Table of Contents
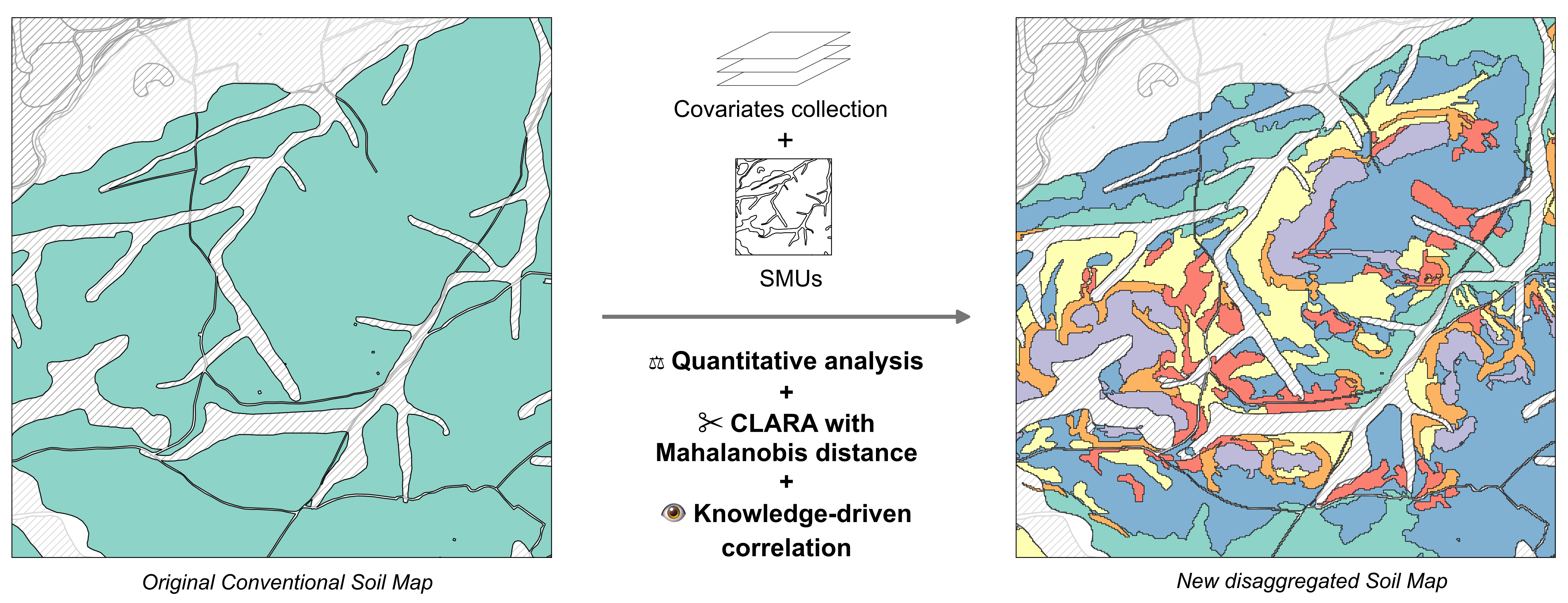
A new methodology for the disaggregation of polytaxic Soil Map Units of conventional soil maps that relies on the detection of soil homogeneous areas with no prior definition. It's based on:
- The unsupervised CLARA classification technique with Mahalanobis distance within a space of selected covariates
- An expert knowledge-driven correlation of the areas with the Soil Taxonomy Units.
Because of them, its application might be geared towards regions where the potential location of STU within SMUs is deemed unclear, and it has a potential to support two-stage strategies (Lázaro-López, 2021). It's implemented in the Designation of Origen Campo de Borja (Gómez-Miguel, 2014).
It's divided into 4 sequential steps covering:
-
Data sources (sources): The selection of remote sensing and DEM data sources, their acquisition and processing for input into the calculations of environmental covariates. It also gets the soil map ready.
-
Covariates (covariates): Calculation, analysis and selection of covariates intended for geo-statistical techniques.
-
Division (division): Division of Cartographic Soil Units by the unsupervised classification method to yield groups of delineations.
-
Disaggregation (disaggregation): Correlation of the delineation groups with the Soil Taxonomic Units to give rise to a new disaggregated soil map with potentially homogeneous Soil Map Units. Then, it's validated with soil observations.
Soil map
A digitalized soil map on top of the model for Soil Resource Inventories (Lázaro-López et al., 2018). It resembles the Soil and Terrain database programme (SOTER) and the National Soil Information System (NASIS) schemas.
Data management
PostgreSQL and its spatial extension PostGIS.
Statistics
The workflow is developed in #Rstats. Main packages are Tidyverse, RPostgres, sf, raster, foreach, bigmemory, ClusterR, Nbclust and RSAGA.
GIS
SAGA and QGIS for data sources processing.
Feel free to send feedback on Twitter @alazarolop or file an issue. Feature requests as well as contributions are always welcome.
Disaggregation of Conventional Soil Maps by Alberto Lázaro-López is licensed under Attribution 4.0 International