This project aims to introduce you to the wonderful world of virtualization. This is my first Virtual Machine in VirtualBox under specific instructions. At the end of this project I will be able to set up my own operating system implementing strict rules
- Operating System: Debian

- Encrypted partitions using LVM (Logical Volume Manager)
- Operating system configured with UFW firewall leaving only port 4242 open
- SSH service running on port 4242 only and block root to connect using it
- Implementation of strong password policy
- Installation and configuration of sudo using strict rules
- In addition to root user, a user with my username present which belogs to sudo and user42 groups
- Creation of simple script called monitoring.sh, developed in bash. At startup the script should display some info in all terminals every 10 minutes.
-
Installing Virtual Box

Oracle VM VirtualBox is a free and open-source hosted hypervisor for x86 virtualization, developed by Oracle Corporation. It enables you to run more than one OS at a time. The download file is available here. -
Download Debian ISO. The one I used was amd64 image ;)

Debian, also known as Debian GNU/Linux, is a Linux distribution composed of free and open-source software, developed by the community-supported Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock on August 16, 1993. It is an operating system for a wide range of devices including laptops, desktops and servers. Users like its stability and reliability since 1993. We provide reasonable default configuration for every package. The Debian developers provide security updates for all packages over their lifetime whenever possible. The image downloaded will be used to install the OS at our Virtual Machine in VBox :) -
Installing Debian on Virtual Machine
In order to install Debian in your Virtual Machine and setup encrypted partitions using LVM, I followed this youtube video. The video teaches you to set up partitions as it is required on Bonus part :)
Settings in VBox while creating a new virtual machine:- OS: Debian 64 bit
- Memory(RAM): 1024 MB
- Hard disk file type: VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image) 8GB
- Storage in physical hard disk: dynamically allocated
- Network attached to bridged adapter (to be able to use ssh into de VM)
Configs while installing debian on first startup of VM:
-
SUDO
Sudo (Super-user do) is a program designed to let system administrators allow some users to execute some commands as root (or another user). The basic philosophy is to give as few privileges as possible but still allow people to get their work done. Sudo is also an effective way to log who ran which command and when.-
Installation
sudo apt-get install sudo
-
Configuration
- Authentication using sudo has to be limited to 3 attempts in the event of an incorrect password.
- A custom message of your choice has to be displayed if an error due to a wrong password occurs when using sudo.
- Each action using sudo has to be archived, both inputs and outputs. The log file has to be saved in the /var/log/sudo/ folder.
- The TTY mode has to be enabled for security reasons.
- For security reasons too, the paths that can be used by sudo must be restricted.
In order to achieve these configurations, we should edit sudo configuration file. We can easily access it with
sudo visudo. Access sudoers manual to understand all possible configurations in sudo.

-
-
UFW firewall
UFW is a program for managing a netfilter firewall. Developed to ease iptables firewall configuration, ufw provides a user friendly way to create an IPv4 or IPv6 host-based firewall. By default UFW is disabled.
UFW will be used to configure our OS and leave only port 4242 open. UFW must be active when the virtual machine is launched. -
Users and groups manipulation
It is required that the additional user is assigned to sudo and user42 groups. Also, in the middle of the defense of the project we will be asked to create a new user and assign it to a group.- Create new user
sudo adduser <username>
- Add user to a group
sudo adduser <username> <group_name>
- Add new group
sudo groupadd <group_name>
- Change user password
sudo passwd <username>
- Current user
whoiam
- See current user groups
groups
-
SSH
Secure Shell is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Typical applications include remote command-line, login, and remote command execution, but any network service can be secured with SSH.- Installation
sudo apt install open-ssh client sudo apt install open-ssh server
- Configuring SSH service to run only in port 4242
The file which determines the port for ssh service issshd_config. Inside this file you will see a commented line withPort 22. Uncomment it and change to4242:)
Also, for security reasons, we should block ssh connections as root by editing or addingPermitRootLogin noAfter changing the config file, you will need the restart ssh service.
sudo systemctl restart ssh
By the end you should be able to connect using ssh through port 4242:

But the service will be refused if tried with any other port:

When trying to login to root, you will see a `Permission Denied` message.

- Installation
-
Strong Password Policy
-
Password aging
- Your password has to expire every 30 days.
- The minimum number of days allowed before the modification of a password will be set to 2.
- The user has to receive a warning message 7 days before their password expires.
We can change
/etc/login.defsto change these configs:

obs: Be aware that this will apply only for future created users. To change to current ones you will need to do it one by one:sudo chage -M 30 -m 2 -W 7 <username>
To check the status of a user:
sudo chage -l <username>
-
Complexity
- Your password must be at least 10 characters long. It must contain an uppercase letter and a number. Also, it must not contain more than 3 consecutive identical characters.
- The password must not include the name of the user.
- The password must have at least 7 characters that are not part of the former password.
- Of course, your root password has to comply with this policy.
We are gonna install libpam-pwquality. This module can be plugged into the password stack of a given service to provide some plug-in strength-checking for passwords. And that is what we are gonna do to enforce our user's passwords ;)
Installationsudo apt install libpam-pwquality
-
-
montoring.sh
This should be a script developed in bash. It should display the following information at all terminals every 10 minutes.- The architecture of your operating system and its kernel version.
- The number of physical processors.
- The number of virtual processors.
- The available RAM on your server and its utilization rate as a percentage.
- The available memory on your server and its utilization rate as a percentage.
- The utilization rate of your processors as a percentage.
- The date and time of the last reboot.
- Whether LVM is active or not.
- The number of active connections.
- The number of users using the server.
- The IPv4 address of your server and its MAC (Media Access Control) address.
- The number of commands executed with the sudo program.
I have created a file called monitoring.sh. This script calculates all required information, saving it to variables.
At the end, the wall command is used to write a message to all users.
Now that we have the bash file, we need to set a job to run it every 10 minutes. We will use cron for that.
But .. what is cron?
The cron is a software utility, offered by a Linux-like operating system that automates the scheduled task at a predetermined time. It is a daemon process, which runs as a background process and performs the specified operations at the predefined time when a certain event or condition is triggered without the intervention of a user.
How do we set the cron job? Via crontab :D
The crontab (abbreviation for “cron table”) is list of commands to execute the scheduled tasks at specific time. It allows the user to add, remove or modify the scheduled tasks. The crontab command syntax has six fields separated by space where the first five represent the time to run the task and the last one is for the command.
Activate/edit crontab:
sudo crontab -eThere is 2 set jobs: one for running every 10 minutes and other for reboot:
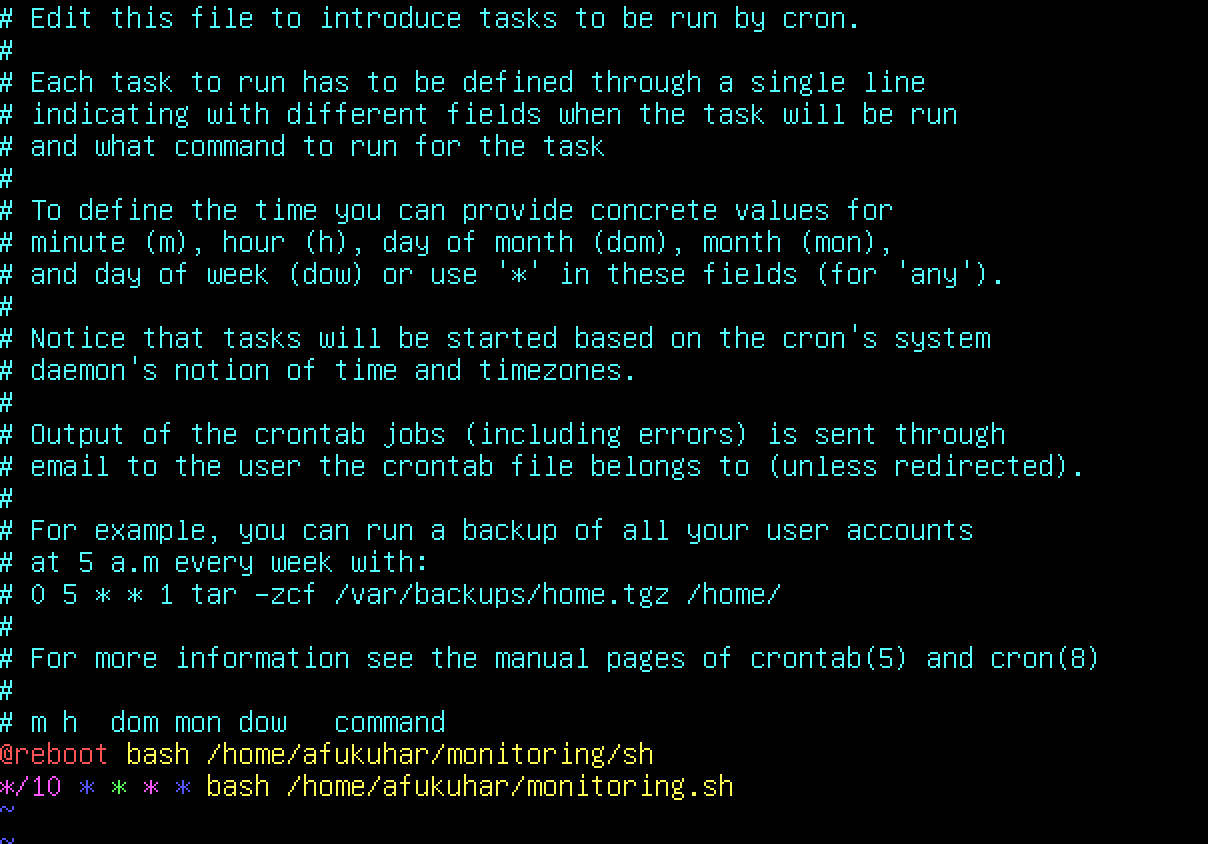
To stop cron via command line:
sudo /etc/init.d/cron stop
To start is again:
sudo /etc/init.d/cron start
Now, every time the minute is 10, it will display the following message to all users:

What is a virtual machine? A virtual machine is a virtual environment that works like a computer within a computer. It runs on an isolated partition of its host computer with its own resources of CPU power, memory, OS and other resources. This allows end-users to run applications on VMs and use them as they normally would on their own workstation.
How a virtual machine works VMs are made possible through virtualization technology. Virtualization uses software to simulate virtual hardware that allows multiple VMs to run on a single machine. The physical machine is known as the host while the VMs running are calling guests. This process is managed by a software known as hypervisor. The hypervisor is responsible for managing and provisioning resources - like memory and storage - from the host to guests. It also schedules operations in VMs so they don't overrun each other when using resources. VMs only work if there is a hypervisor to virtualize and distribute host resources. Virtualbox is a type of hypervisor.
Choice of OS - why Debian? Basic differences between CentOS and Debian Purpose of virtual machines What is aptitude and apt What is APPArmor



