WebAssembly debug information
Input
- there are two type of clients: IDEs and static analysis tool;
- different IDEs provide similar capabilities for different languages, e.g. stepping, inspecting current program state, breakpoints, e.t.c;
- WebAssembly is going to support tremendous amount of different languages;
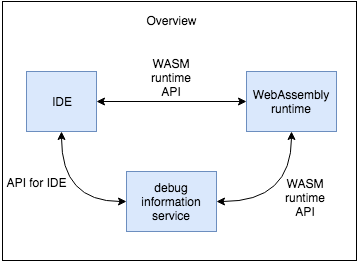
Proposed architecture A
As part of this proposal we need to specify two different APIs:
- WebAssembly runtime API exposed in raw terms without any knowledge about original language:
- something for memory/current stack inspection,
- something for basic debugging features like breakpoints and stepping,
- something for compiled WebAssembly bytecode execution.
- API for IDEs:
- sets of methods which IDE may use to provide debugging experience in terms of original language.
How does it work?
IDE receives some location from runtime using DevTools protocol. It goes to service and ask it about any existing mapping from this raw location to some better location. Service may return location inside original source code. IDE detects that it gets location in some new source file and additionaly request original source file from service.
Advantages
- In modern ecosystem a lot of IDEs (e.g. VSCode, WebStorm) use DevTools protocol (mostly Runtime and Debugger domains) to debug JavaScript, so adding support for new WebAssembly domain should be easy for them.
- It is not required to specify debug information format which will support all existing languages and will be extensible enough to support future languages, with this proposal C/C++ may use something on top of DWARF, JVM languages may prefer some other format. WASM should only have some kind of reference implementation that other developers may use as an example.
- More opportunities for compiler developers, they may output debug information in form of one of the existing format, e.g. SourceMap or DWARF and just reuse existing adapter from this format to IDE API, or they can introduce completely new format and write own adapter or introduce dynamic format which will expose IDE API right away.
- Debug information service:
- may require connection to WASM runtime, e.g. to implement evaluation of expressions in original language;
- may not require connection to WASM runtime, e.g. if it is implemented on top of SourceMap where all information is static;
- may be hybrid when all required information is embedded into format and we can evaluate something but do not need separate connection to WebAssembly format, e.g. DWARF.
Disadvantages
- If we allow service to have connection to WASM runtime then some part of services can be used as part of static analysis tool and some of them can not.
- Two APIs is more then one static format.
- Reliance on third party implementation of debug information service.
- Most likely designing universal IDE API is only a little less complex then designing universal debug information format (since we have less IDEs than languages). Insted of building spec for this API we can only provide developers with reference implementation.
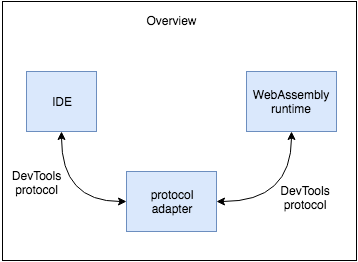
Proposed architecture B
How does it work?
Adapter sits between WebAssembly/JavaScript runtime and IDE. As soon as protocol is about to report something WebAssembly specific, e.g. location inside WebAssembly bytecode, adapter converts these locations to locations inside original source code and generated corresponded scriptPrased event to report fake script for original source code.
Advantages
- Requires only one additional WebAssembly specific domain in DevTools protocol, this domains is required in both proposed architectures.
- This solution is IDE agnostic, the same protocol adapter may be used with any IDE which supports DevTools protocol.
- Protocol adapter should be able to work without connection to WebAssembly runtime to support static analysis tool, it may be harder to implement but at the same time these tools will use the same protocol as IDE use.
Disadvantages
- This approach relies more on third party implementation, proper implementing adapter may require knowledge about IDE implementation details.
- It may be hard to map original language primitives to WebAssembly/JavaScript primitives.
Action items
- describe basic WebAssembly runtime API in form of another DevTools protocol domain
- describe possible IDE API based on most common IDE capabilities, describe how IDE can use this API (at least consider extension for Language Service Protocol)
- implements static debug information service on top of SourceMapV3
- implements dynamic debug information service on top of DWARF for C
- implements protocol adapter as experiment with architecture B