Teleconferencing or Chatting is a method of using technology to bring people and ideas "together" despite the geographical barriers. The technology has been available for years but its acceptance was quite recent. Our project is an example of a chat server. It is made up of two applications the client application, which runs on the user's PC, and the server application, which runs on any PC on the network. To start chatting clients should get connected to a server where they can query the server and chat.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is the simplest Transport Layer communication protocol available in the TCP/IP protocol suite. It involves the minimum amount of communication mechanism. UDP is said to be an unreliable transport protocol but it uses IP services that provide a best-effort delivery mechanism.
In UDP, the client does not form a connection with the server like in TCP and instead just sends a datagram. Similarly, the server need not accept a connection and just waits for datagrams to arrive. Datagrams upon arrival contain the address of the sender which the server uses to send data to the correct client.
- UDP is used when the acknowledgment of data does not hold any significance.
- UDP is a good protocol for data flowing in one direction.
- UDP is simple and suitable for query-based communications.
- UDP is not connection-oriented.
- UDP does not provide a congestion control mechanism.
- UDP does not guarantee the ordered delivery of data.
- UDP is stateless.
- UDP is a suitable protocol for streaming applications such as VoIP, multimedia streaming.
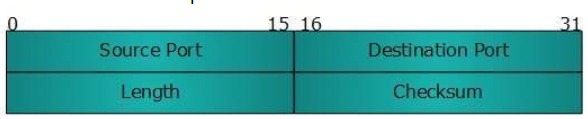
UDP header is as simple as its function.
UDP header contains four main parameters:
- Source Port - This 16-bit information is used to identify the source port of the packet.
- Destination Port - This 16-bit information is used to identify application-level services on the destination machine.
- Length - The length field specifies the entire length of the UDP packet (including the header). It is a 16-bits field and the minimum value is 8-byte, i.e. the size of the UDP header itself.
- Checksum - This field stores the checksum value generated by the sender before sending. IPv4 has this field as optional so when the checksum field does not contain any value it is made 0 and all its bits are set to zero.
Other Applications-
Example 1 : One of the examples where UDP is preferred over TCP is the live coverage of TV channels. In this aspect, we want to transmit as many frames to a live audience as possible not worrying about the loss of one or two frames. TCP being a reliable protocol adds its own overhead while transmission.
Example 2 : UDP is preferred in online multiplayer gaming. In games like counter-strike or call of duty, it is not necessary to relay all the information but the most important ones. It should also be noted that most of the applications in real-life use a careful blend of both UDP and TCP; transmitting the critical data over TCP and the rest of the data via UDP.
| Transmission control protocol(TCP) | User datagram protocol(UDP) |
|---|---|
| TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. Connection-orientation means that the communicating devices should establish a connection before transmitting data and should close the connection after transmitting the data. | UDP is the Datagram-oriented protocol. This is because there is no overhead for opening a connection, maintaining a connection, and terminating a connection. UDP is efficient for broadcast and multicast types of network transmission. |
| TCP is reliable as it guarantees the delivery of data to the destination router. | The delivery of data to the destination cannot be guaranteed in UDP. |
| TCP provides extensive error-checking mechanisms. It is because it provides flow control and acknowledgment of data. | UDP has only the basic error checking mechanism using checksums. |
| An acknowledgment segment is present. | No acknowledgment segment. |
| Sequencing of data is a feature of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). this means that packets arrive in order at the receiver. | There is no sequencing of data in UDP. If the order is required, it has to be managed by the application layer. |
| TCP is comparatively slower than UDP. | UDP is faster, simpler, and more efficient than TCP. |
| Retransmission of lost packets is possible in TCP, but not in UDP. | No retransmission of lost packets in the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). |
| (20-60) bytes variable length header. | 8 bytes fixed-length header. |
| Heavy-weight. | Lightweight. |
| Uses handshakes such as SYN, ACK, SYN-ACK | It's a connectionless protocol i.e. No handshake |
| Doesn't support Broadcasting. | Supports Broadcasting. |
| TCP is used by HTTP, HTTPs, FTP, SMTP and Telnet. | UDP is used by DNS, DHCP, TFTP, SNMP, RIP, and VoIP. |
DatagramSockets are Java's mechanism for network communication via UDP instead of TCP. Java provides DatagramSocket to communicate over UDP instead of TCP. It is also built on top of IP. DatagramSockets can be used to both send and receive packets over the Internet.
- Creation of DatagramSocket: protected DatagramSocket DatagramSocket(int port) a) Parameters: port - port to which socket is to be bound b) Throws SocketException - If the socket cannot be bound to the specific local port. Creates a DatagramSocket and binds to the specified port on the local machine.
- Creation of DatagramPacket: DatagramPacket(byte buf[], int len) Parameters: a) buf - the packet data. b) len - the packet data length. Constructs a DatagramPacket for receiving the data of length "len" in the byte array buf.
- Invoke a send() call on socket object: void send(DatagramPacket packet) throws SocketException a) Parameters: packet - Datagrampacket to send. b) Throws: SocketException - If there is an error in binding. IllegalArgumentException - if the address is not supported by the socket.
- Invoke a receive() call on socket object: void receive(DatagramPacket packet) throws SocketException a) Parameters: packet - Datagrampacket to receive. b) Throws: SocketException - If there is an error in binding. IllegalArgumentException - if the address is not supported by the socket.
The entire codes can be broken down into the following steps :
UDP Server
- Create a UDP socket.
- Bind the socket to the server address.
- Wait until the datagram packet arrives from the client.
- Process the datagram packet and send a reply to the client.
- Go back to Step 3.
UDP Client
- Create a UDP socket.
- Send a message to the server.
- Wait until a response from the server is received.
- Process reply and go back to step 2, if necessary.
- Close socket descriptor and exit.
Pre-Requisite
- The client will be the first to start the communication by sending a query.
- The client should know the IP address of the Server. Reason: As of now, we have assumed our connection to be local and using "localhost". This is to avoid firewall-related security in a network.
Working
- Communication is achieved by transmitting information in one direction from source to destination without verifying the readiness or state of the receiver.
- The client sends the message to the server and changes its state to wait till it receives the reply from the server (as it can either receive or send at a time).
- If the server is up and receives the information, it reads the client IP and PORT from the UDP Header and replies to that address respectively.
- Else the message is lost as no one is available to receive it.
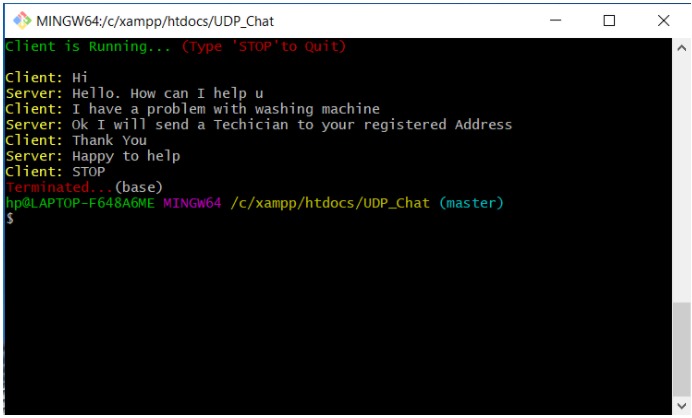
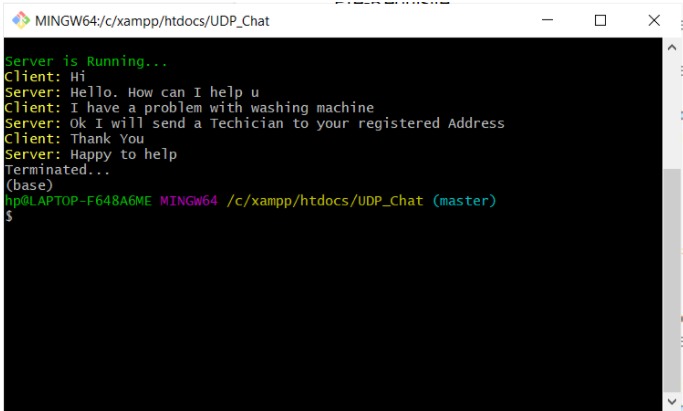
Demo Images
Client Terminal
Server Terminal
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is a communications protocol that is primarily used to establish low-latency and loss tolerating connections between applications on the internet. UDP speeds up transmissions by enabling the transfer of data before an agreement is provided by the receiving party hence connectionless.
UDP other properties like one-way connection, loss of packets, and absence of acknowledgment are also verified.