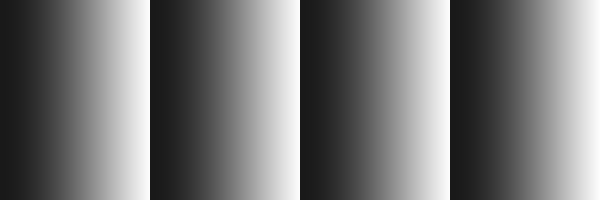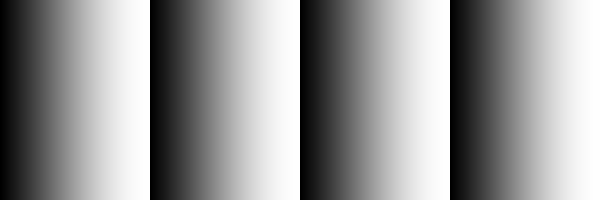- waveform
- data types
- functions
- shaping functions shaping signals in the normalized range [0, 1]
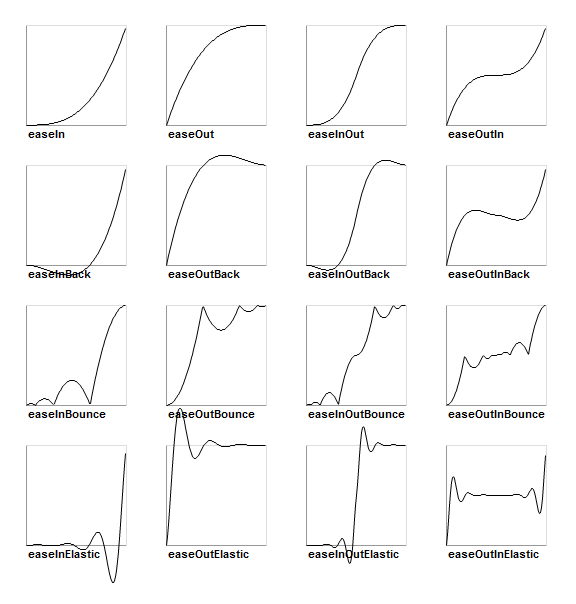
- Easing functions specify the rate of change of a parameter over time
- Tweening functions: The purpose of a tweening function is to deliver a position for a specific time, given the tween’s essential characteristics. These characteristics are beginning position, final position, and duration. It is used in Flash for describe time related motion
- 1D gray color gradient
- Pattern Master
- Unit generators
- Interpolation curves or interpolations
- Parametric acceleration curves for animations
Names or nomenclature comparison
All functions work in the range [0..1].
- take input function f which maps floating point number (x or position) in a normalised range [0.0, 1.0] and gives monotone output ( A monotonically non-decreasing function )
- make function diagram and color gradient ( image of continous color gradient) using above function
- make 3 types of periodic waves for each function type using ModifyPosition function
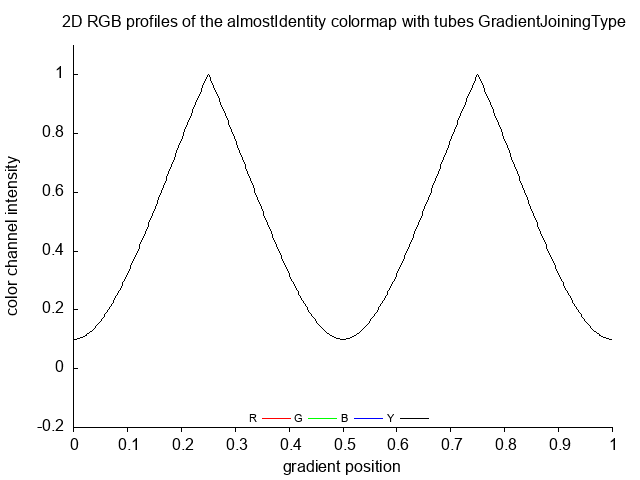
- make color diagram and color gradient for each GradientJoiningType of input function
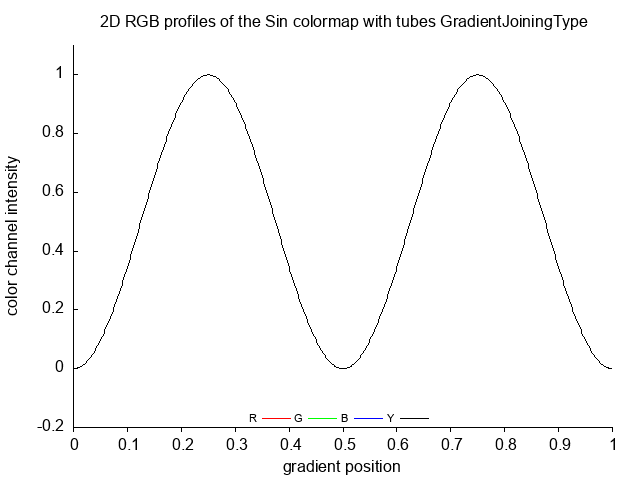
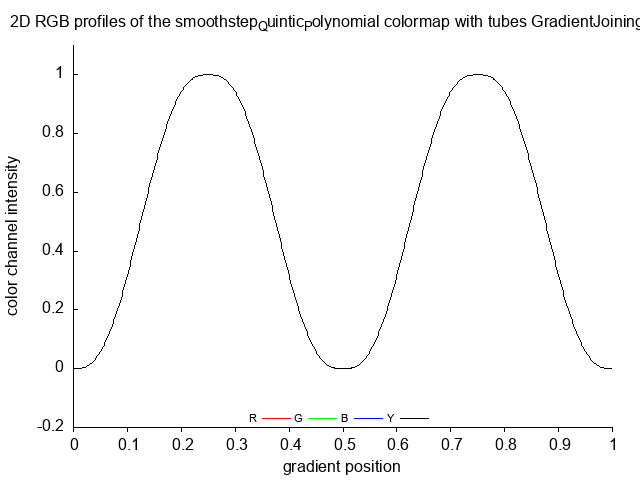
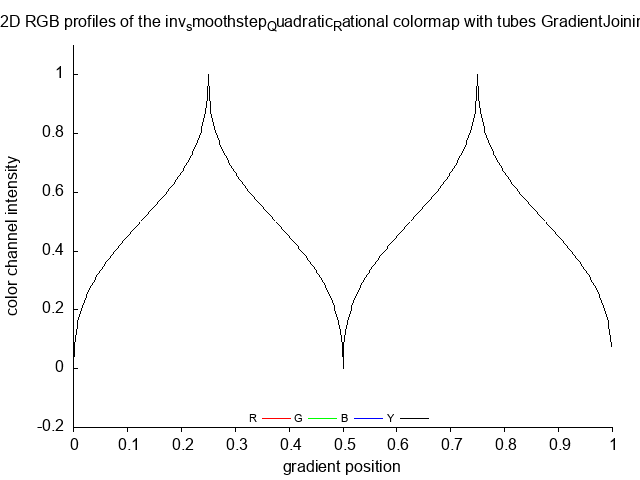
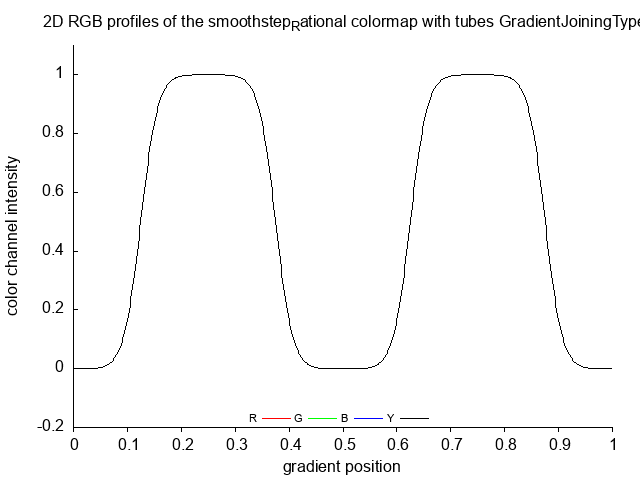
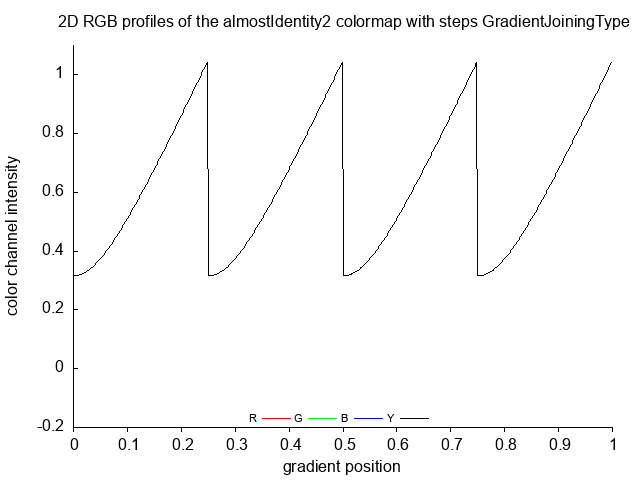
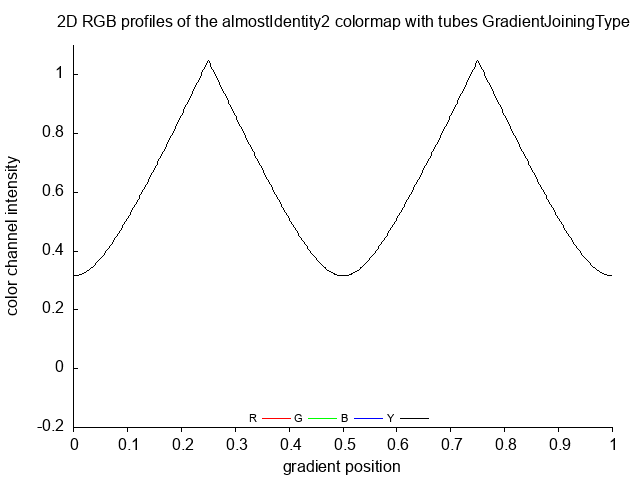
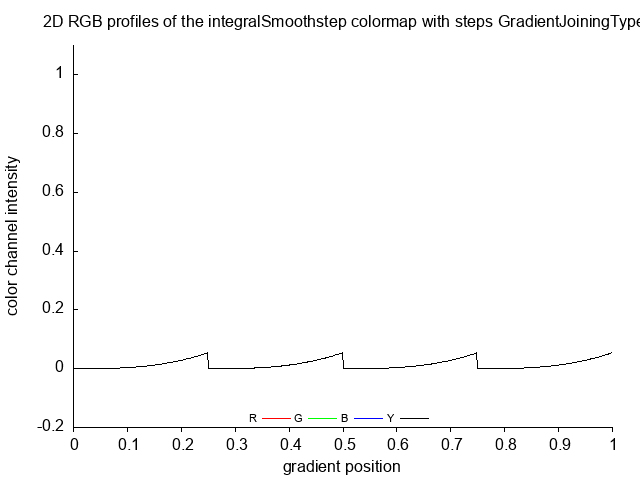
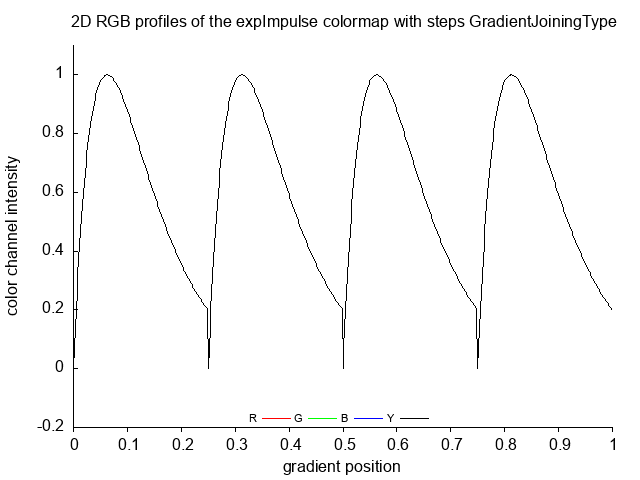
typedef enum {no, steps, tubes } GradientJoiningType;
double ModifyPosition(const double position, const GradientJoiningType GradientJoining){
// input position should be in [0,1] range
double p = position; // p = local copy of position
// if position > 1 then we have repetition of colors = periodic function = wave
switch(GradientJoining){
case no : {break;} // return input position witout modifications
// periodic waves with different joinings
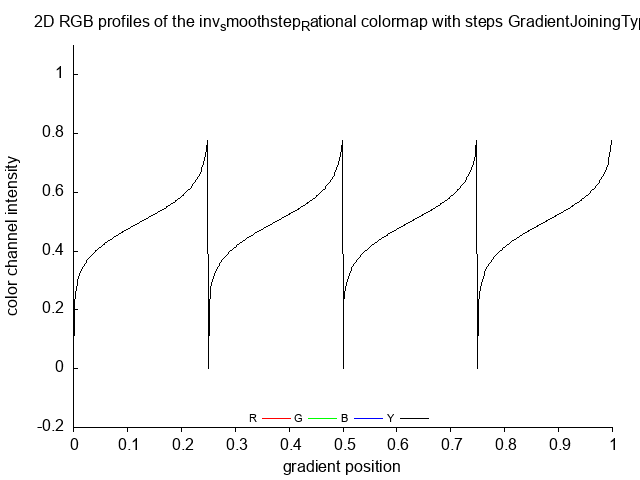
case steps : { p = p * segments; // periodic = change range
p = frac(p);
break;}
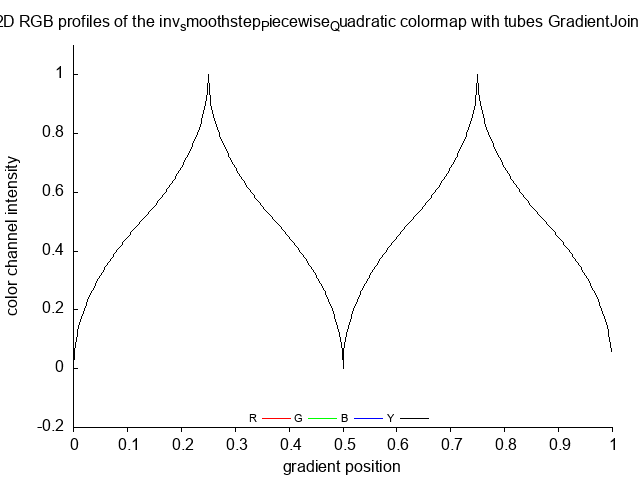
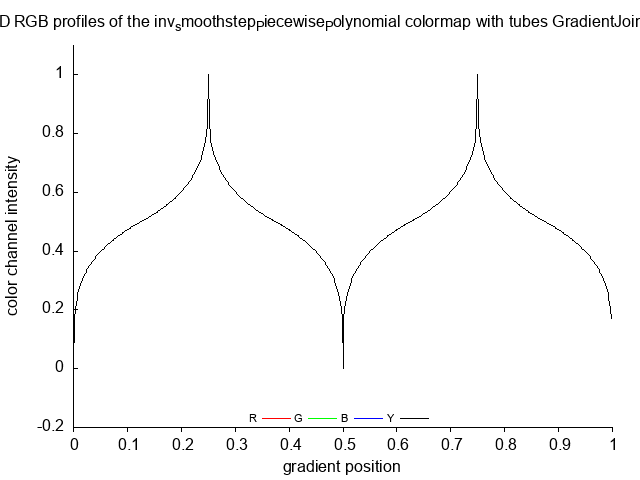
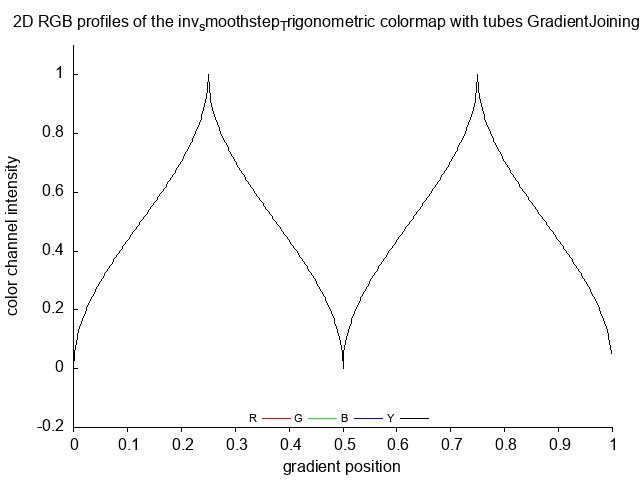
case tubes : { p = p * segments; // periodic = change range
int ip = (int)p;
p = p-ip; // fractional part
if (ip % 2) {p = 1.0-p;} // reverse gradient
break;}
default:{}
}
return p; // output in [0,1] range
}
So important variables:
- coordinate ( integer to float)
- position ( float )
- color (RGB) : float to integer in [0 , 255] range
Linear function graph = made using continous_data function
Step function graph. Made using discrete_data function
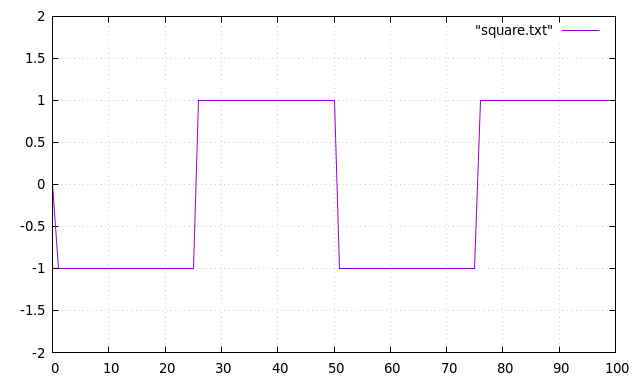
Sawtooth wave graph. Made using sawtooth_data function which includes steps type of joining
Piecewise linear functions: Boxcar function or square waveform or Rectangular function, the simplest step_function. It is made using square_wave function
Triangle wave = made from linear function using tubes type of joining
Linear Linear_no
Linear_steps
Linear_tubes
Quadratic Quadratic_no
Quadratic_steps
Quadratic_tubes
Cubic Cubic_no
Cubic_steps
Cubic_tubes
CubicInv CubicInv_no
CubicInv_steps
CubicInv_tubes
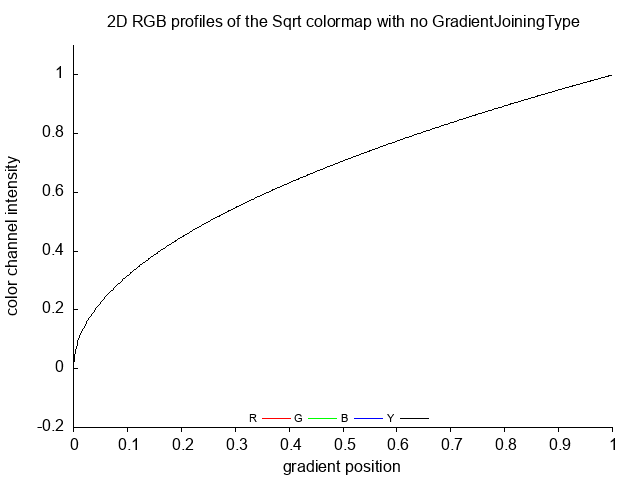
Sqrt Sqrt_no
Sqrt_steps
Sqrt_tubes
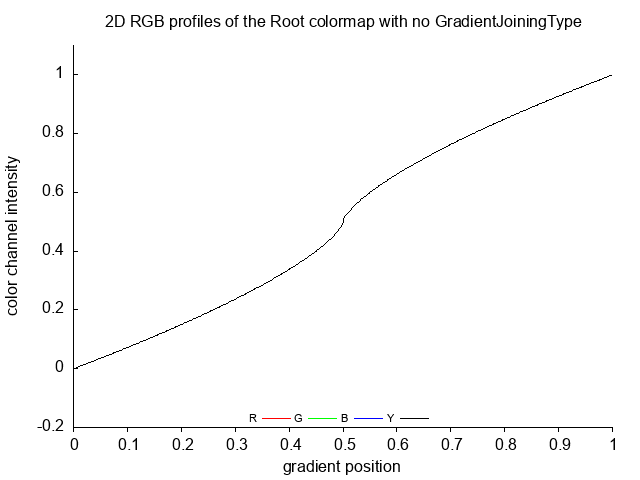
Root Root_no
Root_steps
Root_tubes
Gamma Gamma_no
LSin LSin_no
effect of a sine wave superimposed on a ramp function
It is based on the The Colour Map Test Image by Peter Kovesi
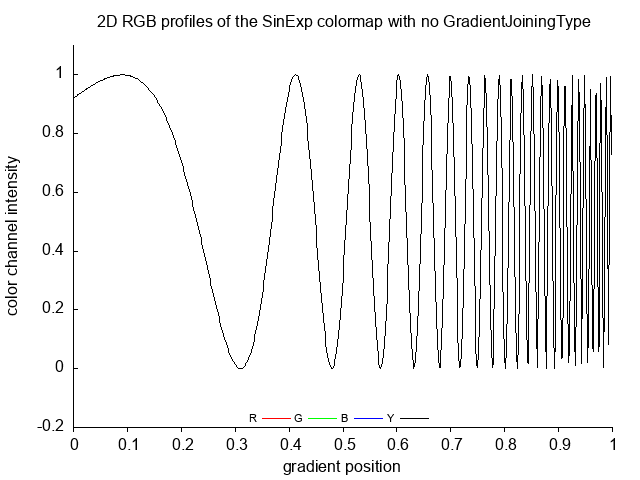
SinExp SinExp_no
Sin Sin_no
Smooth Smooth_no
Tanh Tanh_no
smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial_no
 smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial_steps
smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial_steps
 smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial_tubes
smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial_no
 inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial_steps
inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial_steps
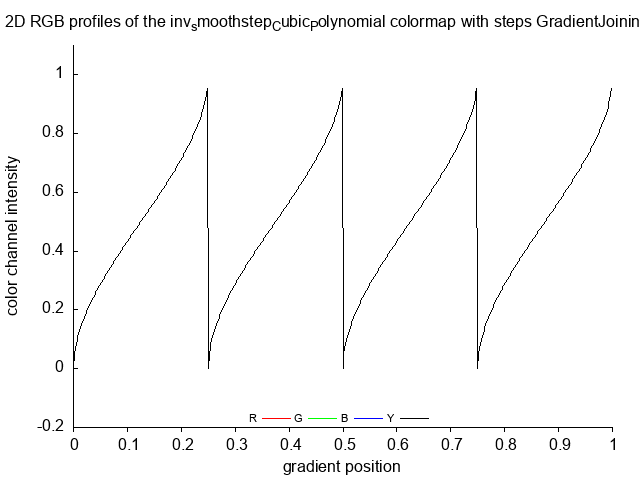 inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Polynomial_tubes
smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial_no
 smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial_steps
smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial_steps
 smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial_tubes
smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial inv_smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial_no
 inv_smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial_steps
inv_smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial_steps
 inv_smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Quartic_Polynomial_tubes
smoothstep_Quintic_Polynomial smoothstep_Quintic_Polynomial_no
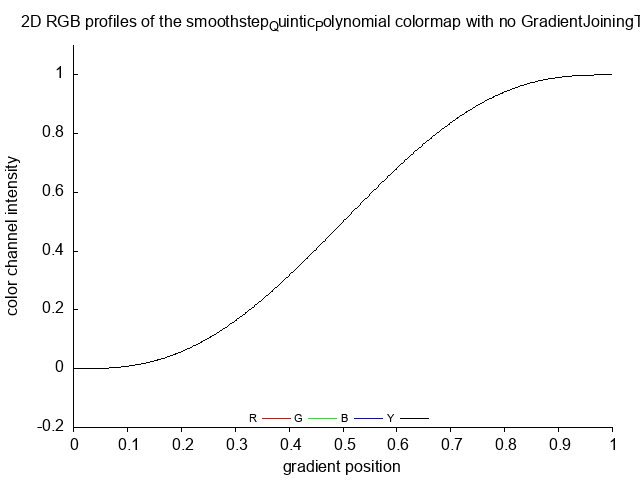 smoothstep_Quintic_Polynomial_steps
smoothstep_Quintic_Polynomial_steps
 smoothstep_Quintic_Polynomial_tubes
smoothstep_Quintic_Polynomial_tubes
smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational_no
 smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational_steps
smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational_steps
 smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational_tubes
smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational inv_smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational_no
 inv_smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational_steps
inv_smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational_steps
 inv_smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Quadratic_Rational_tubes
smoothstep_Cubic_Rational smoothstep_Cubic_Rational_no
 smoothstep_Cubic_Rational_steps
smoothstep_Cubic_Rational_steps
 smoothstep_Cubic_Rational_tubes
smoothstep_Cubic_Rational_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Rational inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Rational_no
 inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Rational_steps
inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Rational_steps
 inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Rational_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Cubic_Rational_tubes
smoothstep_Rational smoothstep_Rational_no
inv_smoothstep_Rational inv_smoothstep_Rational_no
smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic_no
 smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic_steps
smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic_steps
 smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic_tubes
smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic_no
 inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic_steps
inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic_steps
 inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Quadratic_tubes
smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial_no
 smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial_steps
smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial_steps
 smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial_tubes
smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial_no
 inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial_steps
inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial_steps
 inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Piecewise_Polynomial_tubes
smoothstep_Trigonometric smoothstep_Trigonometric_no
 smoothstep_Trigonometric_steps
smoothstep_Trigonometric_steps
 smoothstep_Trigonometric_tubes
smoothstep_Trigonometric_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Trigonometric inv_smoothstep_Trigonometric_no
 inv_smoothstep_Trigonometric_steps
inv_smoothstep_Trigonometric_steps
 inv_smoothstep_Trigonometric_tubes
inv_smoothstep_Trigonometric_tubes
almostIdentity almostIdentity_no
almostIdentity2 almostIdentity2_no
almostUnitIdentity almostUnitIdentity_no
integralSmoothstep integralSmoothstep_no
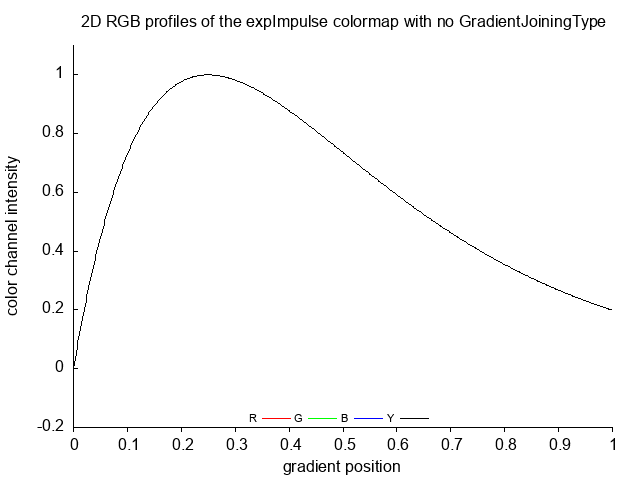
expImpulse expImpulse_no
quaImpulse quaImpulse_no
quaImpulse_steps
quaImpulse_tubes
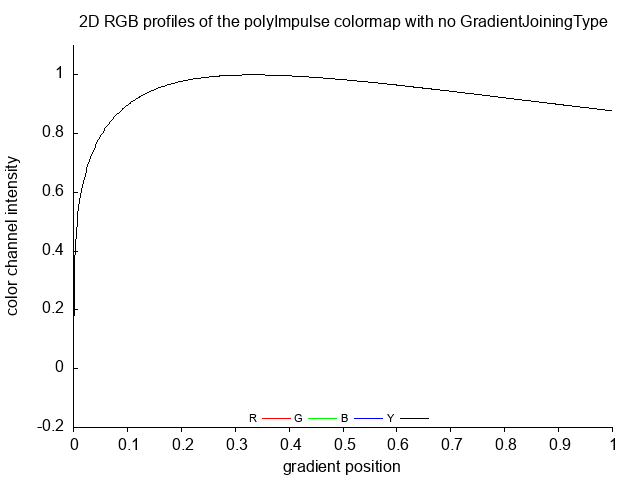
polyImpulse polyImpulse_no
polyImpulse_steps
polyImpulse_tubes
expSustainedImpulse expSustainedImpulse_no
expSustainedImpulse_steps
expSustainedImpulse_tubes
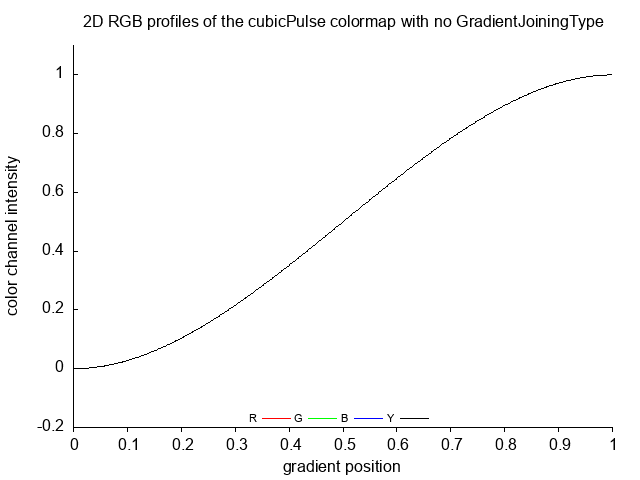
cubicPulse cubicPulse_no
cubicPulse_steps
cubicPulse_tubes
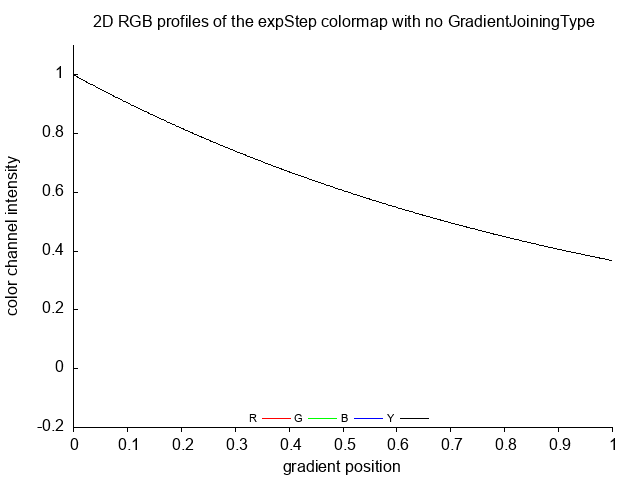
expStep expStep_no
expStep_steps
expStep_tubes
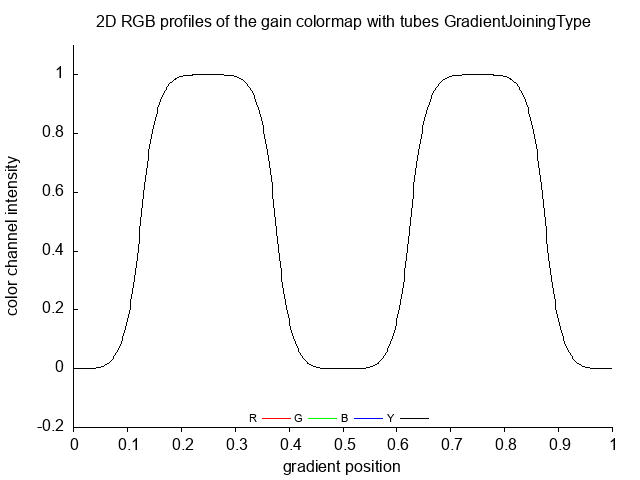
gain gain_no
gain_steps
gain_tubes
parabola parabola_no
parabola_steps
parabola_tubes
pcurve pcurve_no
pcurve_steps
pcurve_tubes
sinc sinc_no
sinc_steps
sinc_tubes
trunc_fallof trunc_fallof_no
trunc_fallof_steps
trunc_fallof_tubes
MRE = minimal reproducible ( working) example = short simple code
One file program that makes all images
- d.c
- results of the program are in the text files (./src/*.txt)
Compile and run the program
gcc d.c -Wall -Wextra -lm
a.out > c.txt
gnuplot
plot "c.txt" with lines
# save image as a c.png
One file program that makes all images. To run it:
make
- add new functions named: Give_s
- add new enum named: s in ColorTransferFunctionType
- use s.c program to compute code for c functions (GiveRGB_Gray and GiveColor) and for gnuplot
- copy code
//
double Give_s(const double position){
double s = position;
return s;
}S directory contains c program for creating code for plot.gp and g.c
Screen shot from online WebGL demo
available animation transition types: (the default transition type, 'linear', was omitted) from the wiki of the Sparrow Framework — the Open Source Game Engine for iOS.
- jQuery easing; illustrated by James Padolsey
- online WebGL demo
- larsenwork: easing-gradients/ Linear gradients often have hard edges where they start and/or end. We can avoid those by controlling the color mix with easing functions.
- FlexMonkey: Interpolation-Playground-
- Easing Functions Cheat Sheet
- 1D-RGB-color-gradient
- Golan Levin: Pattern_Master for Processing
- p5.js-func: Function Generators for p5.js
- Shaping functions in GLSL by Patricio Gonzalez Vivo & Jen Lowe
- curves by kynd.inf
Easing functions
- each easing function has 3 variants: ease-in, ease-out, and ease-in-out
- Easing Equations by @nicmulvaney
- EASING EQUATIONS by Robert Penner - github
- EASING EQUATIONS by Robert Penner - www
- Tweening chapter of Robert Penner's book: Programming Macromedia Flash MX
- AHEasing: A supplemental library of easing functions for C, C++, and Objective-C by Warren Moore
- Parametric acceleration curves in Core Animation, September 9, 2008 by Matt Gallagher
- stackoverflow question: how-to-create-custom-easing-function-with-core-animation
- Robert Penner's easing equations converted to coffeescript. by Jim Jeffers
- Understanding Easing (Explaining Penner’s equations) – JavaScript and ActionScript
- easing-functions in CSS
- easy.c
by Iñigo Quilez
- GraphToy = a tool to visualize GLSL functions in WebGL, only function of 2 variables: f(x,t)
- useful little functions
- smoothsteps/
- smoothstep integral
- mega polynomial curve
Smoothstep
- wikipedia
- Smoothstep - Shader Graph Basics - Episode 15 by Ben Cloward
- smoothstep-looking-for-a-continuous-family-of-interpolation-functions
- RSL: Using smoothstep
- interpolations tricks or How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the 0..1 Range by Jari Komppa
Shaping functions
Polynomial Shaping Functions: This page presents a collection of polynomial functions for shaping, tweening, and easing signals in the range [0...1]. Functions include:
- Blinn-Wyvill Approximation to the Raised Inverted Cosine
- Double-Cubic Seat
- Double-Cubic Seat with Linear Blend
- Double-Odd-Polynomial Seat
- Symmetric Double-Polynomial Sigmoids
- Quadratic Through a Given Point
- Exponential Ease-In and Ease-Out
- Double-Exponential Seat
- Double-Exponential Sigmoid
- The Logistic Sigmoid
Circular & Elliptical Shaping Functions
- Circular Interpolation: Ease-In and Ease-Out
- Double-Circle Seat
- Double-Circle Sigmoid
- Double-Elliptic Seat
- Double-Elliptic Sigmoid
- Double-Linear with Circular Fillet
- Circular Arc Through a Given Points
Bezier and Other Parametric Shaping Functions
- Quadratic Bezier
- Cubic Bezier
- Cubic Bezier (Nearly) Through Two Given Points
- Linear Interpolation
- Smooth Step
- Smoother Step
- Smoothest Step
- Squared
- Inverse Squared
- Cubed
- Sin
- Catmull-Rom
- Elastic In
- Elastic Out
- Wobble
- Gaussian
This work is a spiritual descendent (not to say derivative work) of works done by the following individuals:
- Robert Penner: Created the first flexible, reusable Easing functions …which are the cornerstone of all JS animation techniques today
- Golan Levin
- Warren Moore
- George McGinley Smith
- James Padolsey
- Authors of jQuery
- Matt Gallagher
- Jesse Crossen
- Iñigo Quilez
- Andrey Sitnik
- Jim Jeffers
- lerp = linear interpolation
- Easing functions specify the rate of change of a parameter over time.
- Exponential decay
- Exponential growth: Exponential growth is the inverse of logarithmic growth
- Logarithmic growth: Logarithmic growth is the inverse of exponential growth and is very slow
- linear growth ( linear function): y = f(x) ; proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio
- Quadratic_growth
- Hyperbolic_growth: If the output of a function is inversely proportional to its input, or inversely proportional to the difference from a given value x0, the function will exhibit hyperbolic growth, with a singularity at x0
- Big O notation, see Orders of common functions
git add README.md
git commit -m "first commit"
git branch -M main
git remote add origin git@github.com:adammaj1/Waveform.git
git push -u origin main
mkdir images
git add *.png
git mv *.png ./png
git commit -m "move"
git push -u origin main
then link the images:

to overwrite
git mv -f
~/Dokumenty/c/Waveform
File LICENSE must be in main repo directory to be read by github
Github
Math equation inside README.md
$\sqrt{3x-1}+(1+x)^2$