indicates that the cell is currently executing.
There are several ways to execute the code cells in your notebook:
- One cell at a time.
- Select the cell, and then press the
Playbutton in the toolbar.
- Select the cell, and then press the
- Batch mode, in sequential order.
- From the
Cellmenu bar, there are several options available. For example, you canRun Allcells in your notebook, or you canRun All Below, that will start executing from the first cell under the currently selected cell, and then continue executing all cells that follow.
- From the
- At a scheduled time.
- Press the
Schedulebutton located in the top right section of your notebook panel. Here you can schedule your notebook to be executed once at some future time, or repeatedly at your specified interval.
- Press the
Under the File menu, there are several ways to save your notebook:
Savewill simply save the current state of your notebook, without any version information.Save Versionwill save your current state of your notebook with a version tag that contains a date and time stamp. Up to 10 versions of your notebook can be saved, each one retrievable by selecting theRevert To Versionmenu item.
You can share your notebook by selecting the “Share” button located in the top right section of your notebook panel. The end result of this action will be a URL link that will display a “read-only” version of your notebook. You have several options to specify exactly what you want shared from your notebook:
Only text and output: will remove all code cells from the notebook view.All content excluding sensitive code cells: will remove any code cells that contain a sensitive tag. For example,# @hidden_cellis used to protect your dashDB credentials from being shared.All content, including code: displays the notebook as is.- A variety of
download asoptions are also available in the menu.