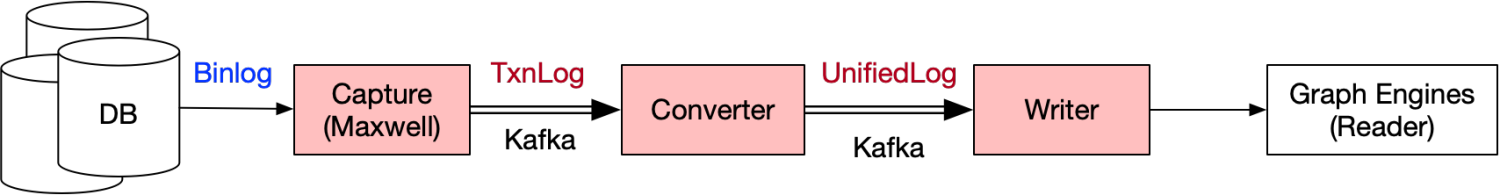
GART is an in-memory system extended from HTAP systems for hybrid transactional and graph analytical processing (HTGAP).
Hybrid transactional/analytical processing (HTAP) is a new trend that processes OLTP and online analytical processing (OLAP) in the same system simultaneously. Analogously, we term dynamic graph analysis processing workloads on transactional datasets as hybrid transactional/graph-analytical processing (HTGAP). GART reuses transaction logs to replay graph data online for freshness instead of offline data migration for freshness and performance.
GART captures the data changes in different (relational) data sources (e.g., database systems, streaming systems) and converts them to graph data according to user-defined rules.
In detail, the workflow of GART can be broken into the following steps:
-
1. Preprocess (Capturer & Parser): GART captures data changes from data sources by logs (e.g., Binlogs in SQL systems). Then, it parsers these logs into a recognized format, called as TxnLog. Currently, we use Maxwell as the log capturer.
-
2. Model Convert (RGMapping Converter): This step is an important step for GART. The conversion between different data models for HTGAP workloads requires more semantic information. For example, it needs the mapping between relational tables and vertex/edge types, and the mapping between relational attributes and vertex/edge properties. The GART administrator (such as DBA) can define the rules of relation-graph mapping (RGMapping) once by the interfaces provided by GART. GART will convert relational data changes into graph data changes in the unified logs (UnifiedLog) automatically.
-
3. Graph Store (Dynamic GStore): GART applies the graph data changes on the graph store. The graph store is dynamic, which means the writes from GART and the reads from the graph analysis processing can be executed on the store concurrently.
GART should fulfill two unique goals not encountered by HTAP systems.
To adapt to rich workloads flexibility, GART proposes transparent data model conversion by graph extraction interfaces, which define rules of relational-graph mapping.
We provide a sample definition file called rgmapping-ldbc.json.
[TBD: format fo RGMapping]
To ensure the performance of graph analytical processing (GAP), GART proposes an efficient dynamic graph storage with good locality that stems from key insights into HTGAP workloads, including:
- an efficient and mutable compressed sparse row (CSR) representation to guarantee the locality of scanning edges;
- a coarse-grained MVCC to reduce the temporal and spatial overhead of versioning;
- a flexible property storage to efficiently run various GAP workloads.
git clone https://github.com/GraphScope/GART.git gart
cd gart
mkdir build; cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
make -jThe dependencies can be installed by scripts/install-deps.sh in a proper directory.
Before running GART, we need to configure the data source to capture its logs. Take MySQL as an example.
-
Kafka configuration file
$KAFKA_HOME/config/server.propertiesdelete.topic.enable=true -
MySQL configuration file
/etc/mysql/my.cnf:[mysqld] # Prefix of the binlogs log-bin=mysql-bin # Binlog Format: row-based logging, maxwell needs binlog_format=row binlog_format=row # The databases captured. GART will capture all databases if not specified. binlog-do-db=ldbc # change the name to your database binlog-do-db=... # change the name to your database -
Create a MySQL user for the log capturer (Maxwell)
# Create a user call "maxwell" with password "123456" # The host name part of the account name, if omitted, defaults to '%'. CREATE USER 'maxwell'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '123456'; # Grant replication and read-only privileges GRANT SELECT, REPLICATION CLIENT, REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'maxwell'@'localhost'; # Grant privileges on the database "maxwell" GRANT ALL ON maxwell.* TO 'maxwell'@'localhost';
You can launch GART by the gart script under the build directory, like:
export KAFKA_HOME=/path/to/kafka
export MAXWELL_HOME=/path/to/maxwell
./gart --user maxwell --password 123456
The arguments of --user and --password is the user name and the password in the database for Maxwell.
The full usage of gart can be shown as:
./gart --help
You can stop GART by:
./stop-gart
-
Download test datasets (use
ldbc_sample)git clone https://github.com/GraphScope/gstest.git -
Initialize database schema in MySQL (need a user with necessary privileges)
pip3 install pymysql cryptography cd gart ./apps/mysql/init_scehma.py --user [username] --password [password] --db ldbcIf you have no such user, you can create the user (called
test) before runninginit_scehma.pylike:CREATE USER test IDENTIFIED BY '123456'; GRANT SELECT, CREATE, DROP, INSERT, DELETE ON ldbc.* TO test;MySQL and its dependencies can be installed by scripts/install-mysql.sh.
-
Lanch GART
export KAFKA_HOME=/path/to/kafka export MAXWELL_HOME=/path/to/maxwell cd build ./gart --user maxwell --password 123456 --db-name ldbc --v6d-sock ldbc.sock --etcd_endpoint 127.0.0.1:23760 -
Start transactional data insertion
./insert_db.py --user maxwell --password 123456 --db ldbc --data_dir /path/to/gstest/ldbc_sample -
Start graph analysis
./apps/run_gart_app --etcd_endpoint 127.0.0.1:23760
GART is released under Apache License 2.0. Please note that third-party libraries may not have the same license as GraphScope.
[USENIX ATC' 23] Bridging the Gap between Relational OLTP and Graph-based OLAP. Sijie Shen, Zihang Yao, Lin Shi, Lei Wang, Longbin Lai, Qian Tao, Li Su, Rong Chen, Wenyuan Yu, Haibo Chen, Binyu Zang, Jingren Zhou. USENIX Annual Technical Conference, Boston, MA, USA, July 2023.